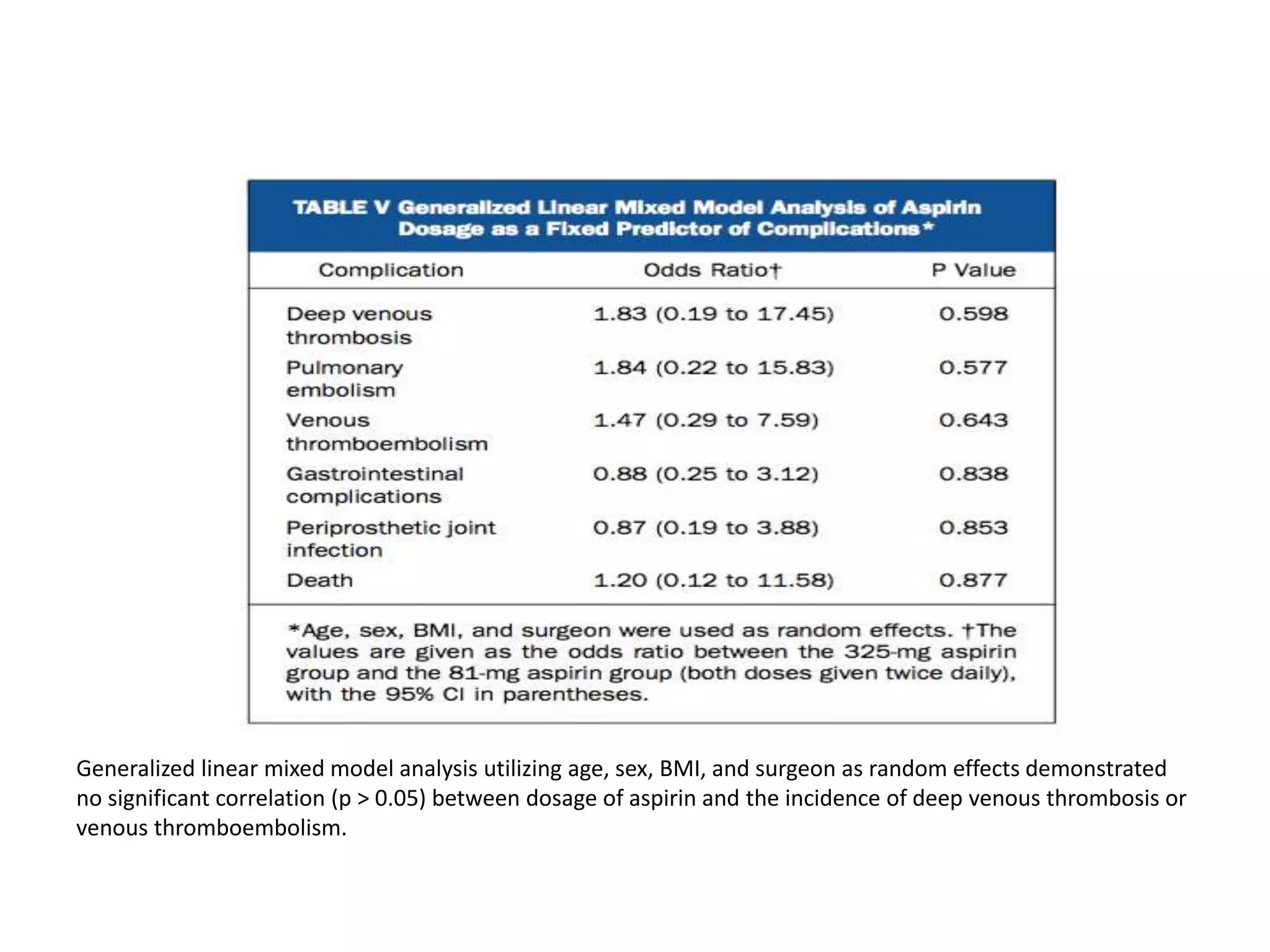
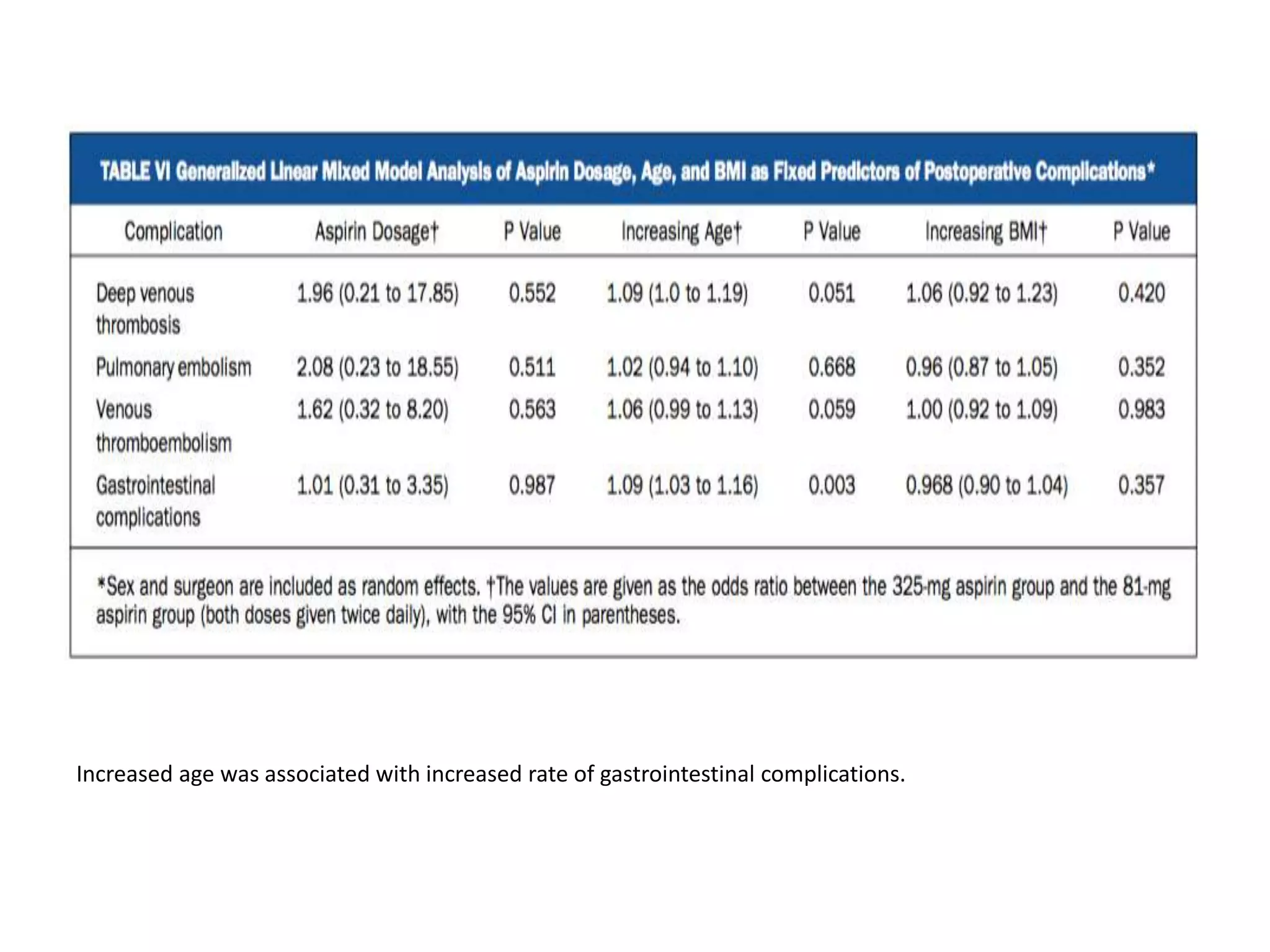
This study compared the effectiveness of low-dose aspirin (81 mg twice daily) to high-dose aspirin (325 mg twice daily) for preventing venous thromboembolism (VTE) following total joint arthroplasty. The study included over 4,600 patients undergoing primary total joint replacement who received either low-dose or high-dose aspirin for 4 weeks post-operatively. The results found no significant difference in VTE rates between the low-dose and high-dose aspirin groups, indicating low-dose aspirin is not inferior to high-dose aspirin for VTE prophylaxis after total joint arthroplasty.












