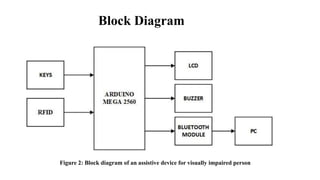
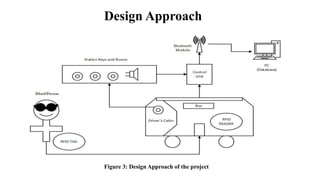
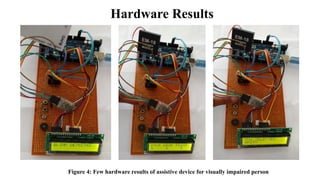
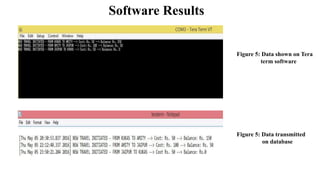
This document describes an assistive device designed for visually impaired persons using RFID, Bluetooth, and a microcontroller. The device allows visually impaired individuals to travel independently on public transportation. It works by using RFID cards assigned to each user to identify them and deduct fares when they board and depart stops. The updated balance and travel information is sent via Bluetooth to a database. When a user reaches their destination stop, a buzzer alerts them. The design aims to help visually impaired persons travel more easily and prevent fraud.

![Introduction
As per the WHO data base 39 million persons are blind and 246 have low vision and
they need constant support to attain their daily activity [2]. The advancement in
technology has not only given comfort to the normal person but the person with
disabilities too. Many advancement in technology has been seen from past years for
the Visually Impaired Person, for example:
(i) Assistive devices (White cane) [6]
(ii) Wearable assisting devices (Bionic Eyes, Finger Reader) [4-5]
(iii) Softwares (Screen Reading) [3]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation11-160624055703/85/assisting-device-for-visually-impaired-person-3-320.jpg)
![Figure 1:Wearable Assisting Devices (Adapted from [1])](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation11-160624055703/85/assisting-device-for-visually-impaired-person-4-320.jpg)