This document discusses cloud computing, including:
1. It defines cloud computing as internet-based computing where virtual servers provide resources like software, infrastructure, platforms and devices to customers on a pay-as-you-use basis.
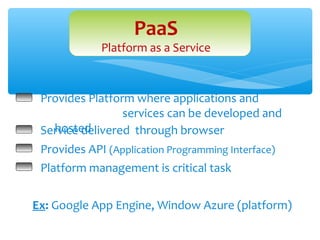
2. It describes the main types of clouds: SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS which provide software, platforms, and infrastructure as services respectively.
3. It outlines some key advantages like pay-as-you-use, location independence, instant scalability, and abstraction which allows enterprises to focus on their core business.