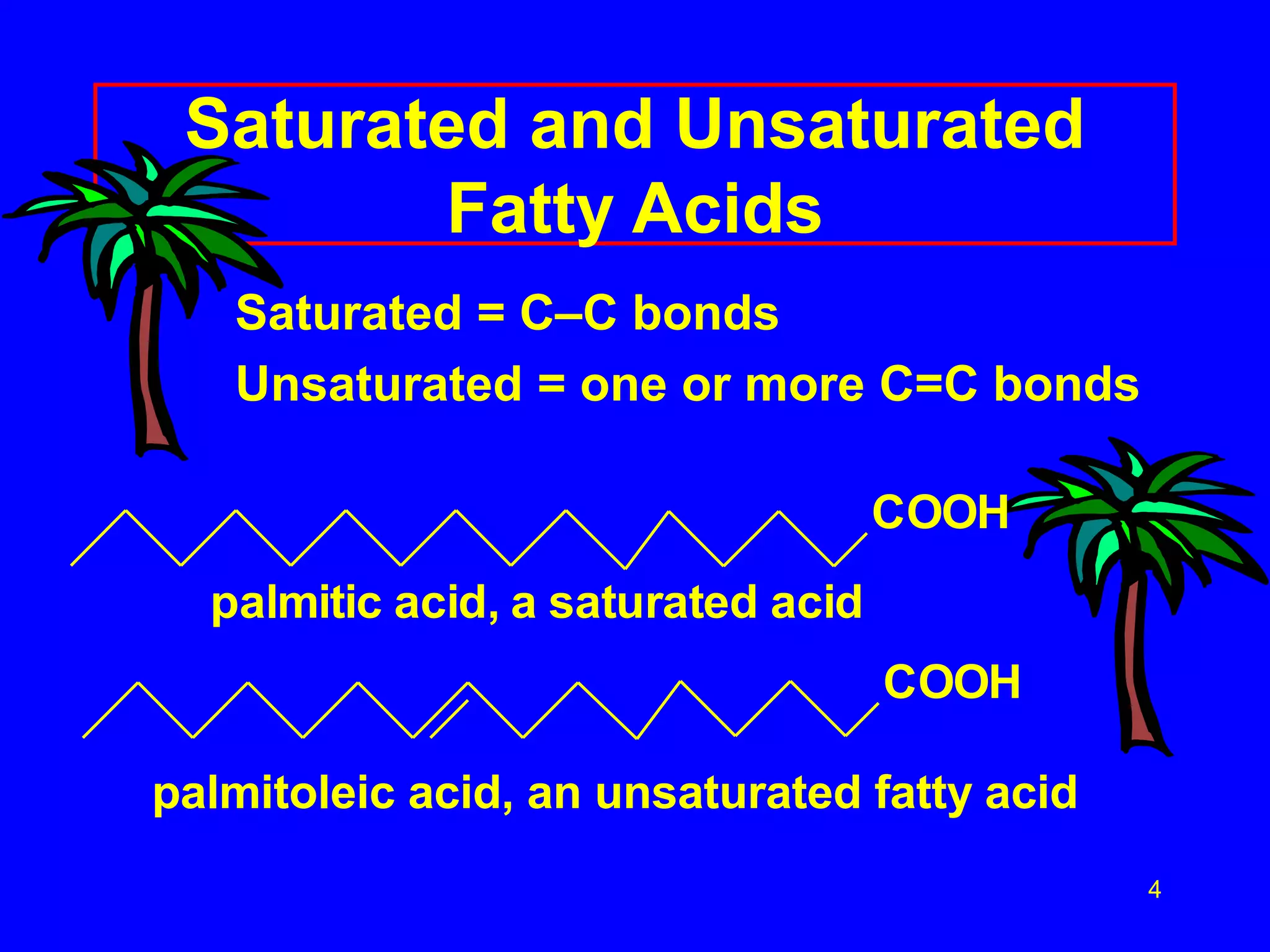
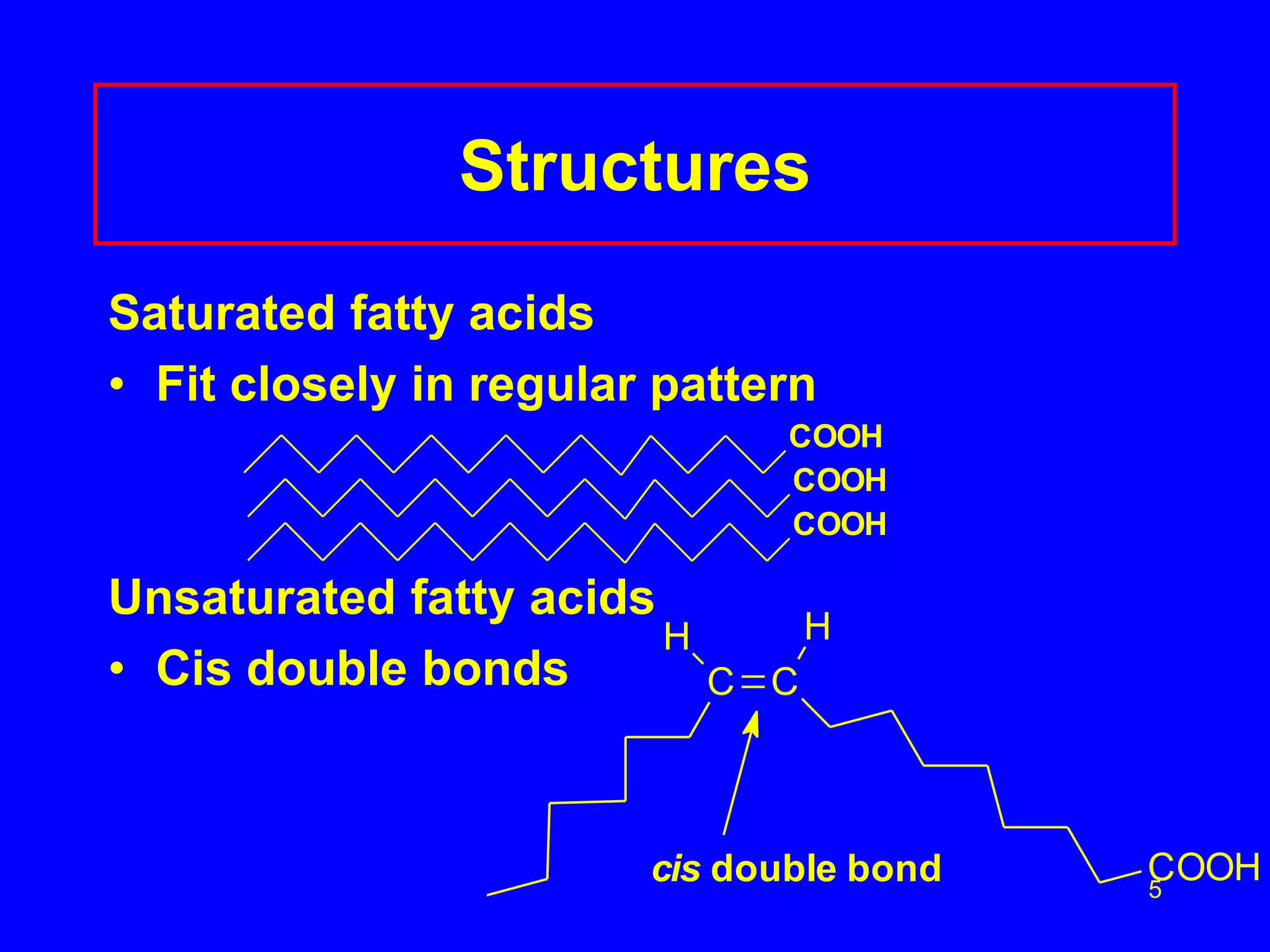
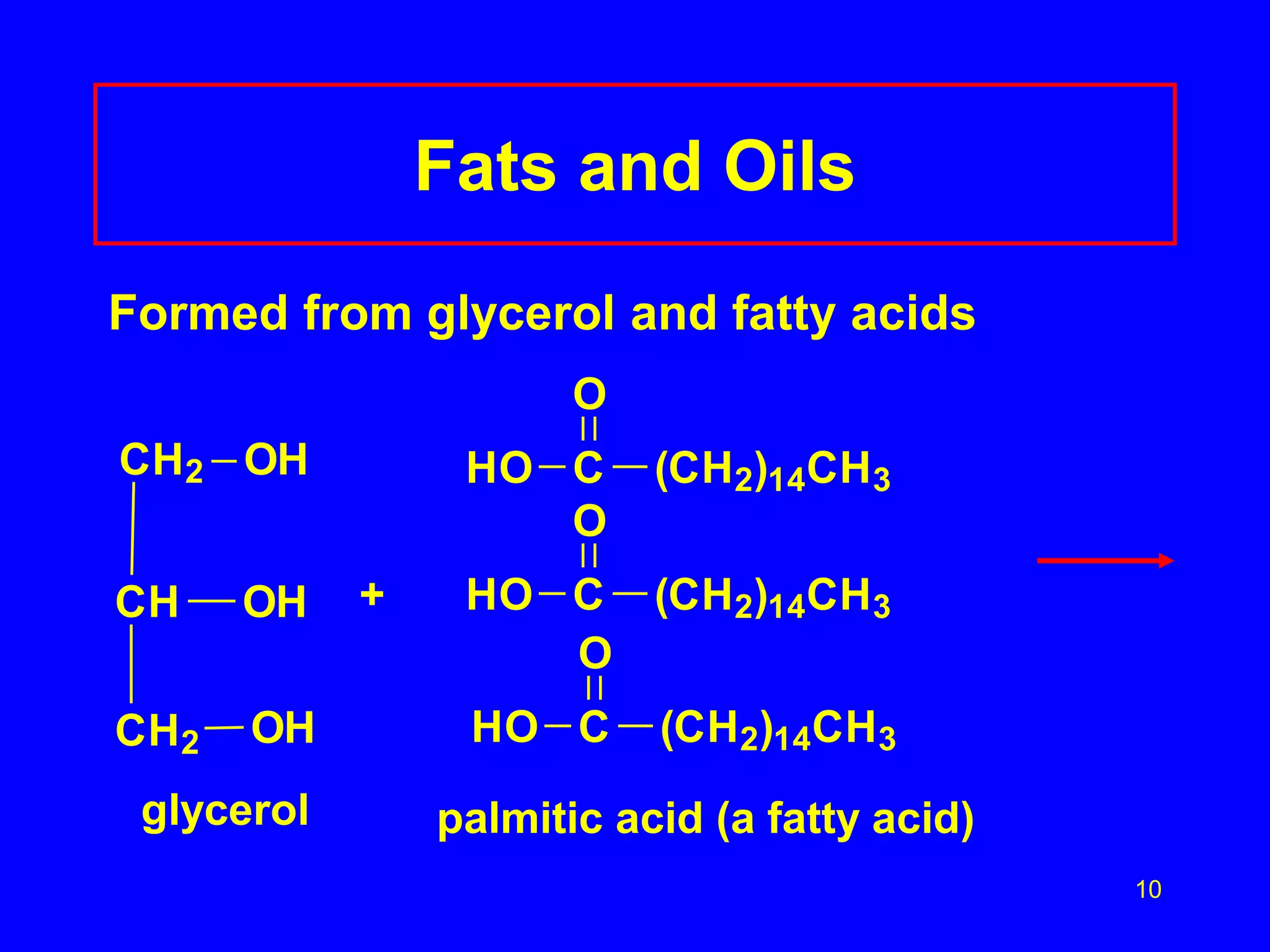
