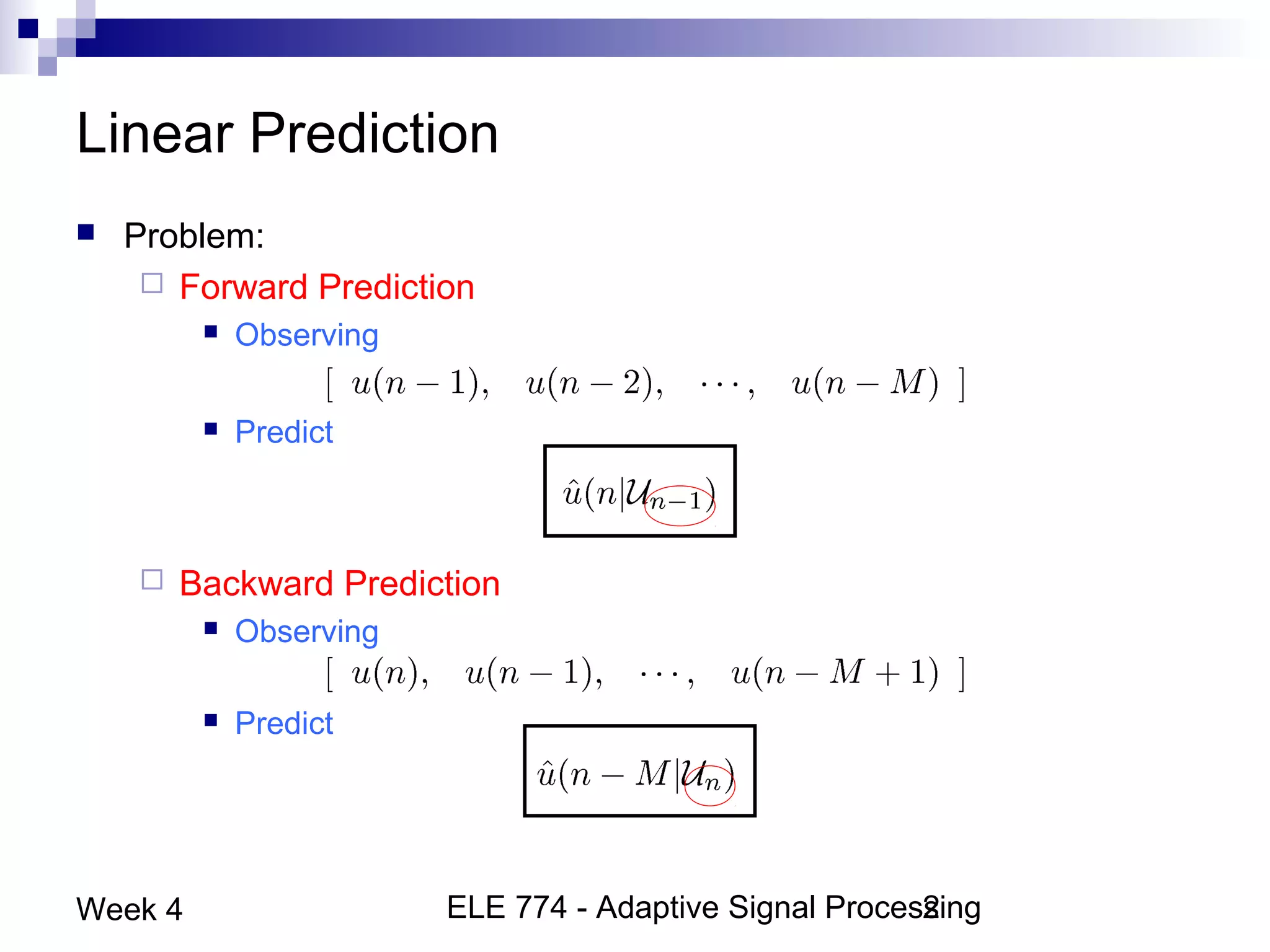
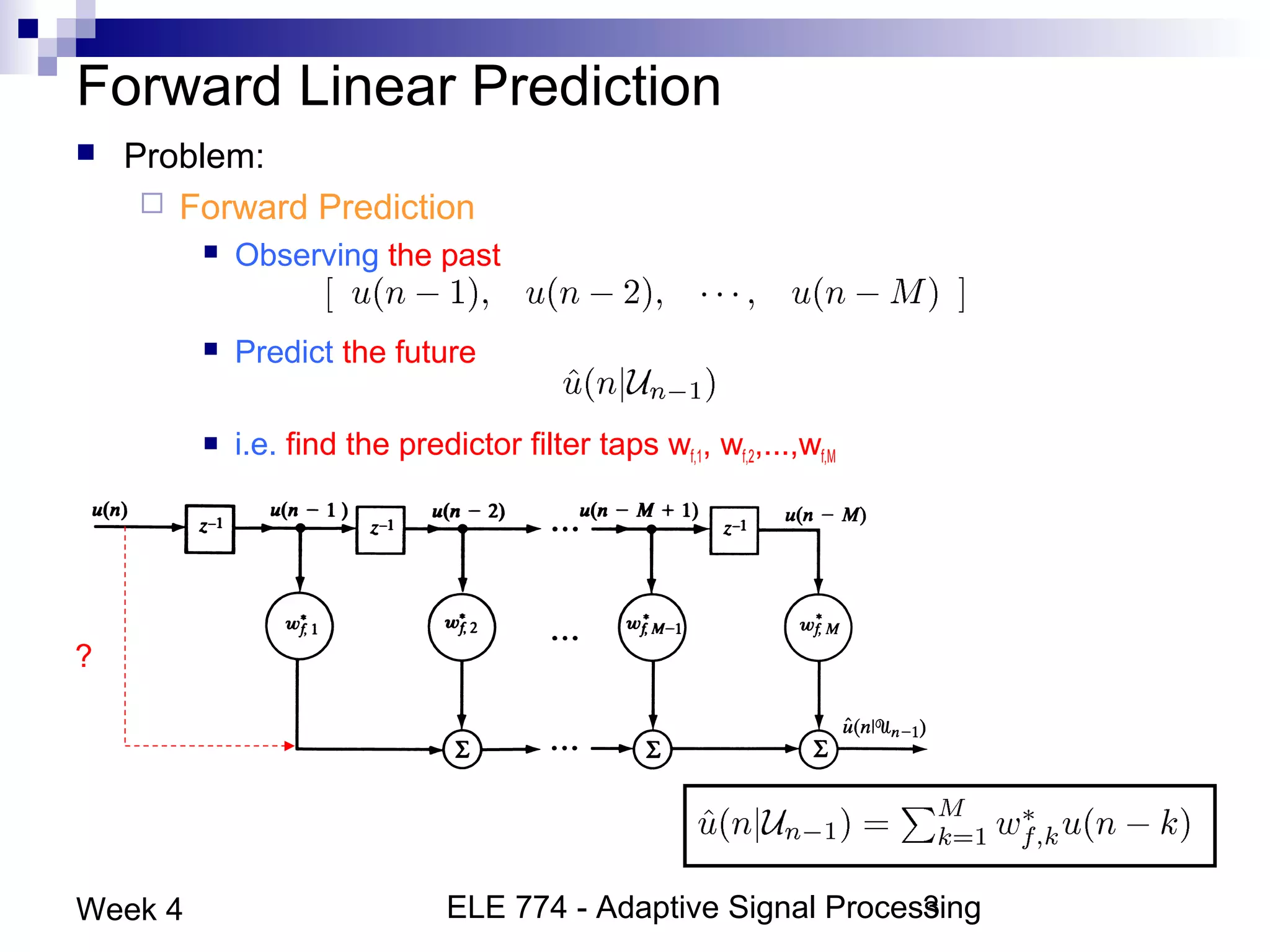
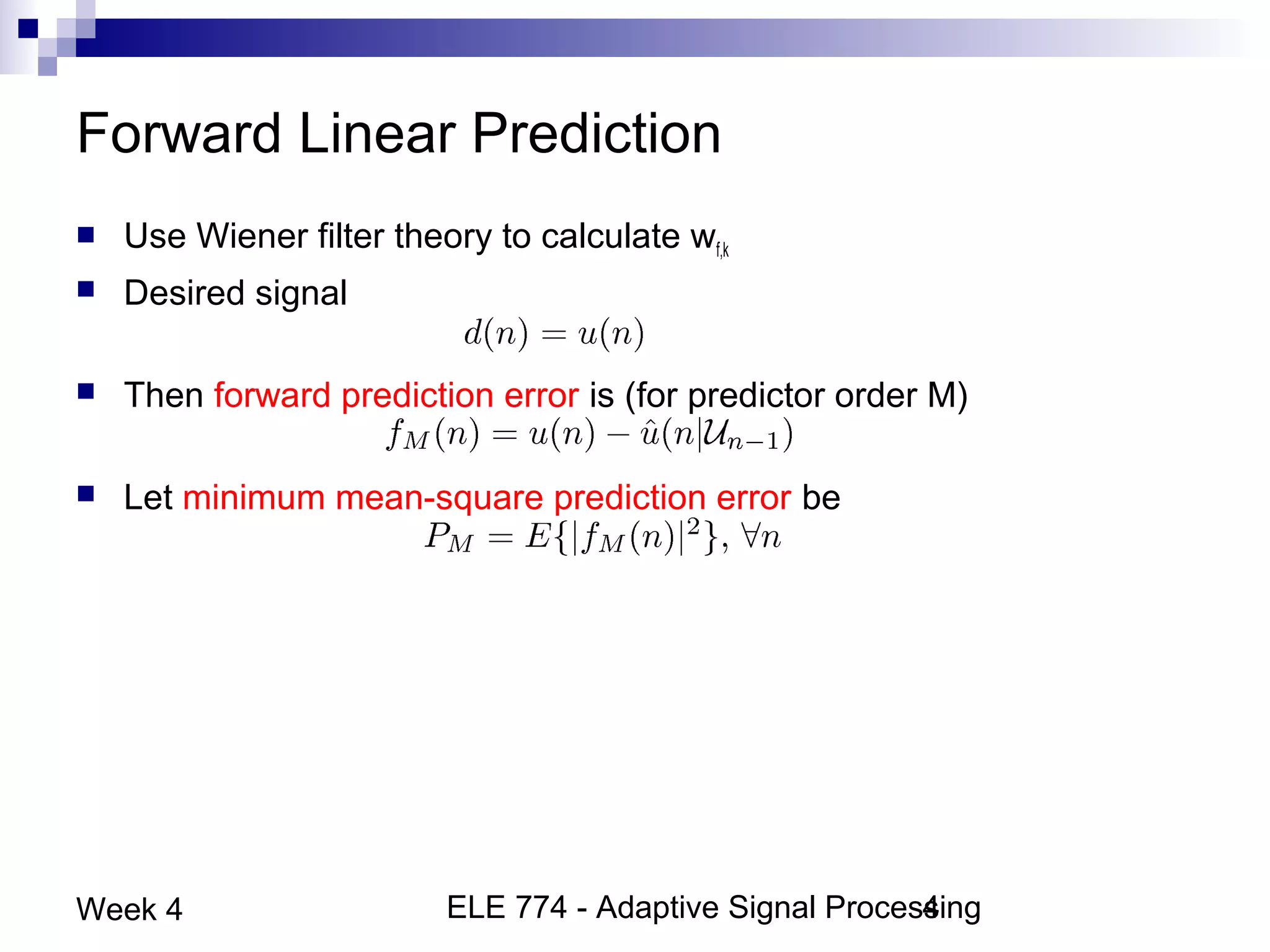
