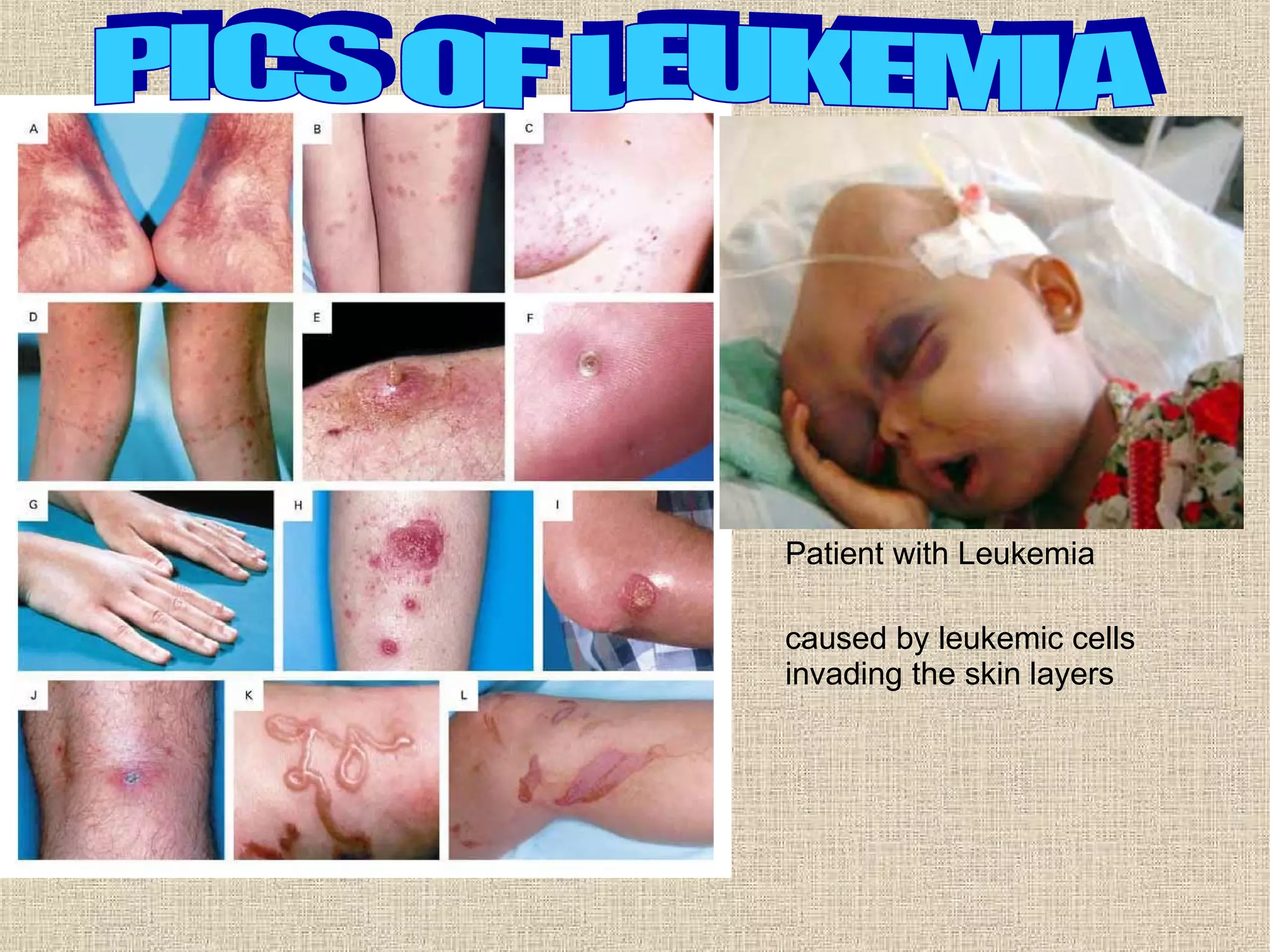
Leukemia is a type of cancer that affects the white blood cells. There are two main types, acute and chronic, with acute developing more quickly. Possible causes include radiation, chemicals, viruses, and genetic factors. Symptoms can include fever, infections, headaches, bleeding easily, and enlarged organs. Treatment involves chemotherapy, radiation therapy, immunotherapy, and stem cell transplants, which can have short and long term side effects. Researchers are investigating new drug combinations and treatments.