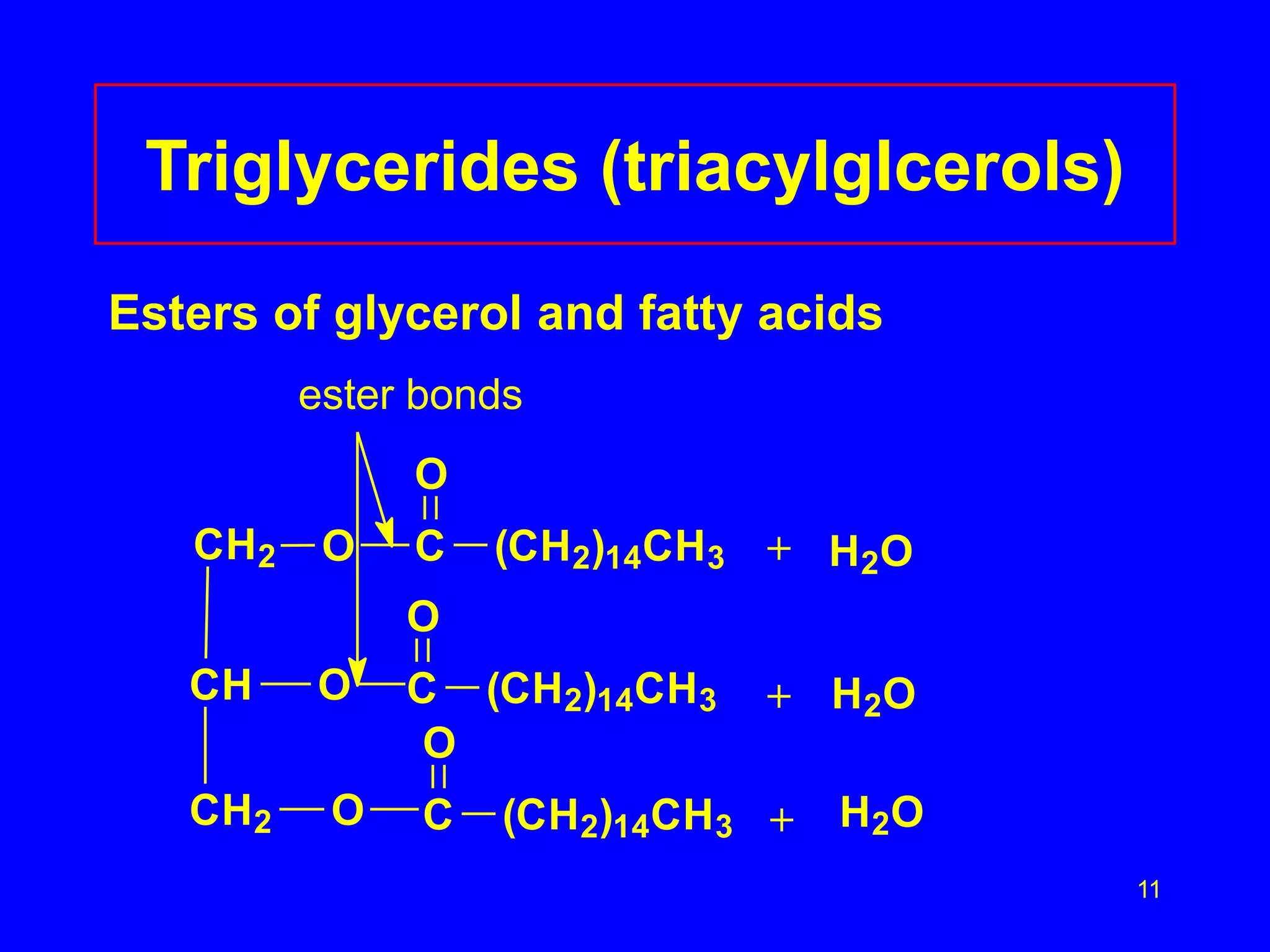
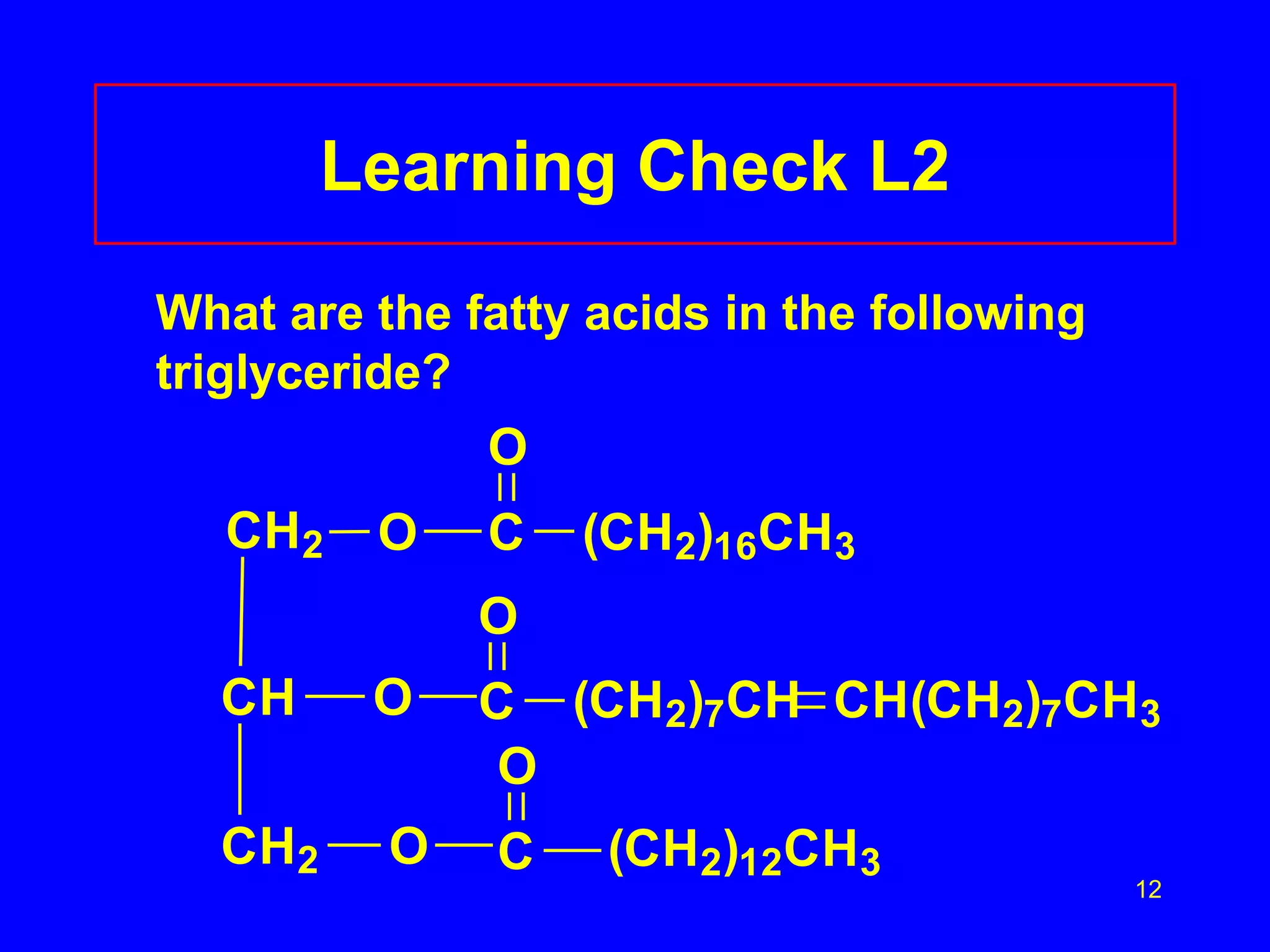
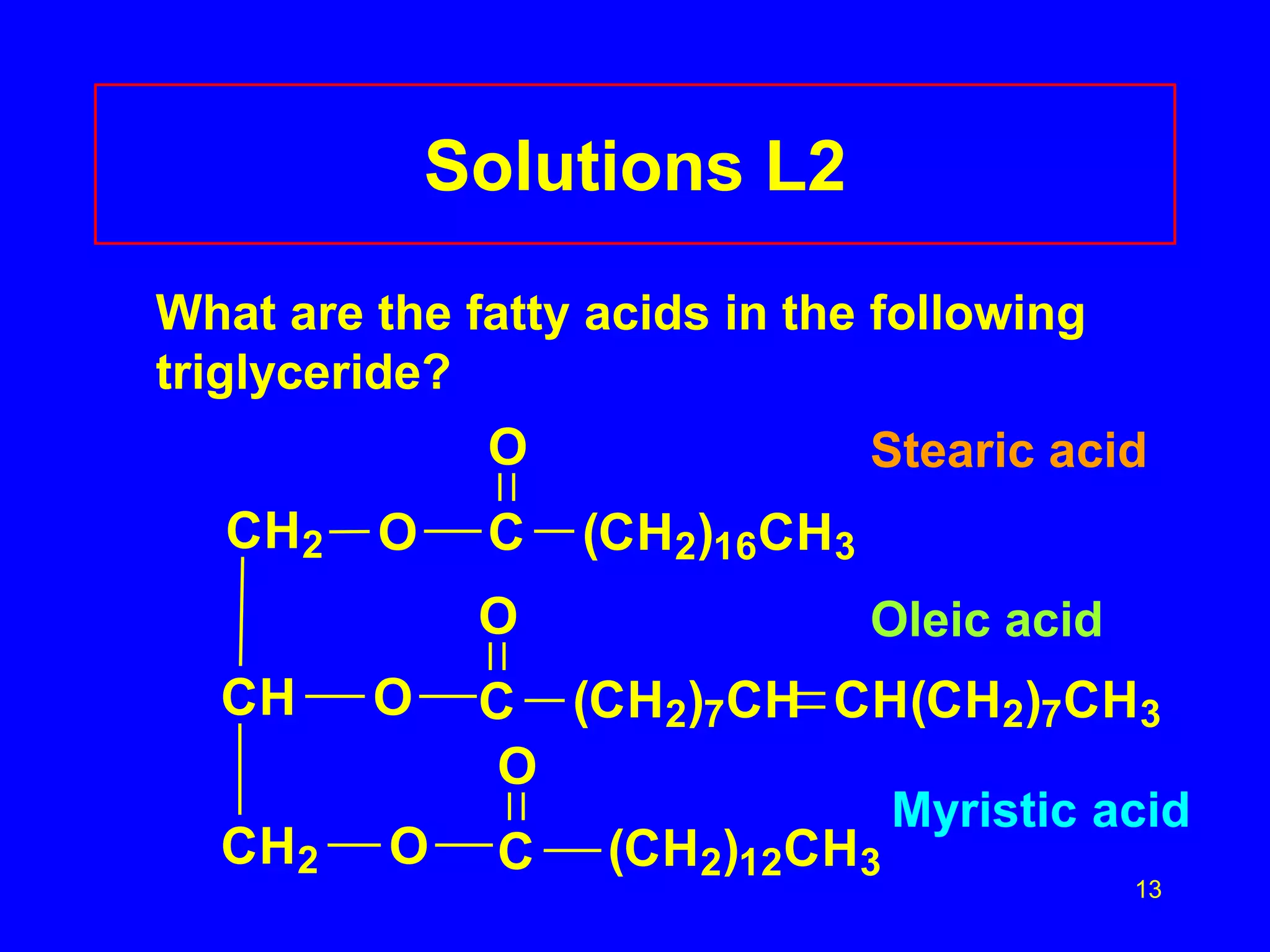