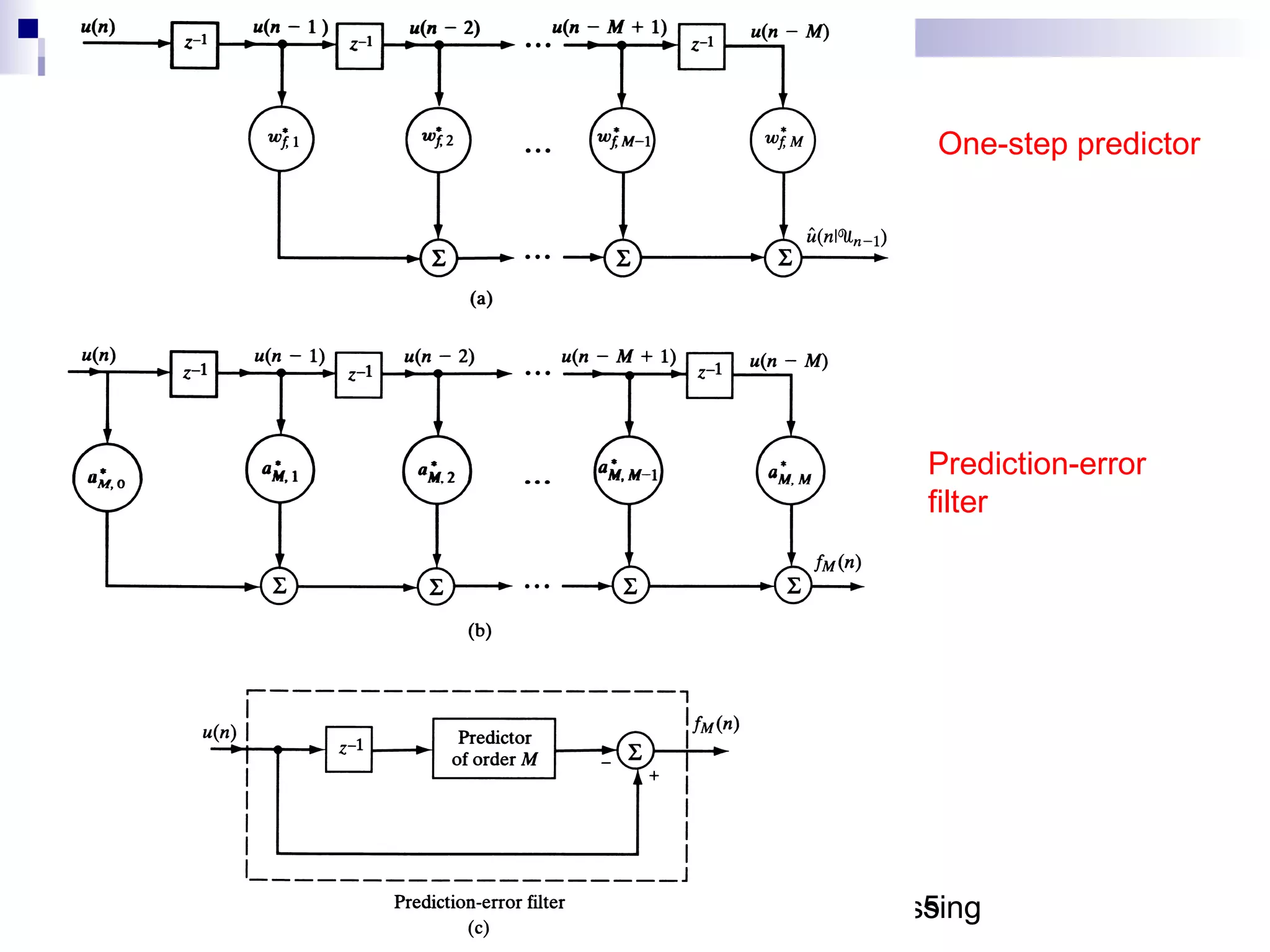
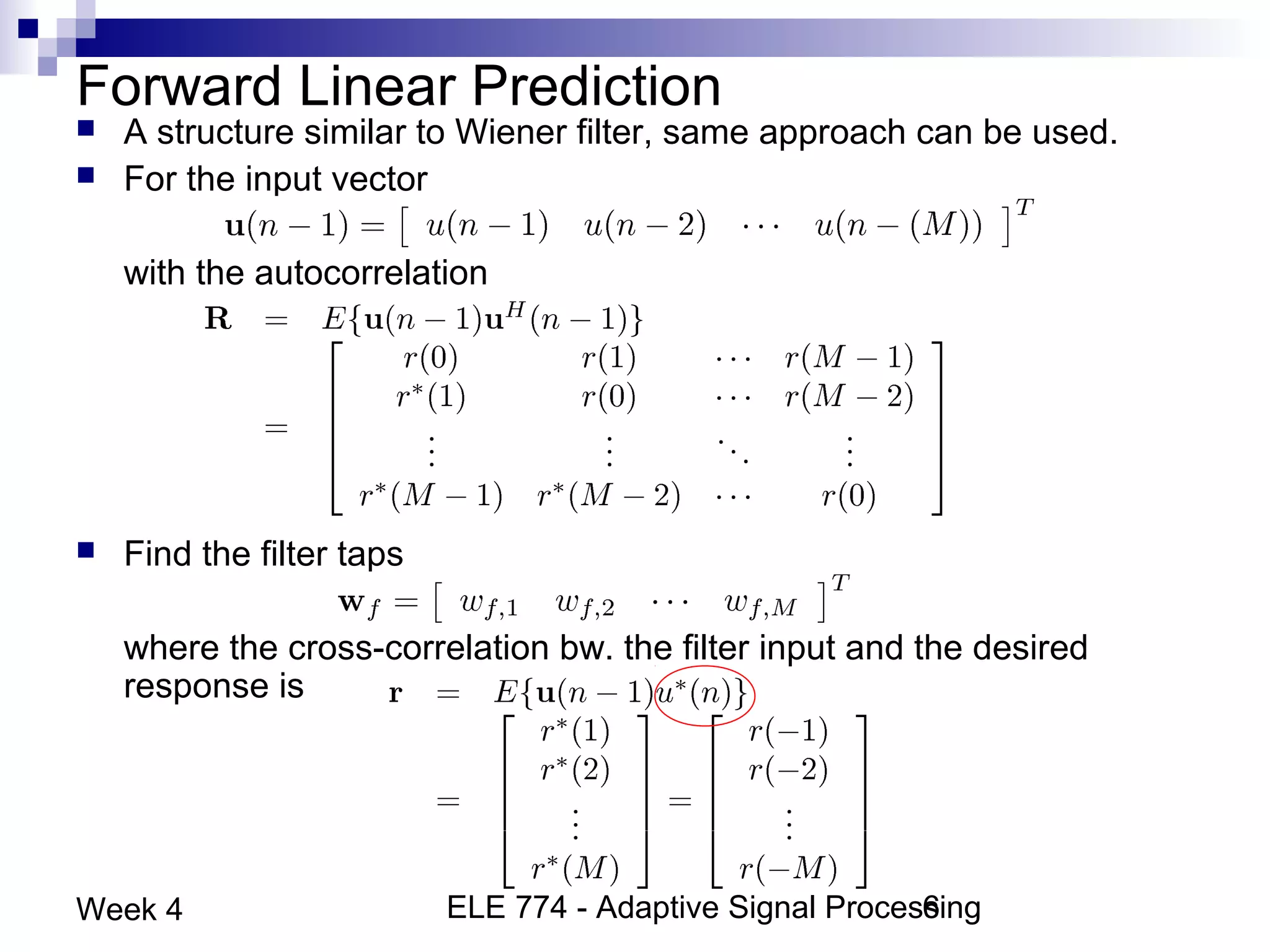