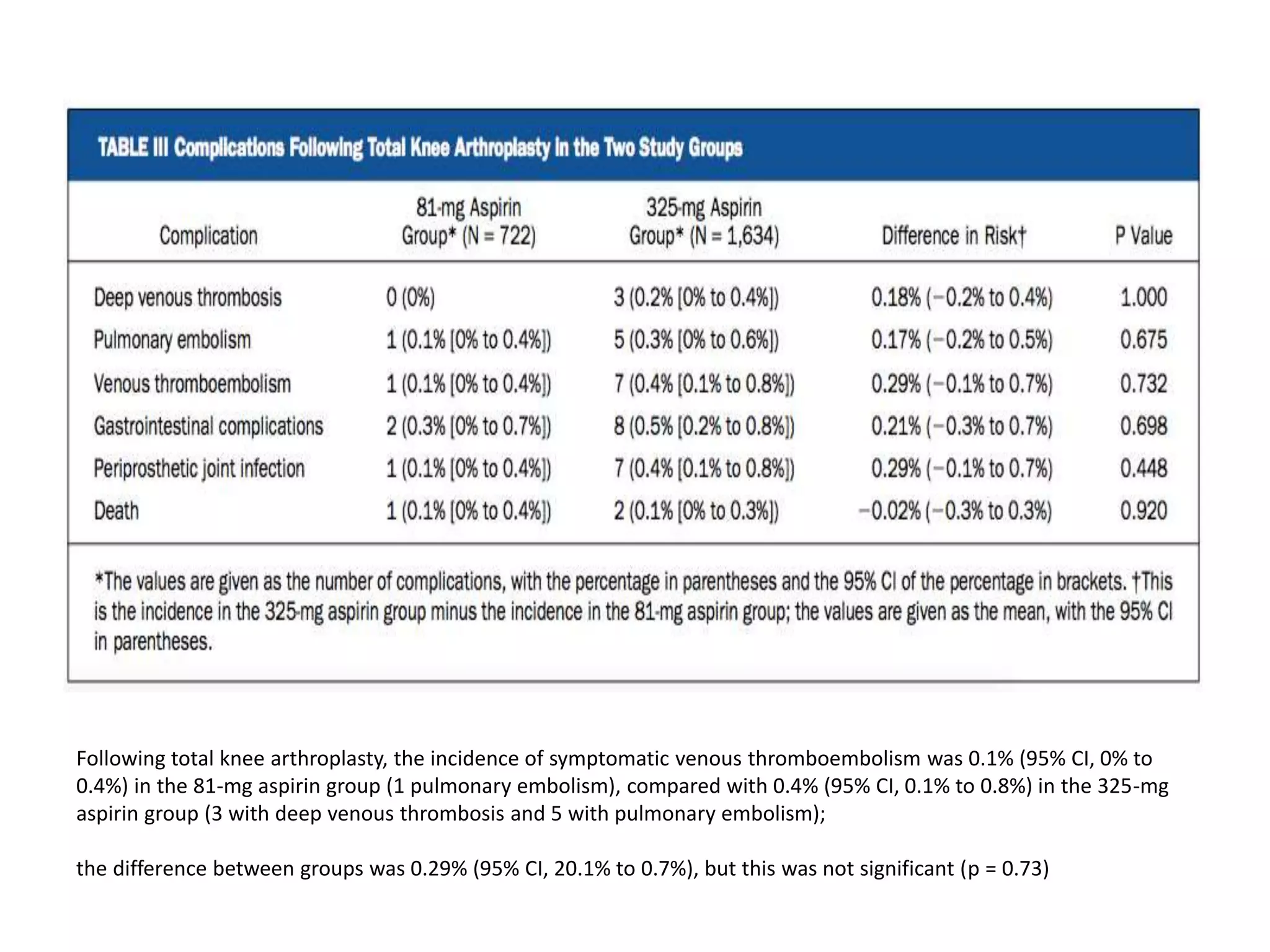
![There was no significant difference (p = 0.35) in the incidence of venous thromboembolism between the two
aspirin dose groups: 0.1% (95% confidence interval [CI], 0% to 0.3%) in the 81-mg aspirin group (1 distal deep
venous thrombosis in a patient who received plain 81-mg aspirin; the difference between groups was 0.21%
(95% CI, 0.03% to 0.5%)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lowdoseaspirin-170318125639/75/Low-dose-aspirin-13-2048.jpg)