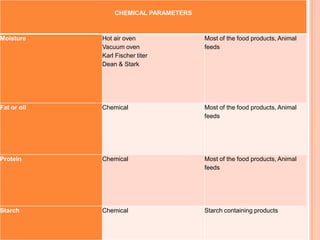
This document discusses food quality parameters and methods for analyzing food products. It outlines factors that contribute to food quality like appearance, taste, and nutritional value. Physical, chemical, and microbiological tests are used to analyze raw materials and finished products to ensure safety and purity. Parameters like moisture, fat, protein, and packaging materials are evaluated using methods like the hot air oven test and chemical analysis. Instrumental techniques like gas chromatography-olfactometry and electronic nose are also used to objectively measure organoleptic properties and identify volatile compounds that influence flavor.