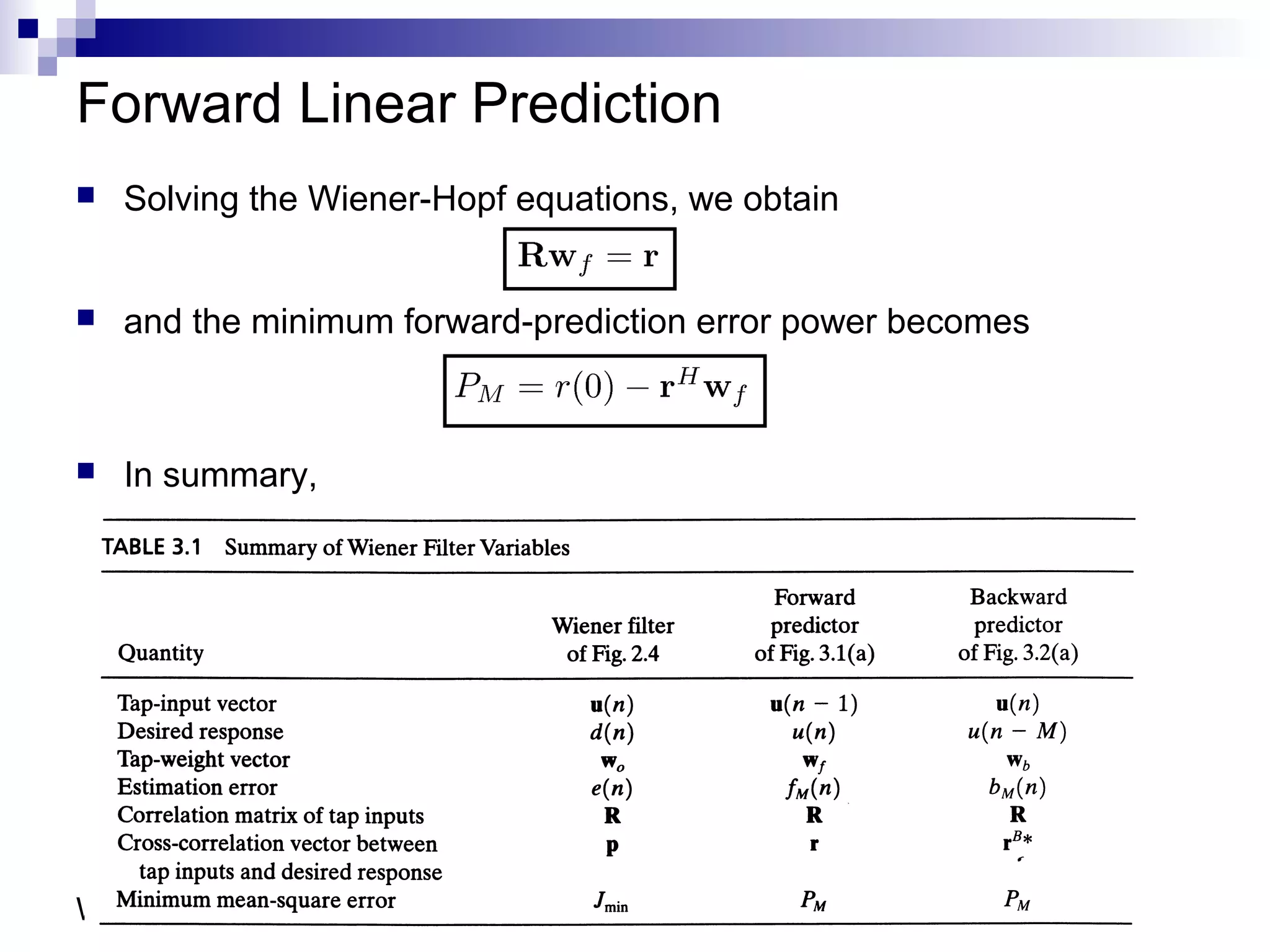
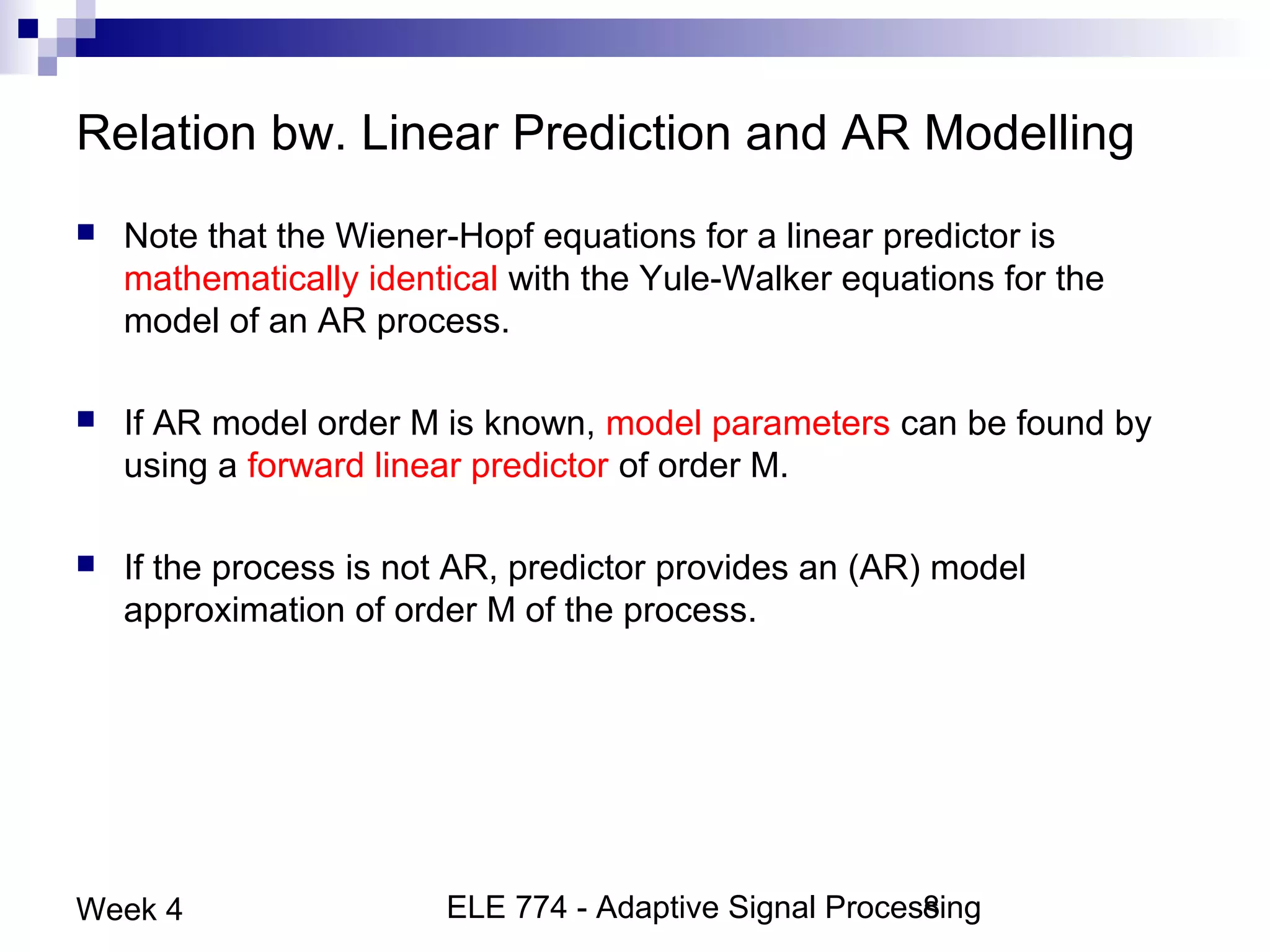
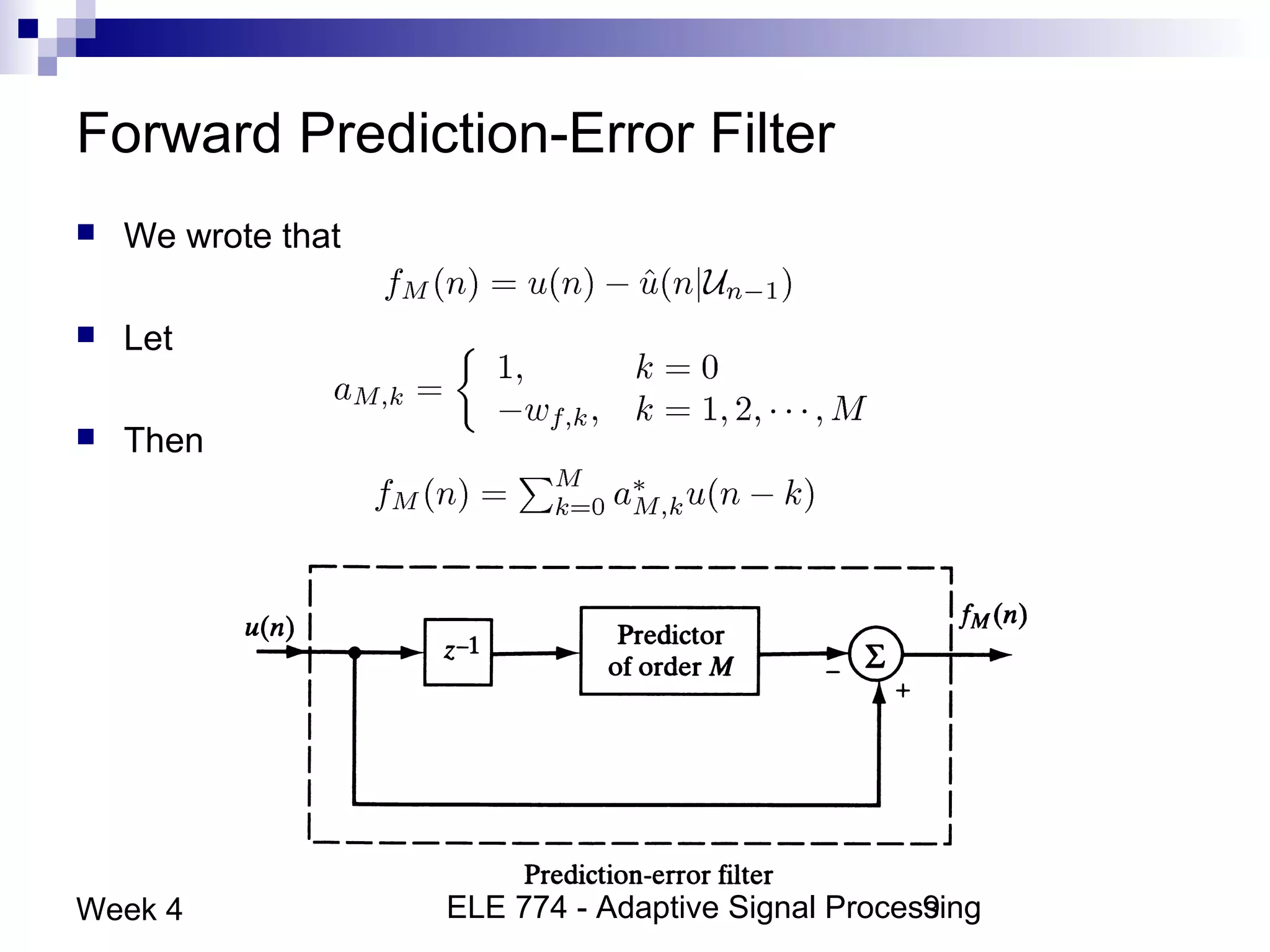