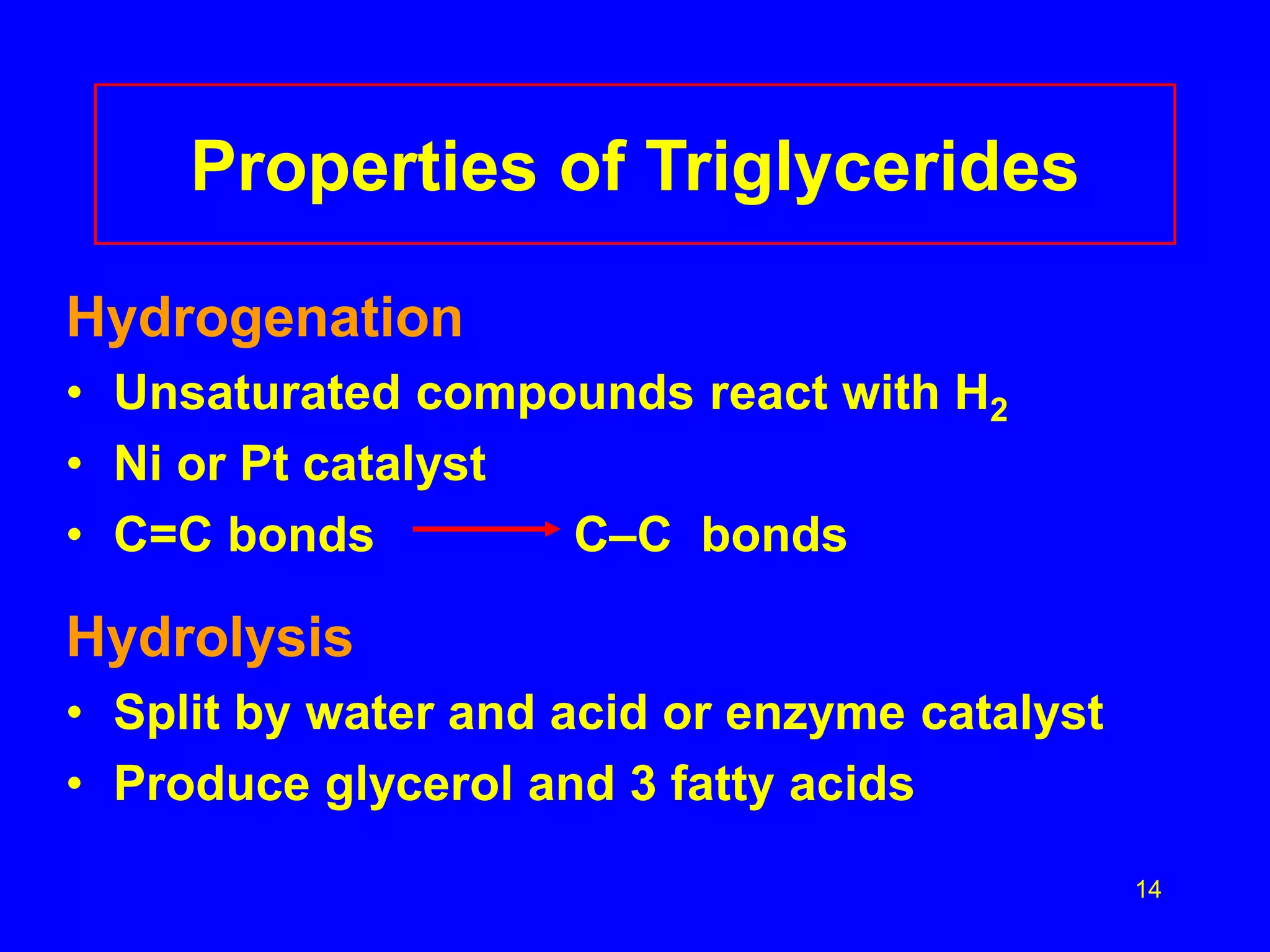
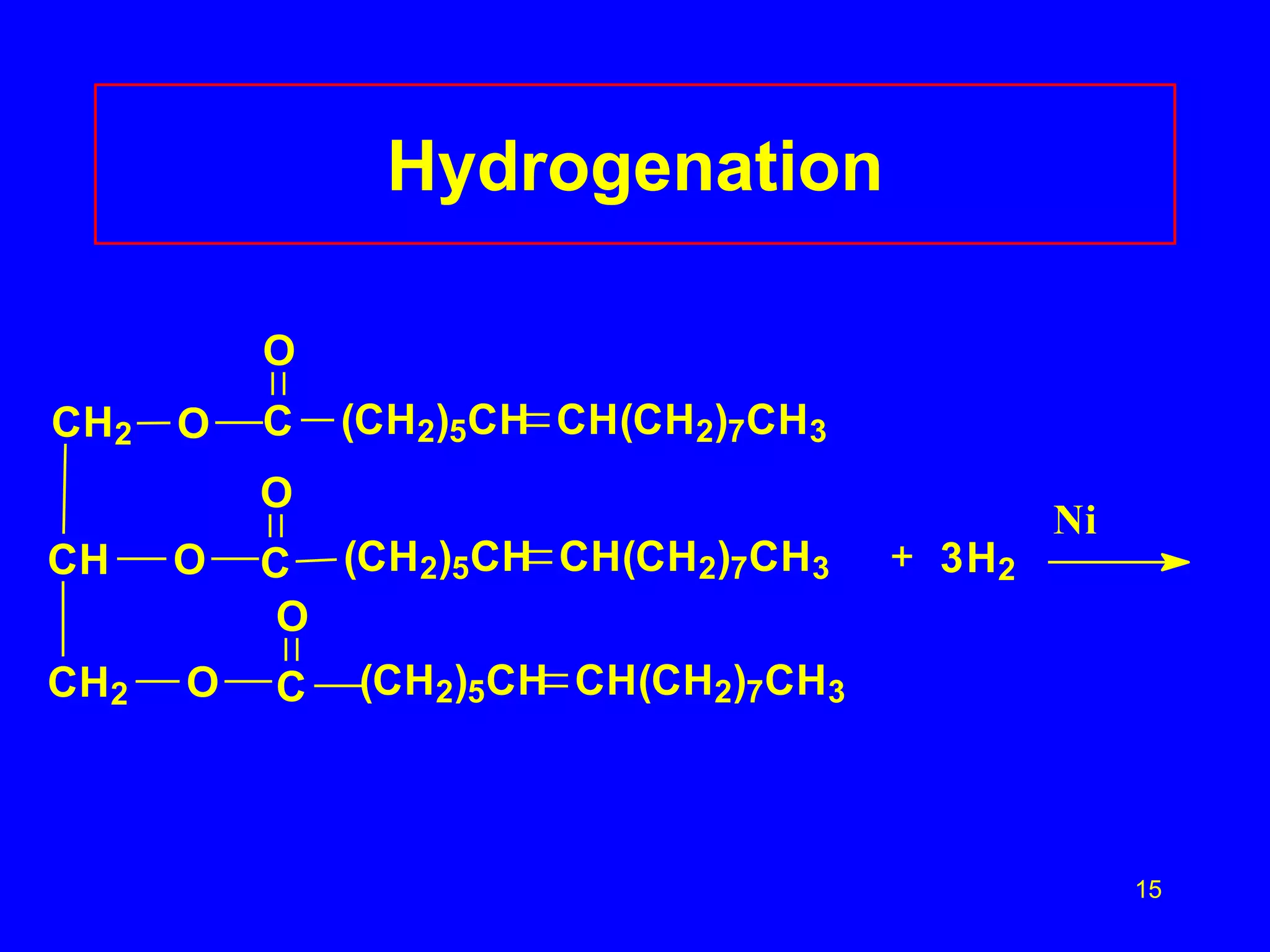
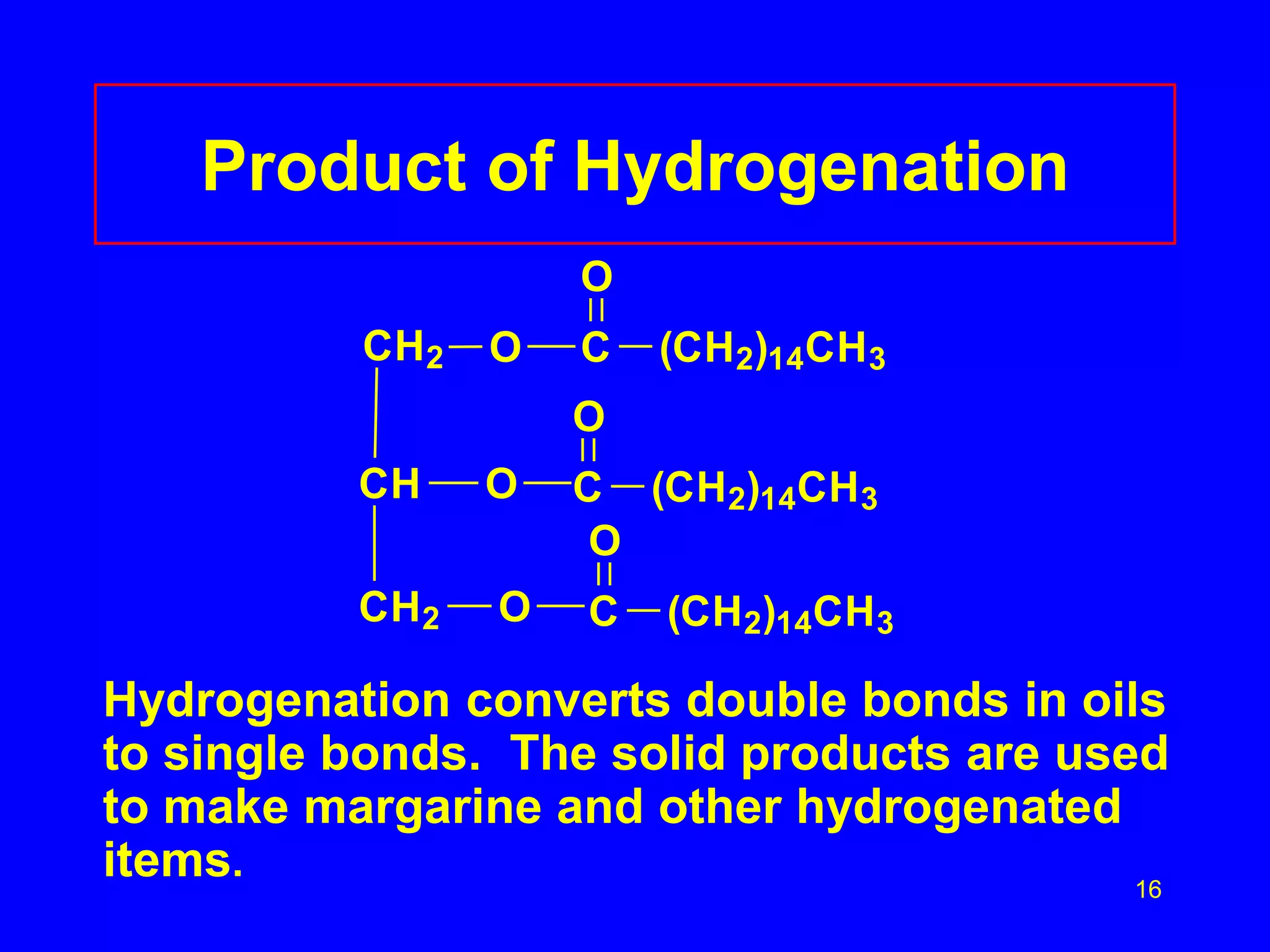
