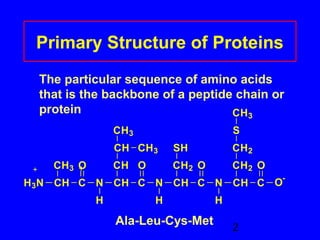
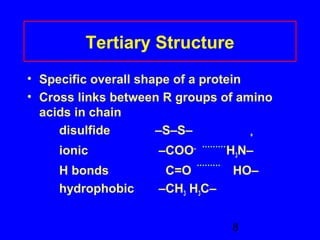
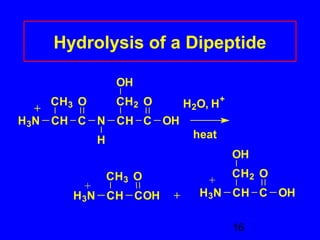
This document discusses the primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary structures of proteins. It defines each structure and provides examples. Primary structure refers to the sequence of amino acids in the polypeptide chain. Secondary structures include the alpha helix, beta pleated sheet, and triple helix. Tertiary structure describes the overall 3D shape of a protein formed by interactions between amino acid R groups. Quaternary structure involves proteins with two or more polypeptide chains. The document also covers protein hydrolysis, which breaks peptide bonds, and denaturation, which disrupts higher-order protein structures.