The document summarizes three major theories of language acquisition:
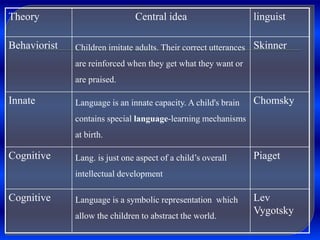
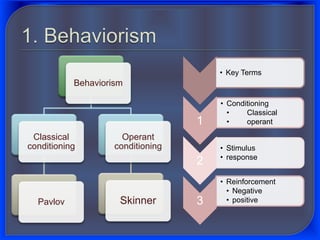
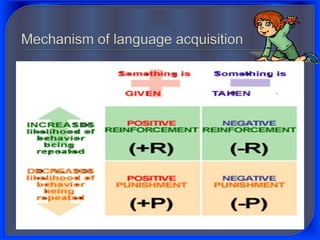
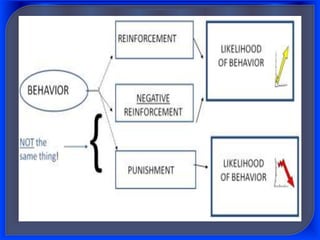
1. Behaviorist theory proposes that language is learned through imitation and reinforcement of behaviors. Children imitate adults and are rewarded for correct utterances.
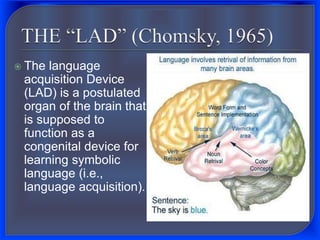
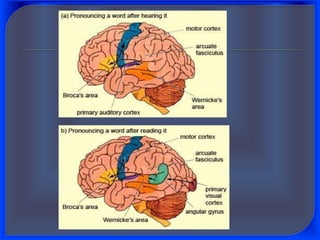
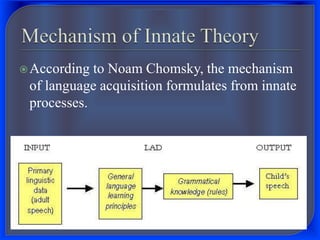
2. Innatist theory, proposed by Noam Chomsky, argues that humans are born with an innate language acquisition device in the brain that allows them to learn language according to innate linguistic principles and parameters.
3. Cognitive theory views language acquisition as one part of a child's overall intellectual development, and sees language as a symbolic representation that allows children to abstract the world.