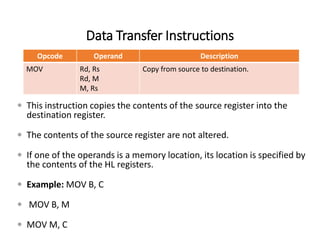
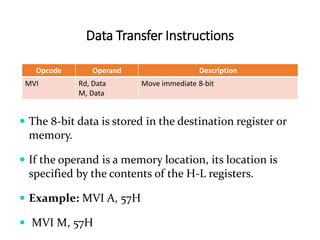
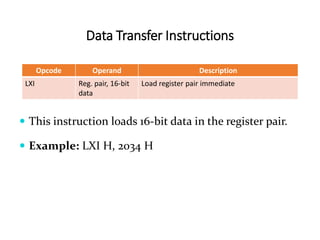
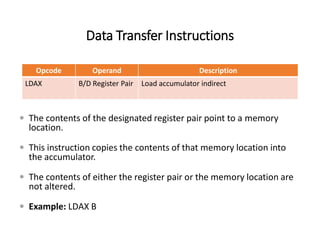
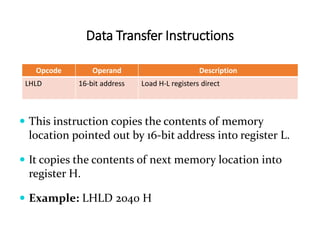
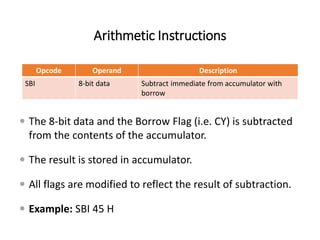
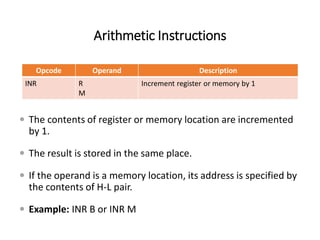
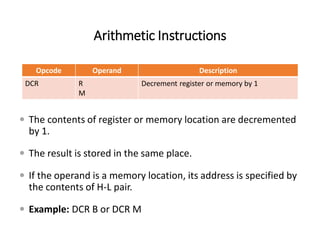
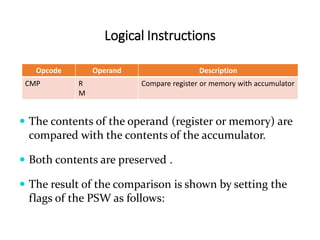
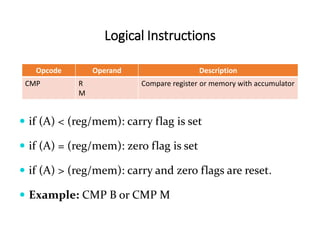
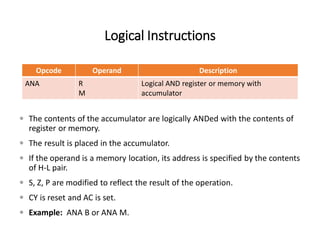
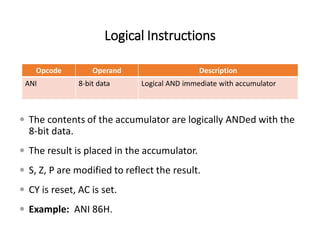
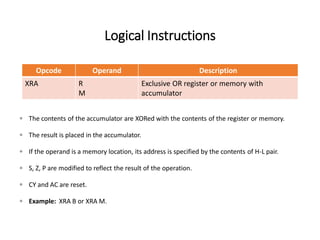
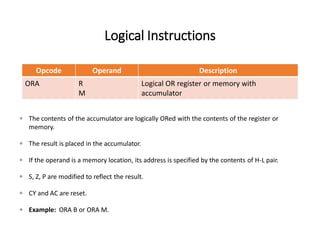
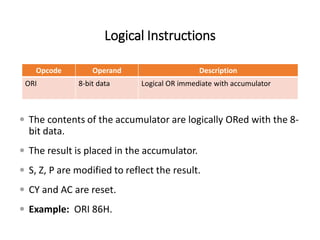
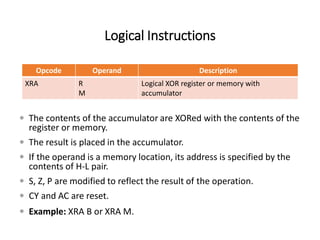
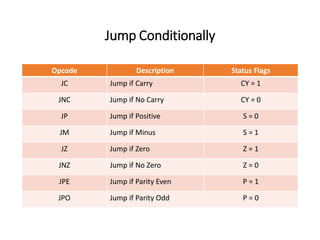
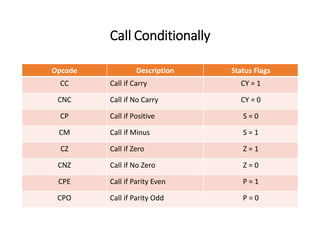
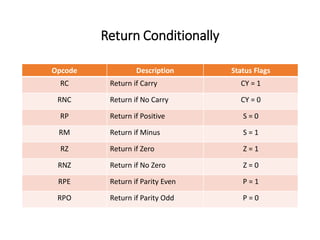
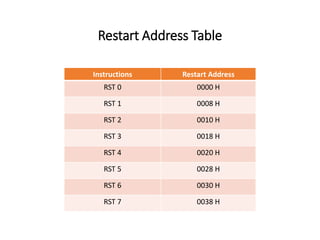
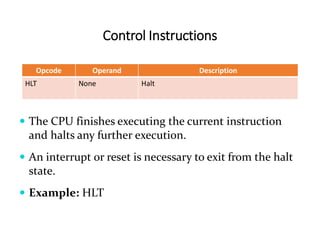
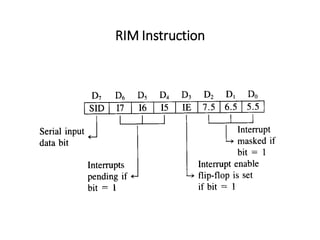
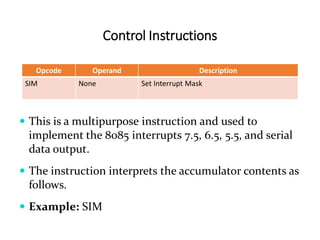
The 8085 microprocessor has 246 instructions that are represented by 8-bit binary opcodes. The instruction set includes data transfer instructions to move data between registers and memory, arithmetic instructions to perform operations like addition and subtraction, logical instructions for AND, OR, XOR operations, branching instructions to change program flow, and control instructions. Common data transfer instructions include MOV, MVI, LXI, LDA, STA. Arithmetic instructions include ADD, SUB, INR, DCR. Logical instructions include AND, OR, XOR, CMP, CMA.