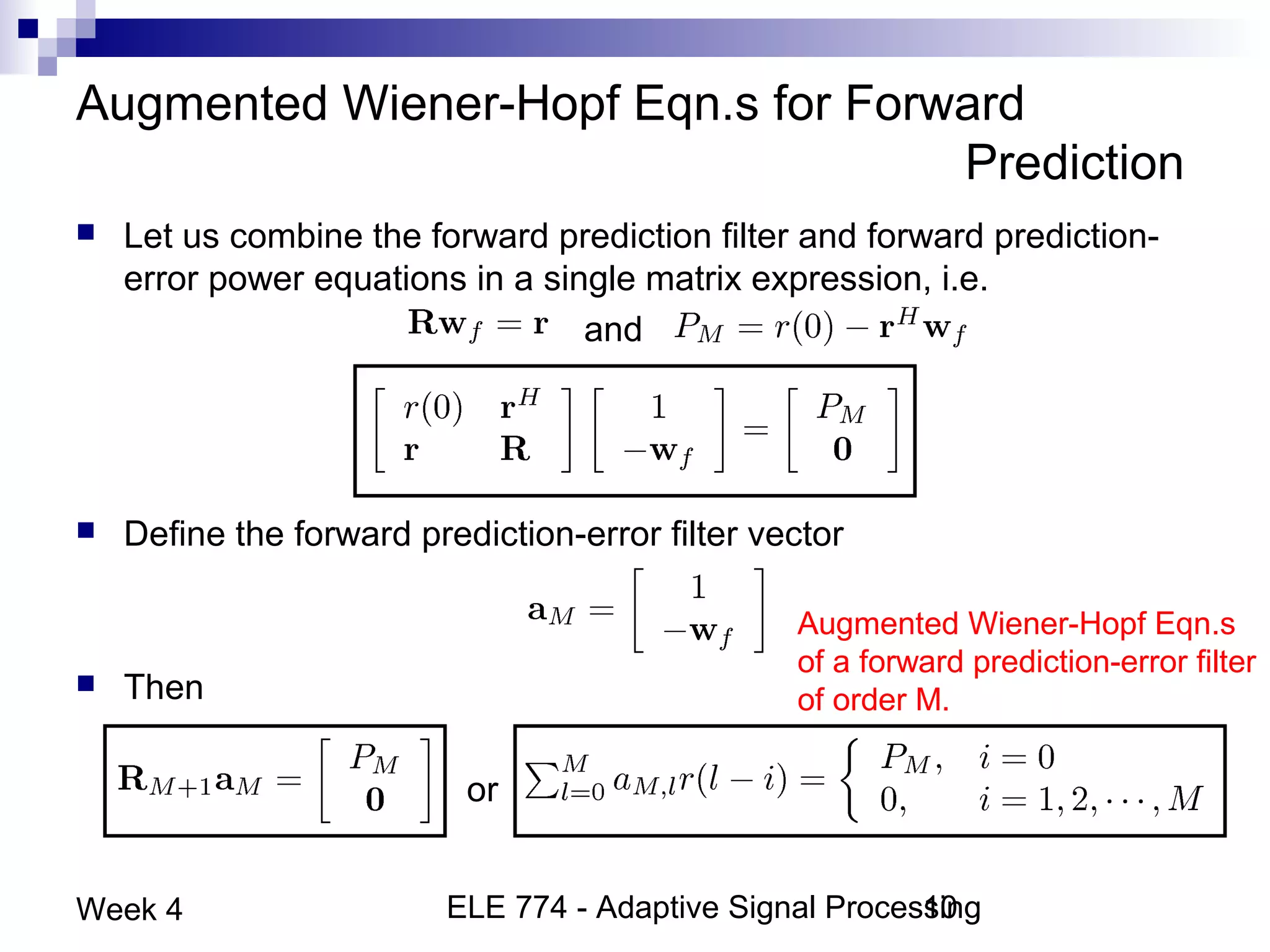
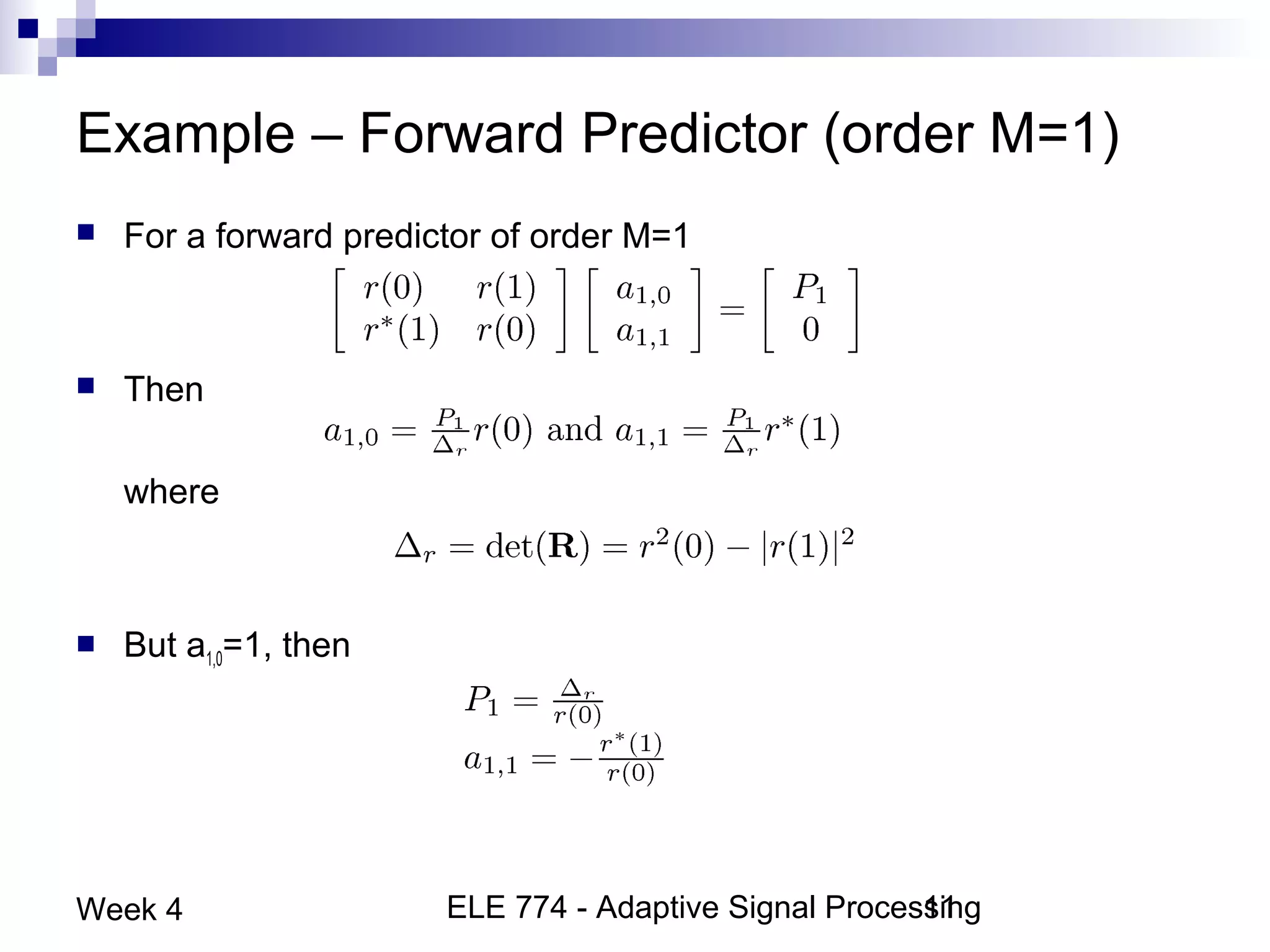
