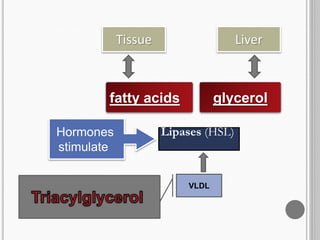
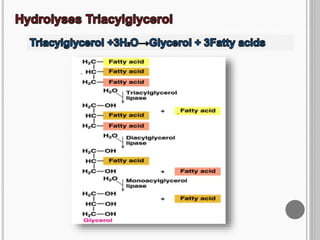
This document summarizes the process of lipolysis. Lipolysis is the breakdown of triglycerides stored in fat cells into fatty acids and glycerol. It occurs mainly in adipose tissue to release fatty acids for energy. Triglycerides are transported to tissues like adipose and muscle via lipoproteins. Hormones such as epinephrine activate hormone-sensitive lipase in adipose tissue to break down triglycerides into glycerol and fatty acids. Glycerol enters the bloodstream and is converted to glucose by the liver, while fatty acids bind to albumin for transport and are broken down in mitochondria to produce energy.