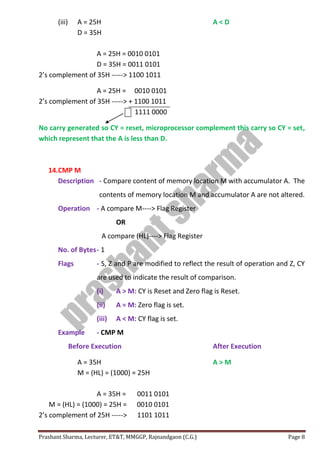
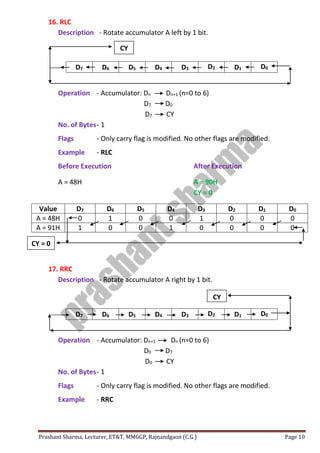
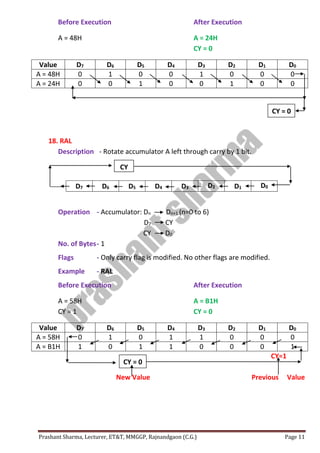
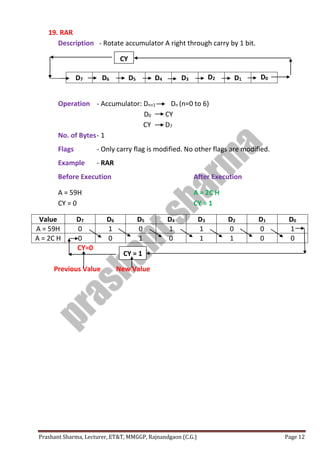
The passage discusses the importance of protecting privacy and limiting data collection in the digital age. It notes that large technology companies now collect vast amounts of personal data on users through their devices and online activities. However, unchecked data collection could threaten privacy and enable unanticipated uses of personal information that people did not consent to sharing.