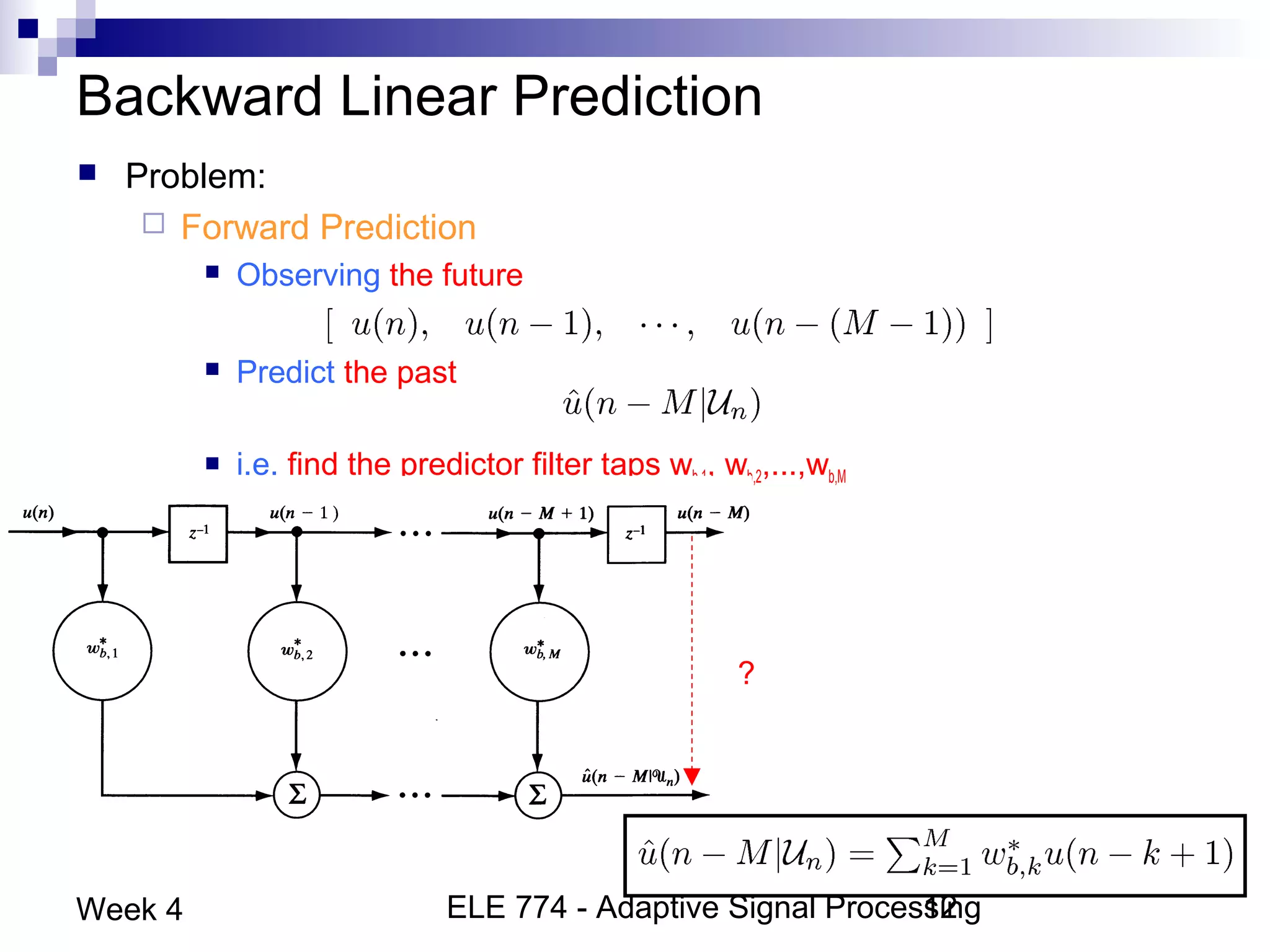
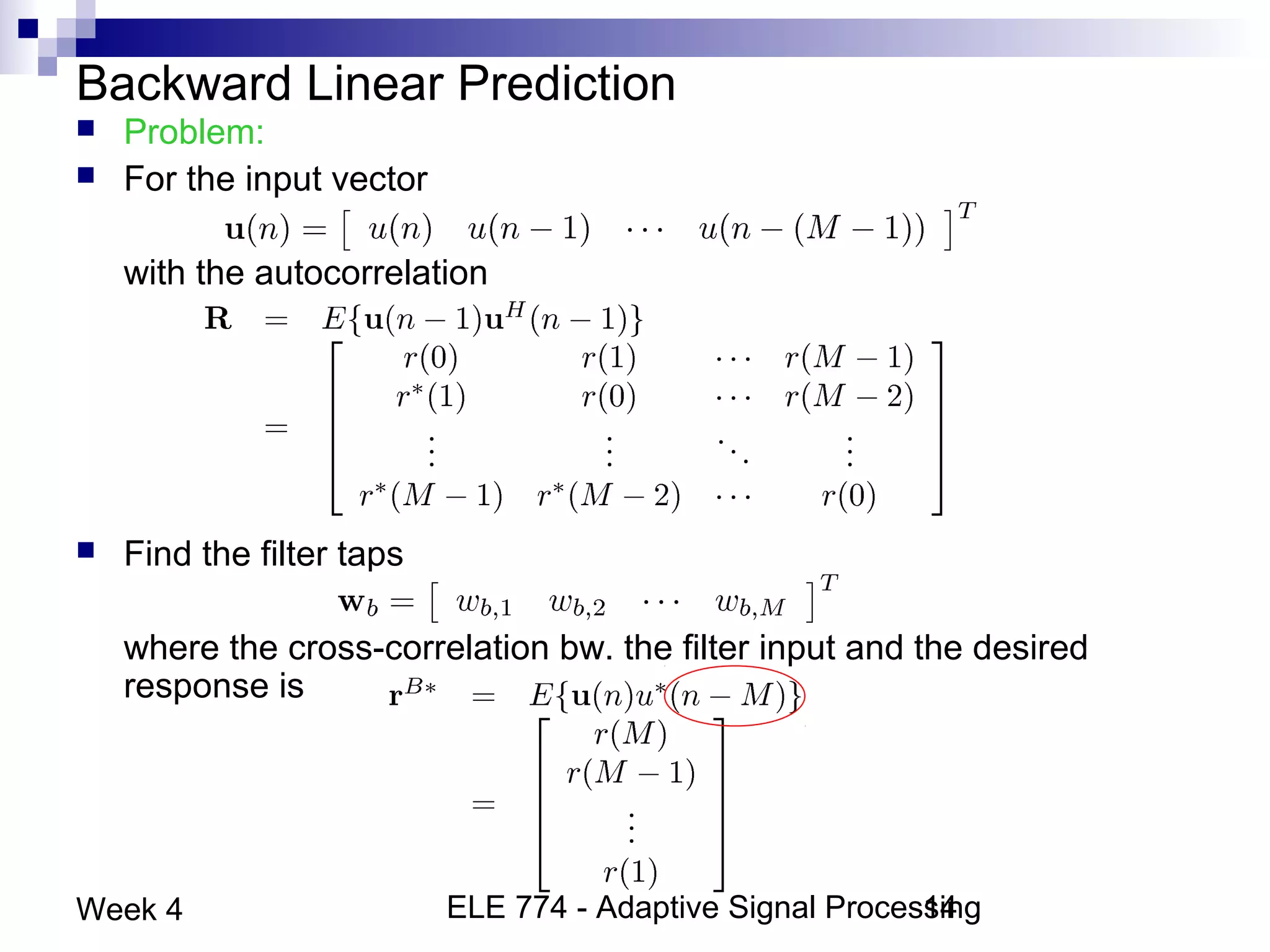
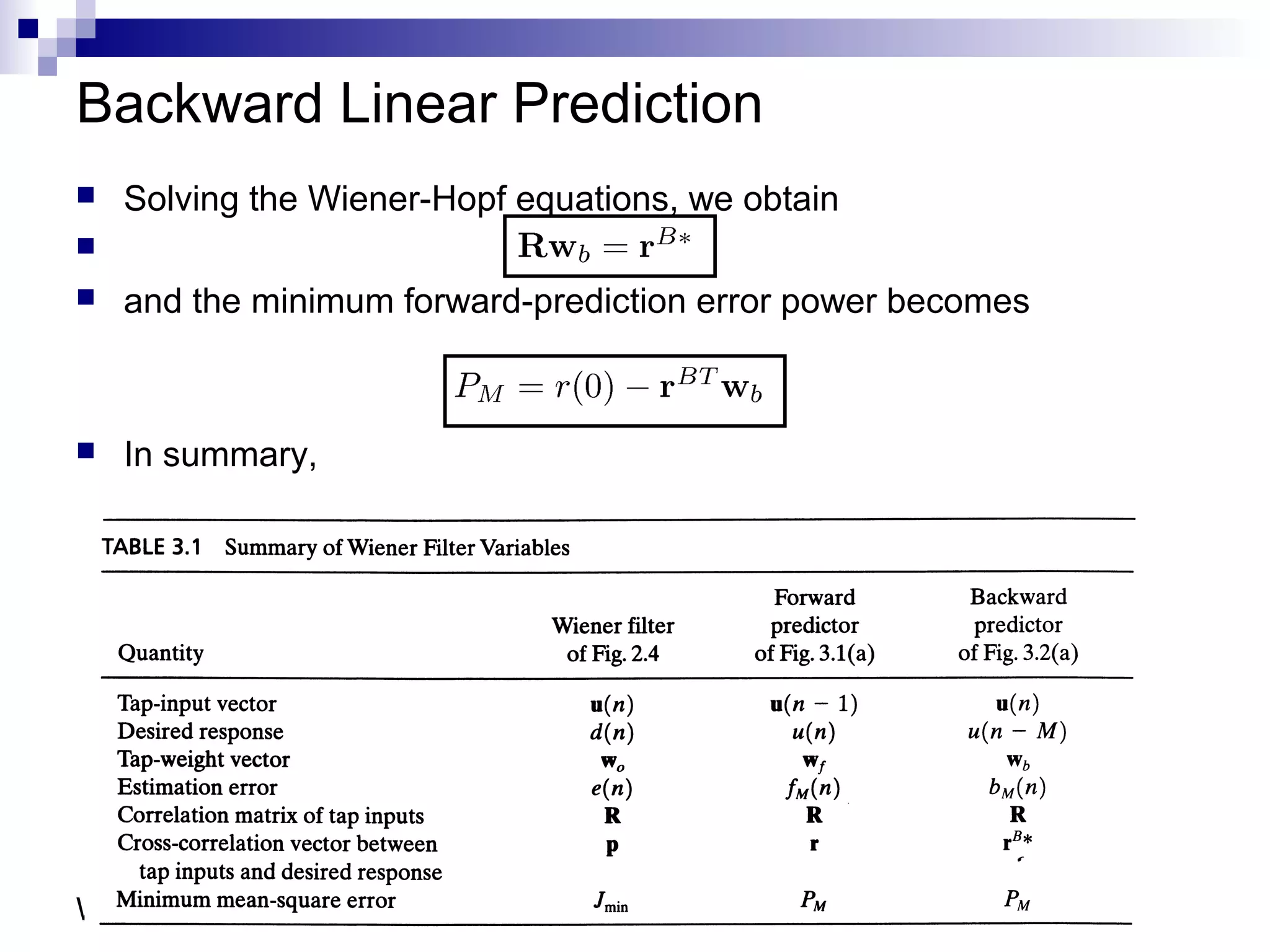
