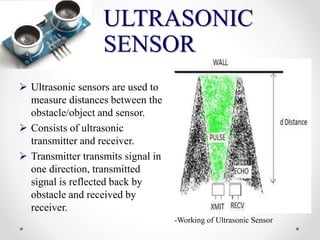
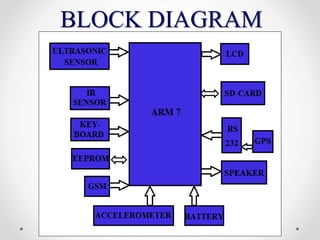
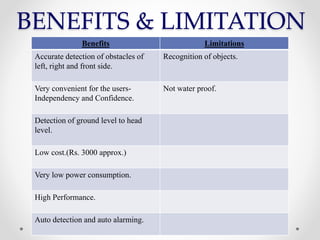
The seminar focused on a voice navigation stick designed for blind individuals, integrating GPS, GSM, and obstacle sensors to enhance independent navigation. It addresses the limitations of existing methods like blind canes and guide dogs, providing a more accurate and convenient solution for obstacle detection. The system aims to improve the safety and confidence of visually impaired users while highlighting its benefits and limitations.