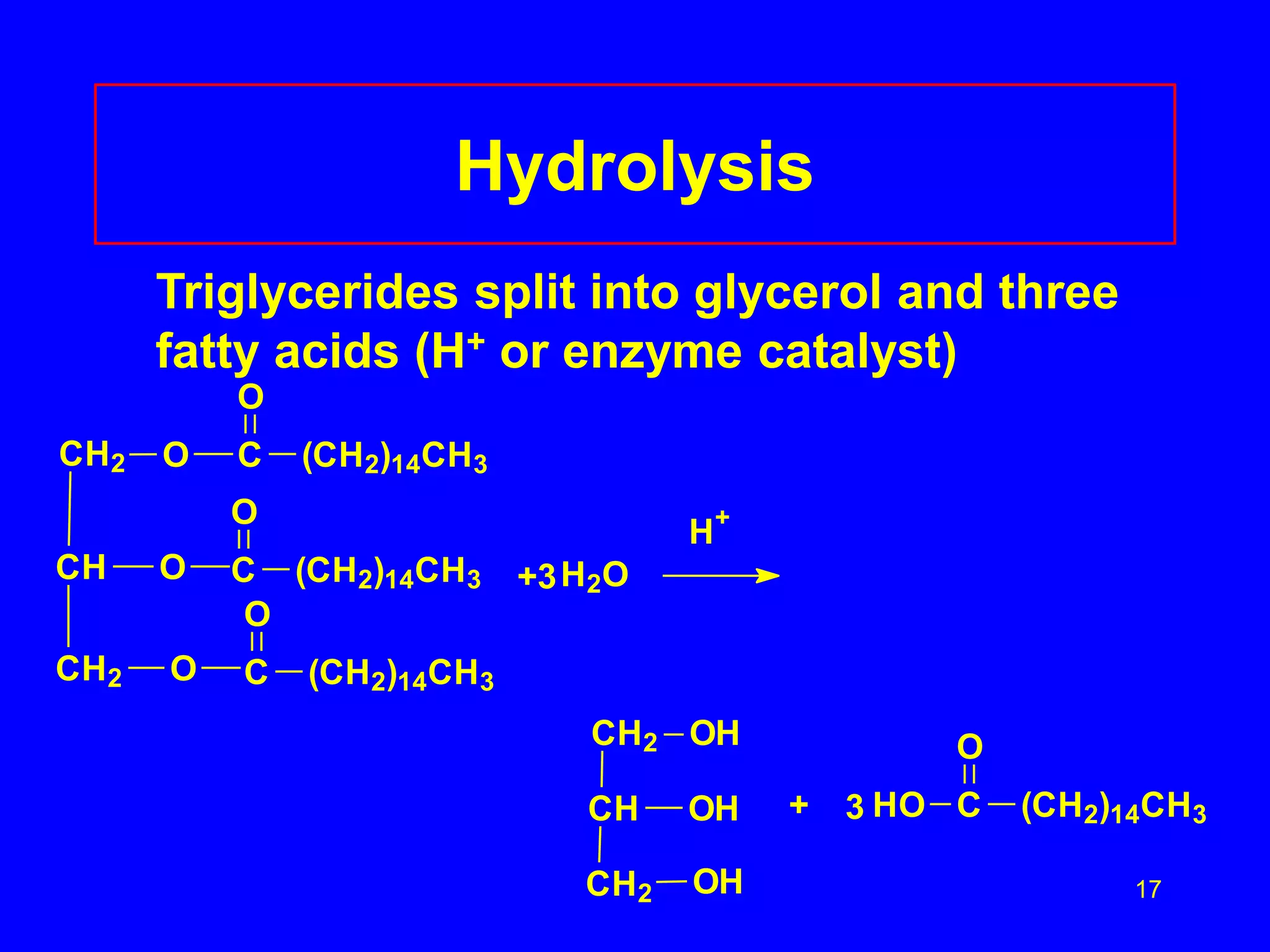
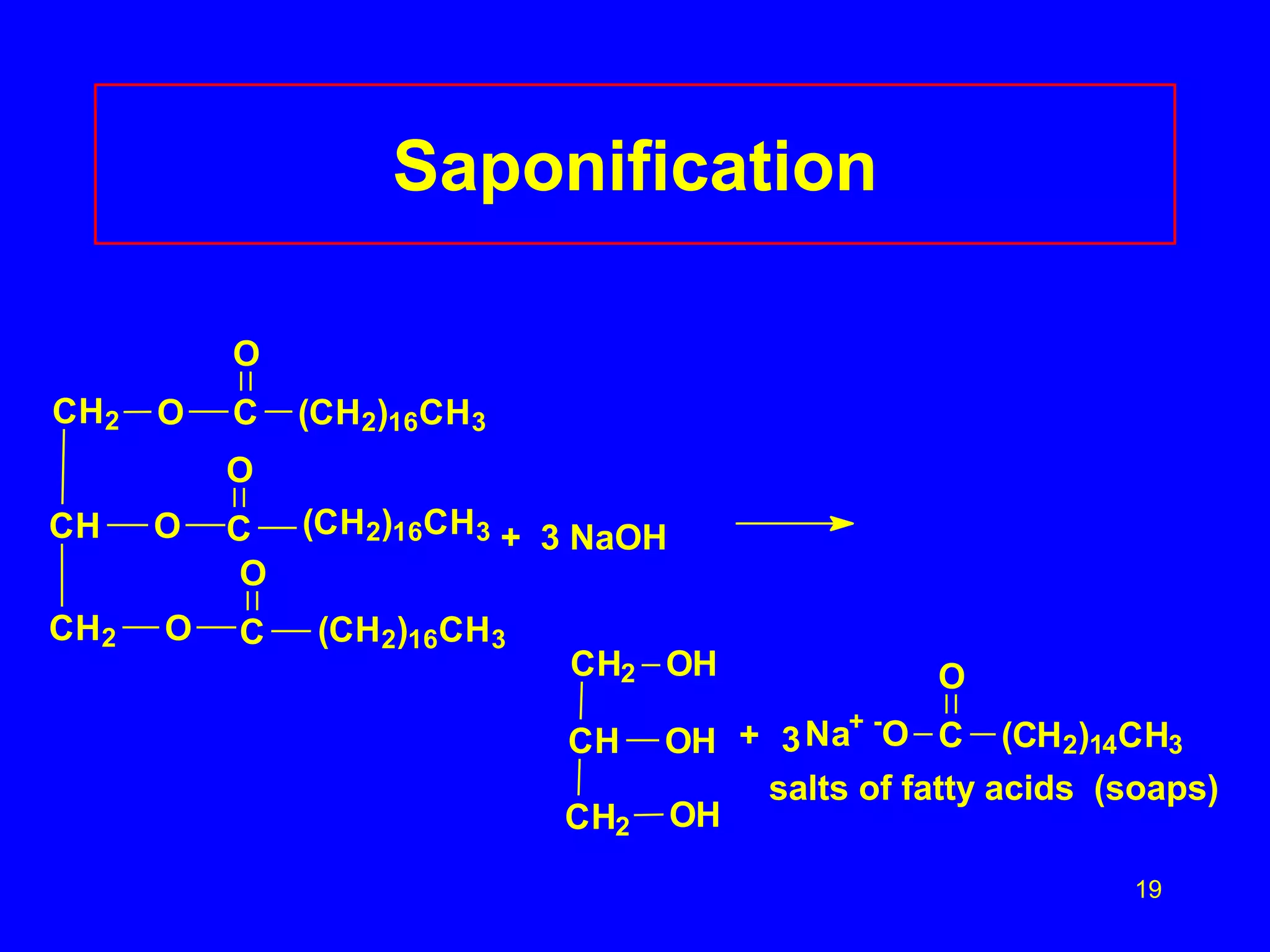
This document discusses lipids such as fatty acids, fats, and oils. It describes the different types of lipids including those with and without fatty acids. Fatty acids are long-chain carboxylic acids that can be saturated or unsaturated. Fats and oils are formed from glycerol and fatty acids and are known as triglycerides. Triglycerides can undergo hydrogenation to convert double bonds to single bonds or hydrolysis to split into glycerol and fatty acids. Saponification uses a strong base to split triglycerides into glycerol and soap.