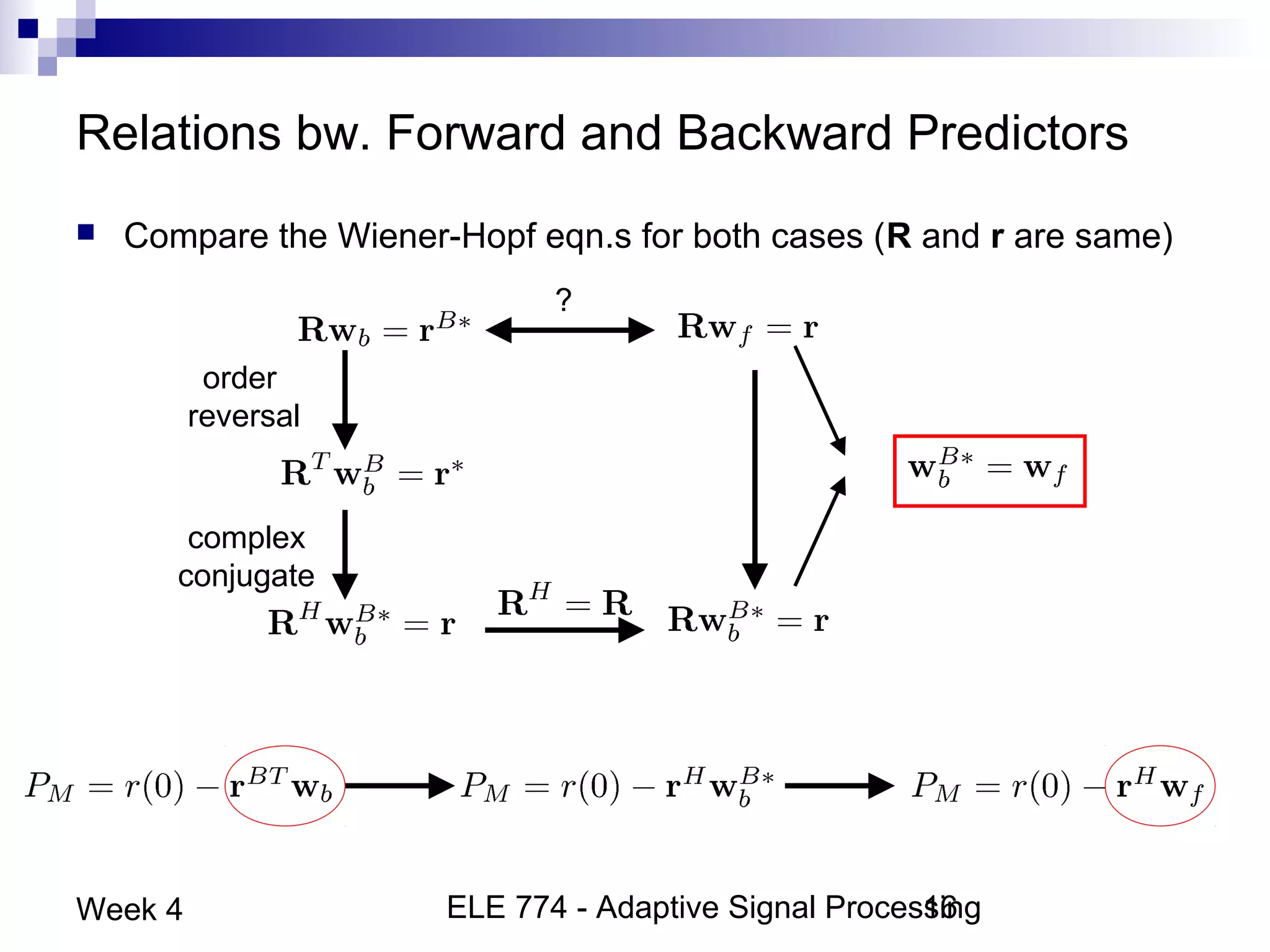
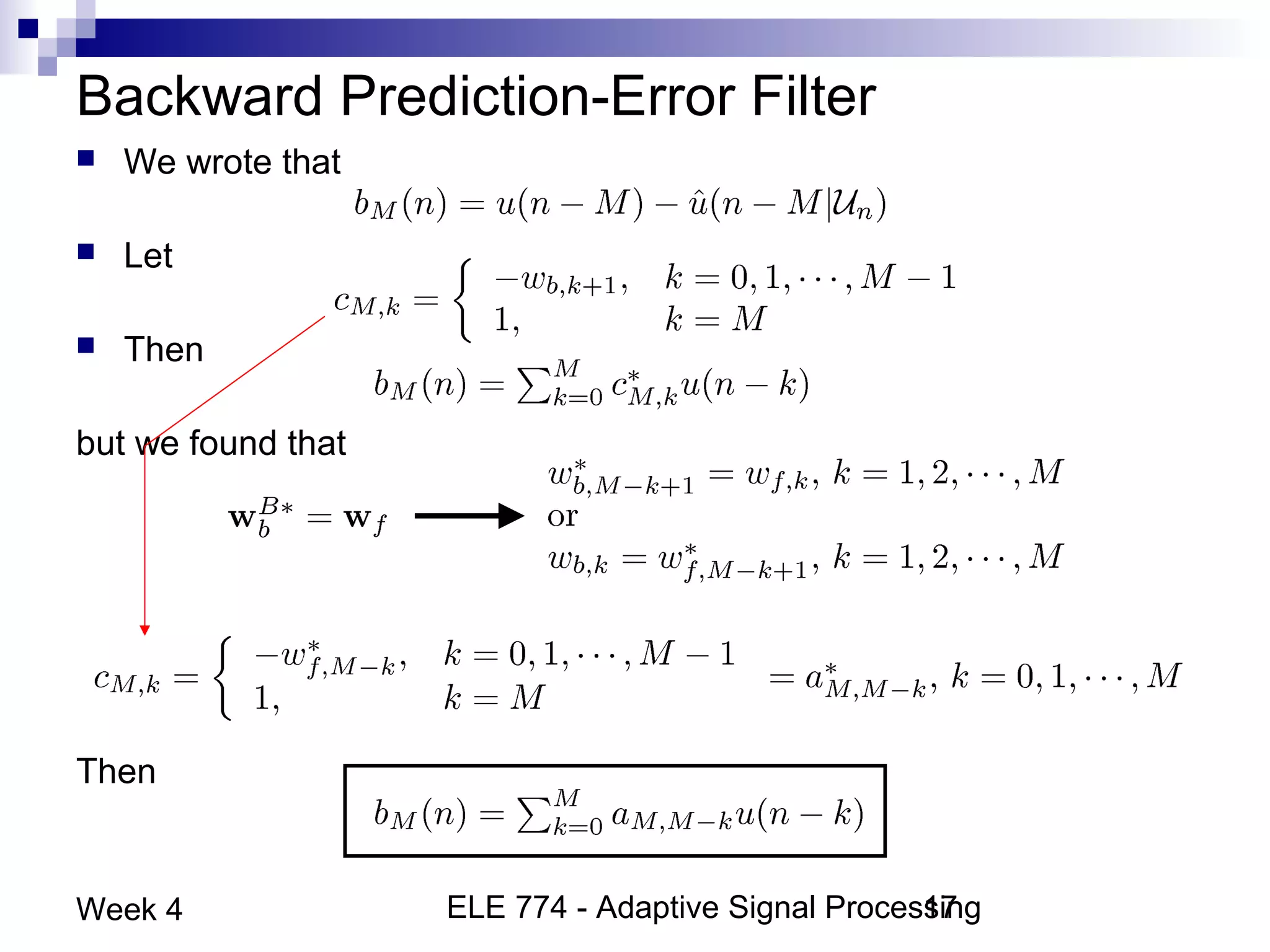
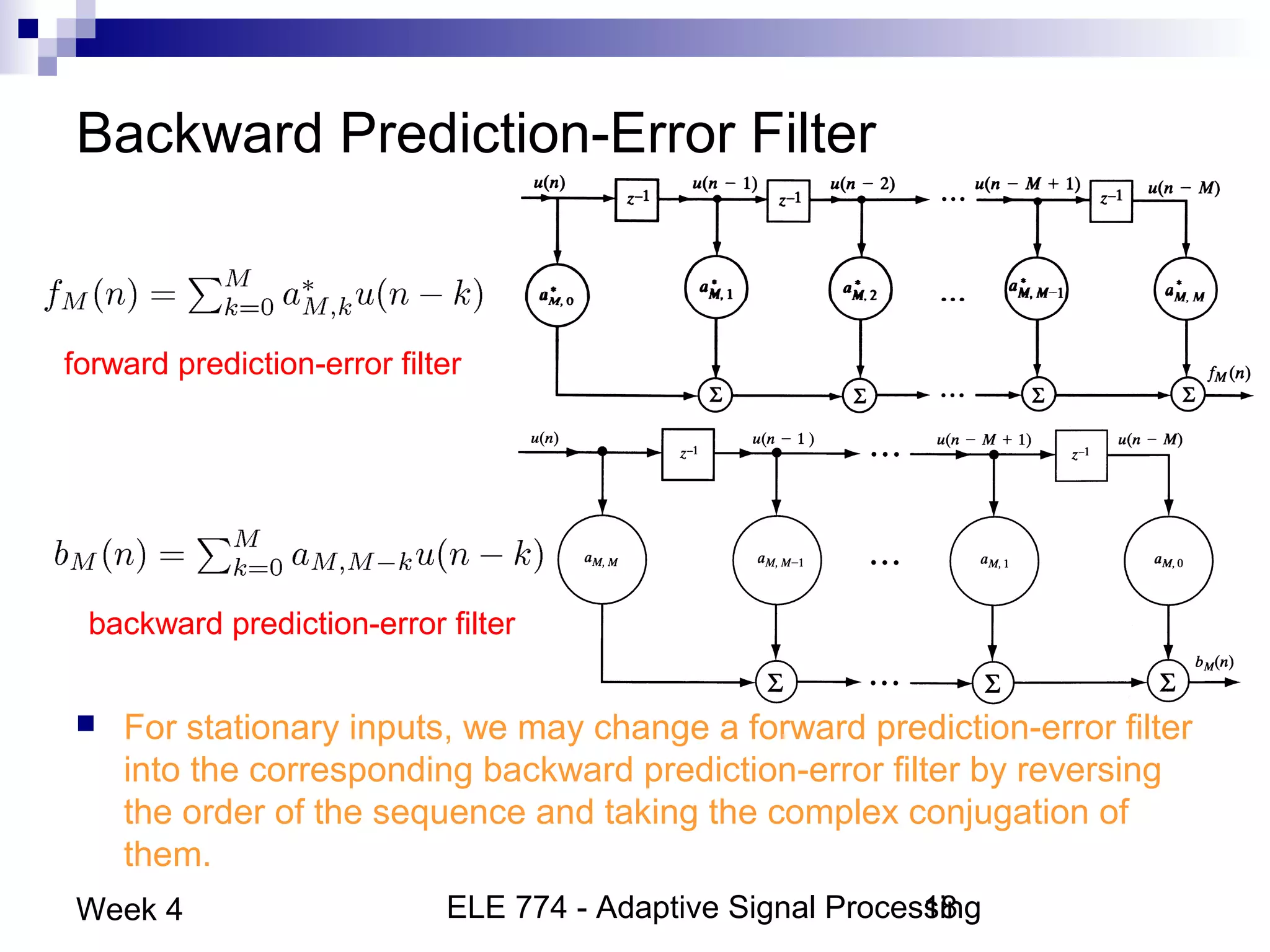
