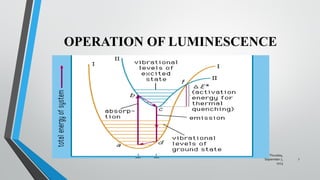
The document is a presentation on luminescence for an analytical chemistry course, outlining its definition, types, operations, and applications. Luminescence is described as light emission produced without heat, with key forms including chemiluminescence, phosphorescence, fluorescence, and bioluminescence. The document also provides examples of luminescent materials and their various applications, such as in fluorescent lamps and LED technology.