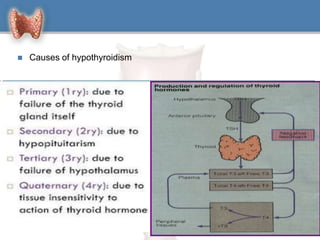
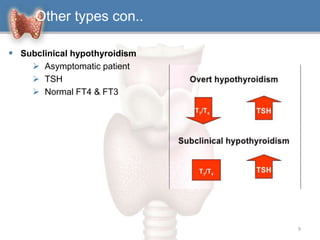
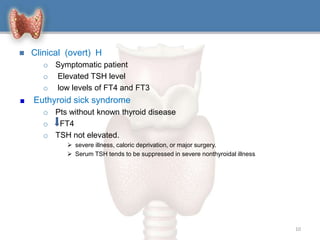
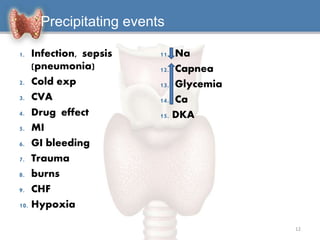
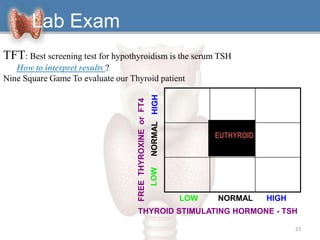
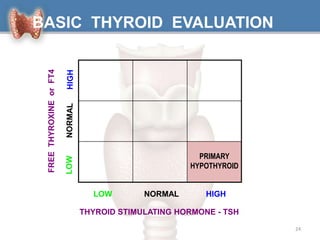
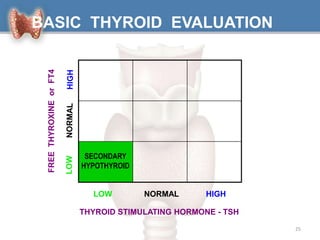
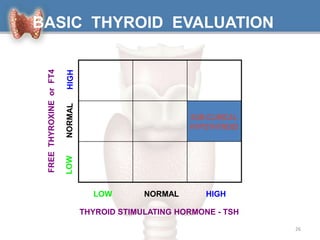
1. Hypothyroidism is a clinical syndrome where the thyroid gland fails to produce sufficient thyroid hormones.
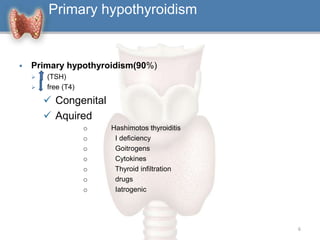
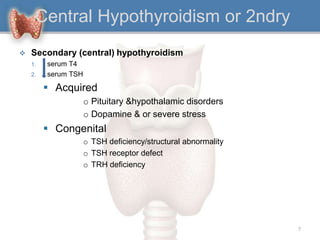
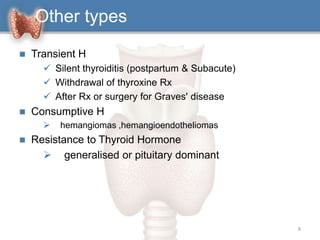
2. It can be primary, meaning it is caused by problems with the thyroid gland itself, or central/secondary, caused by problems with the pituitary gland or hypothalamus.
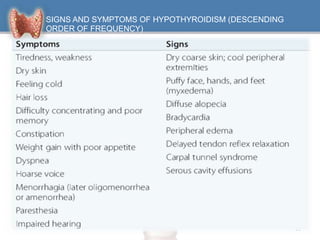
3. Symptoms affect many body systems and include fatigue, weight gain, dry skin, constipation, muscle weakness, decreased heart rate, impaired cognition and more.