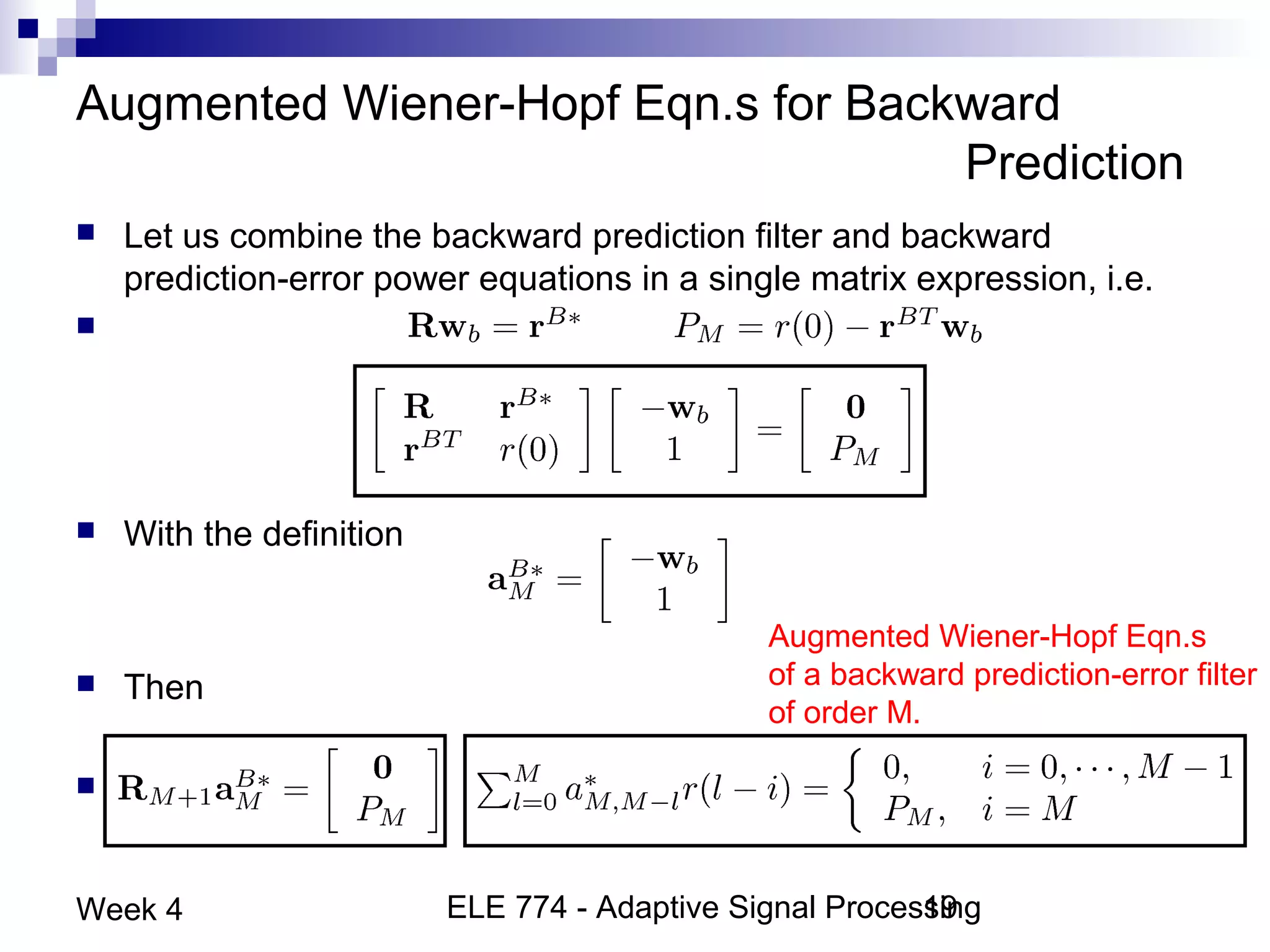
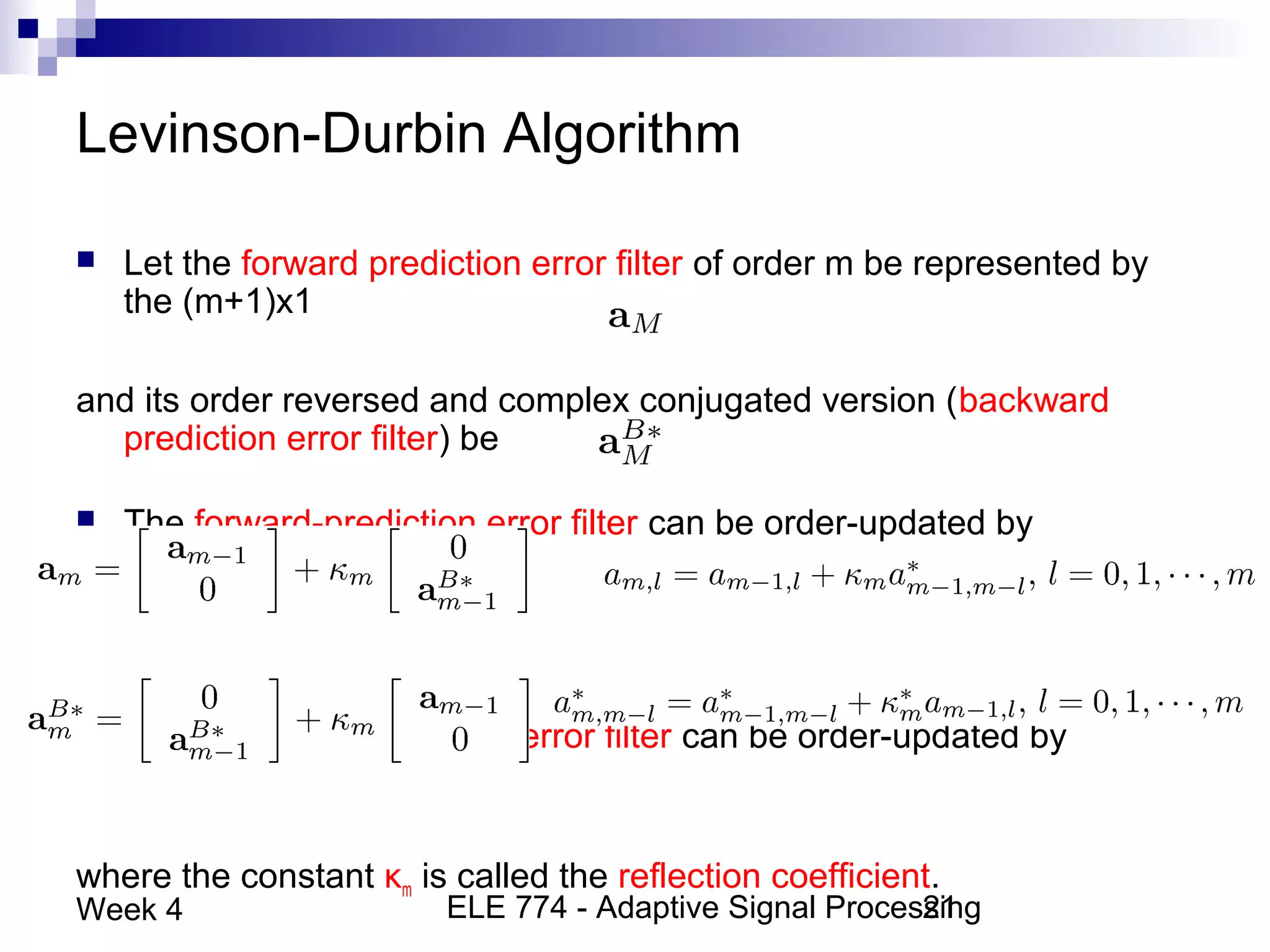
