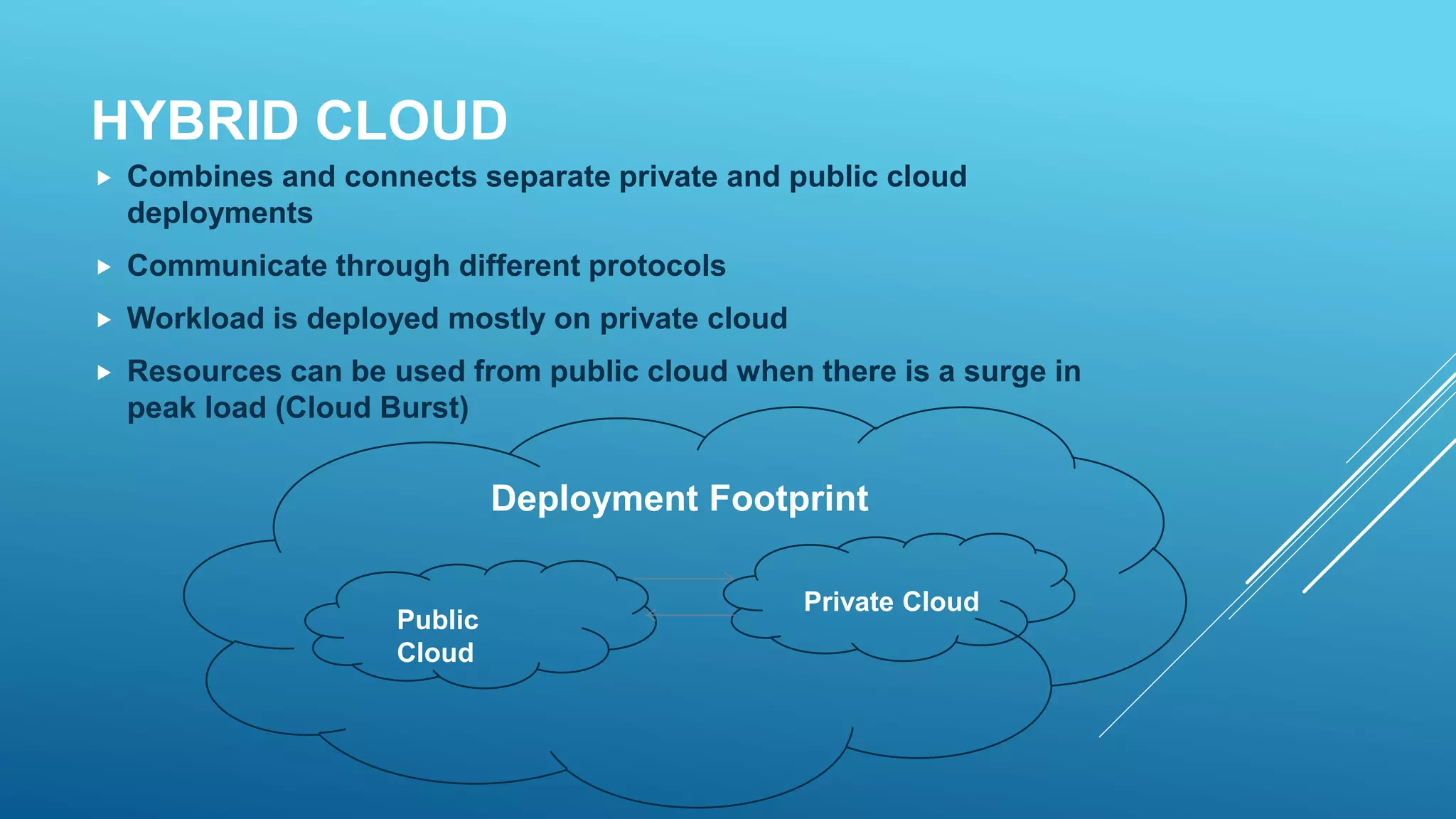
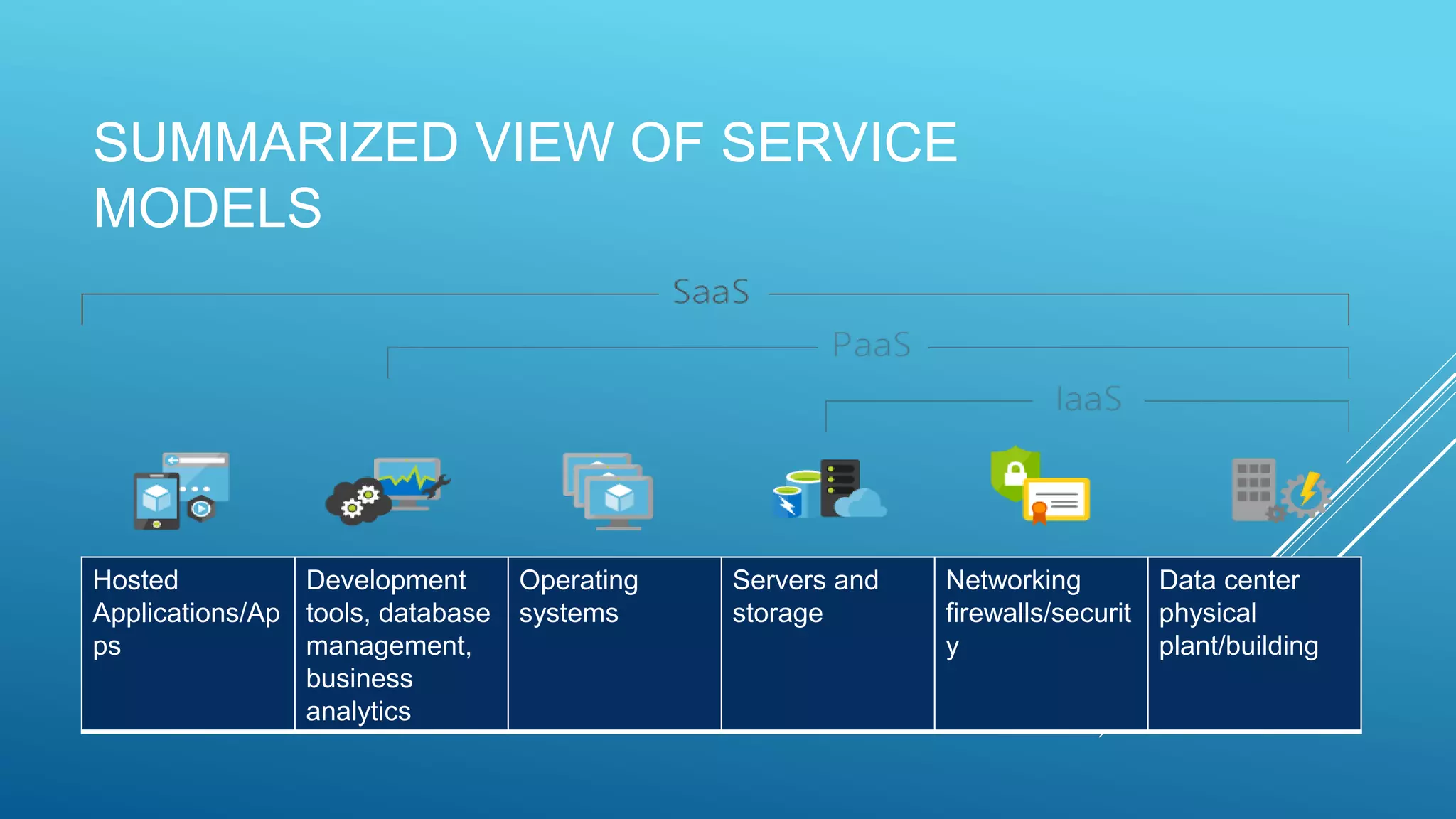
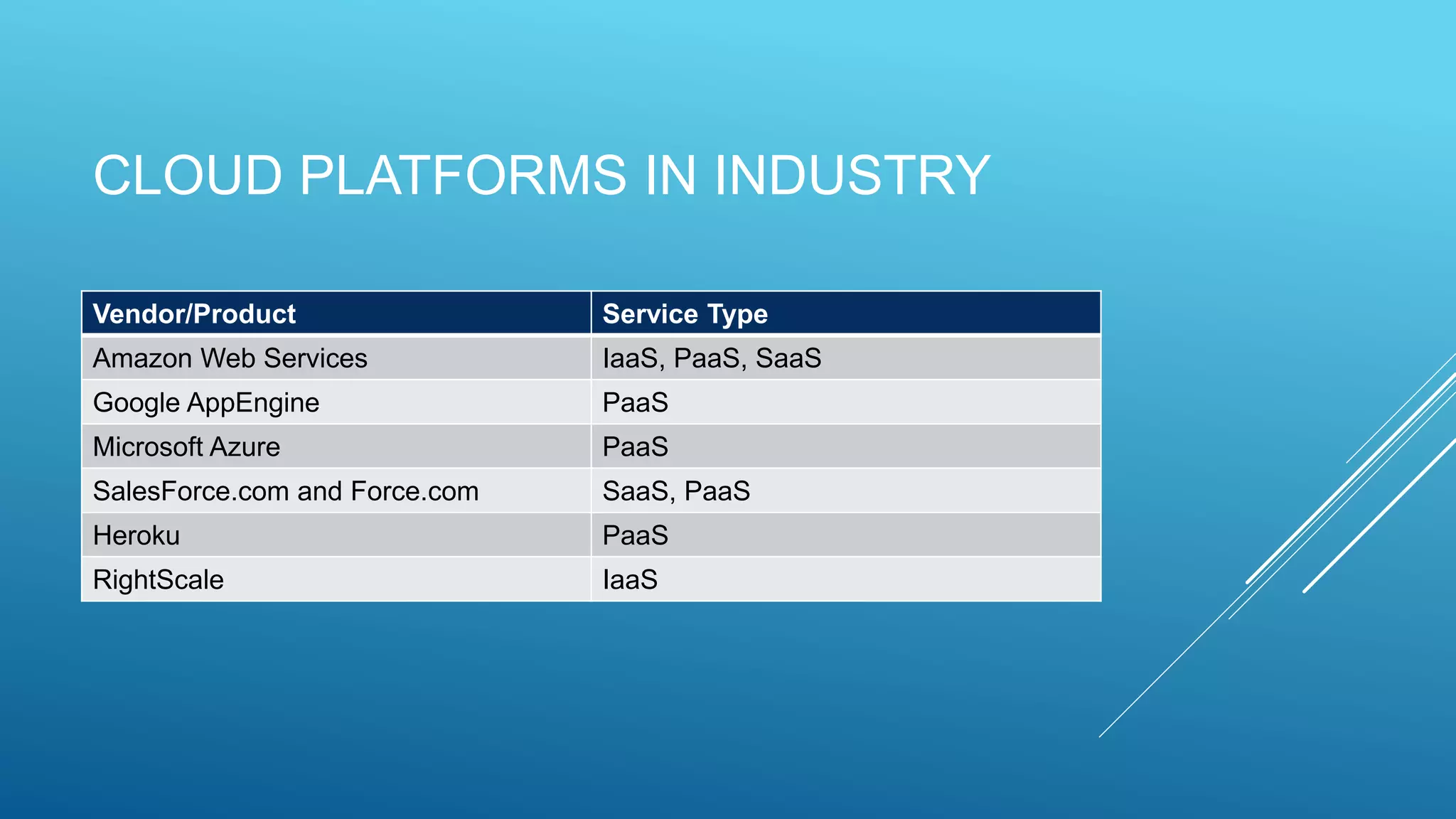
This document provides an overview of cloud computing, including what it is, its uses, benefits, types of cloud deployment, service models, and major cloud platforms. Cloud computing delivers computing services over the internet, allowing companies to access servers, storage, databases and more on demand. It provides benefits like reduced costs, increased speed and scalability, reliability, and productivity. The main types of cloud deployment are public, private, and hybrid cloud. Infrastructure as a service (IaaS), platform as a service (PaaS), and software as a service (SaaS) are the three standard service models. Major cloud platforms include Amazon Web Services, Google AppEngine, Microsoft Azure, and Salesforce.com.