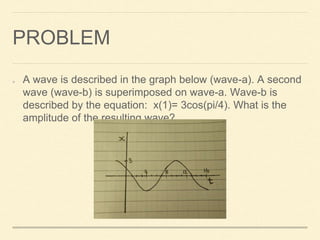
This document describes how to find the resulting amplitude when two waves with the same wavelength, frequency and direction interfere. It provides an equation that calculates the resulting amplitude based on the phase difference between the two waves. It then works through an example problem, finding that the resulting amplitude of two interfering waves - one described by a graph and one by an equation - is 5.543m.