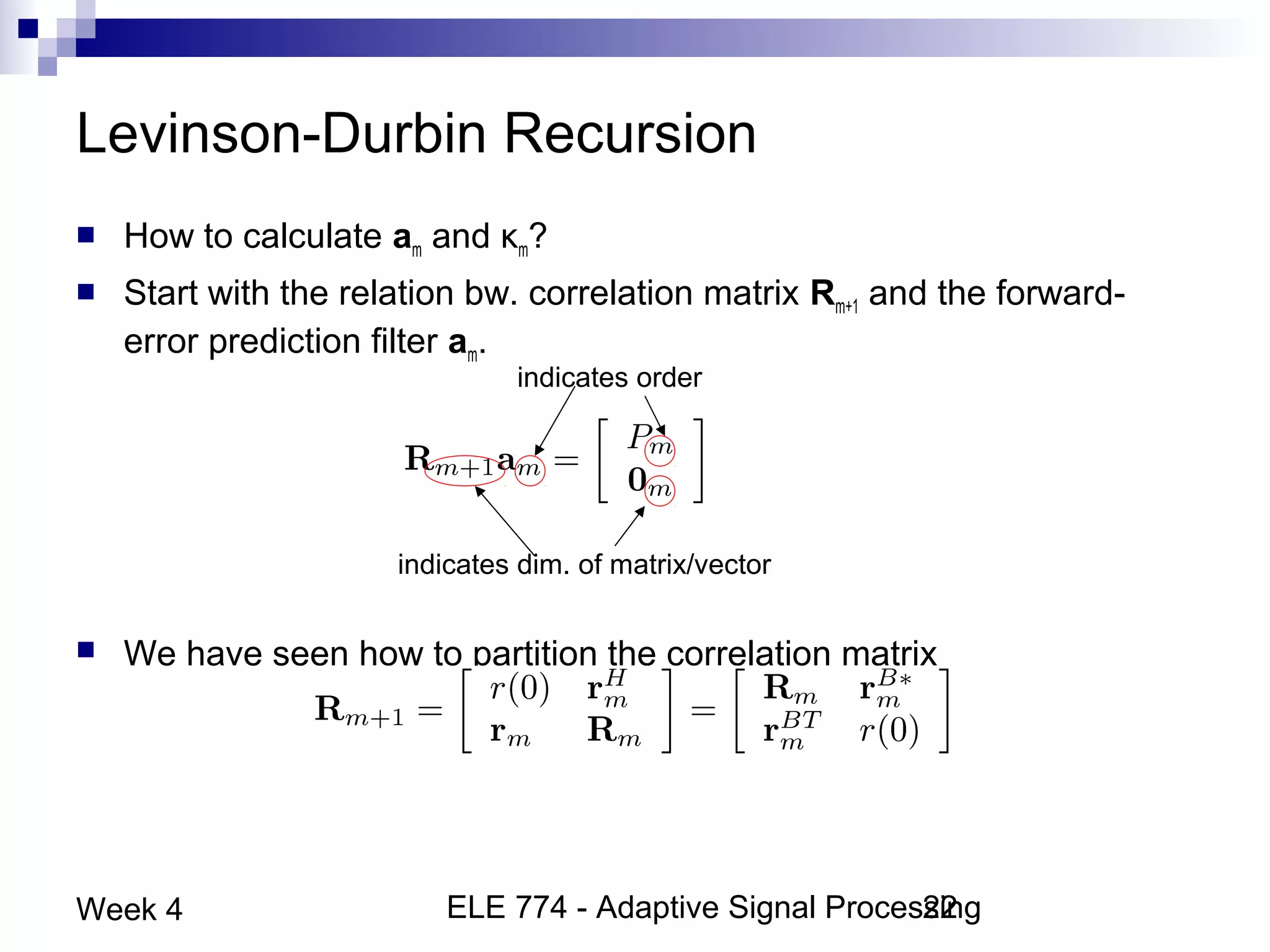
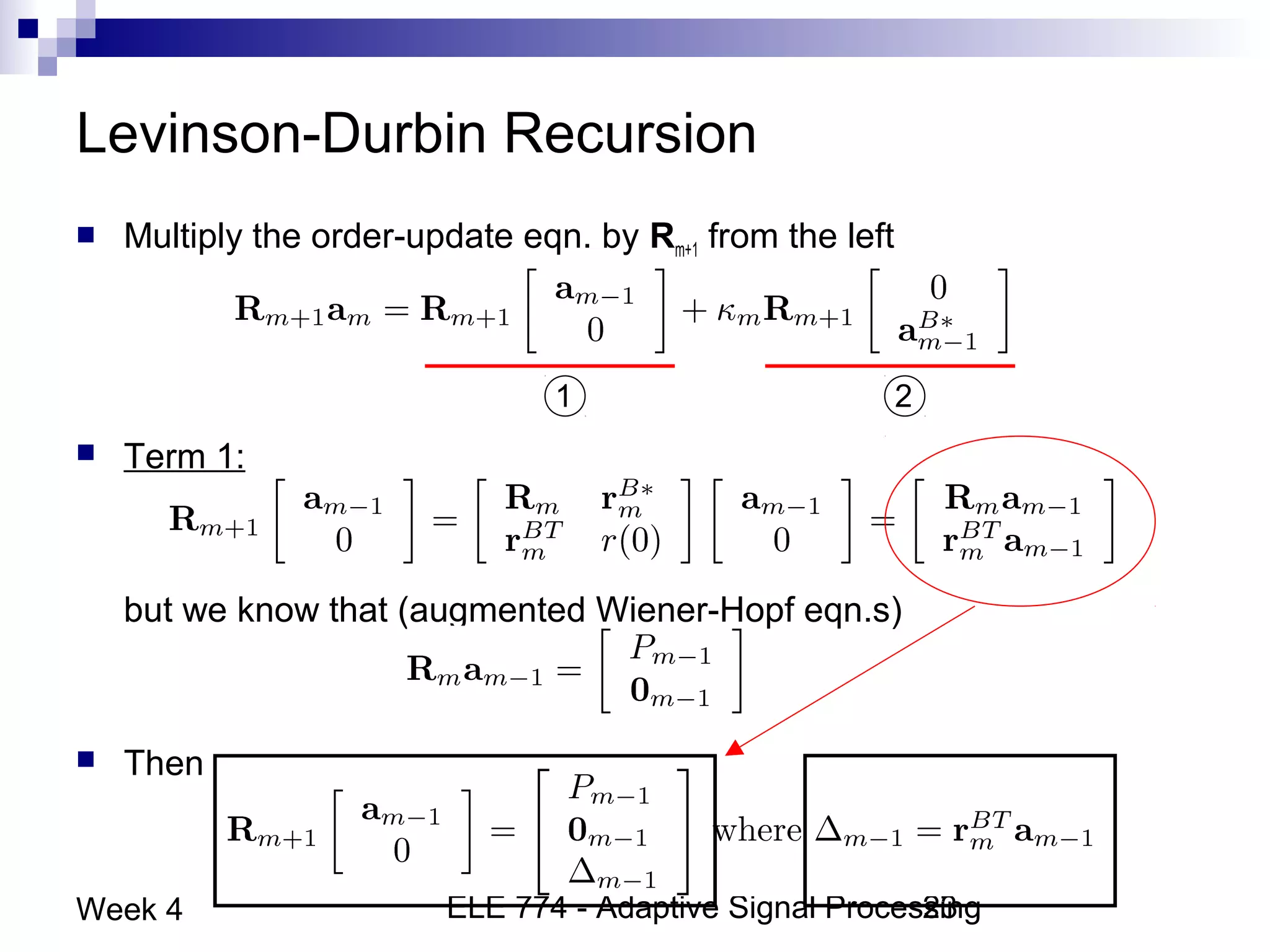
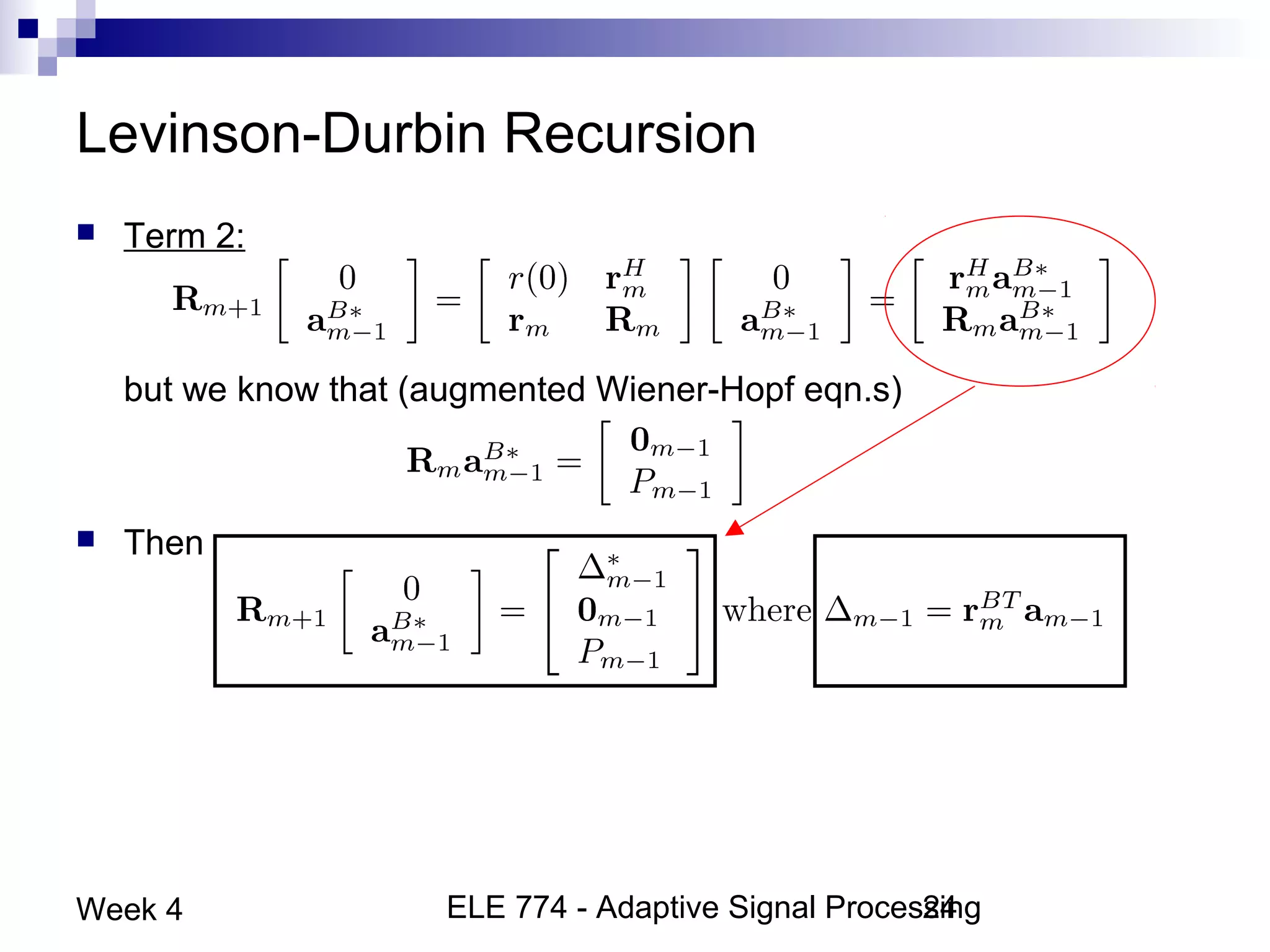
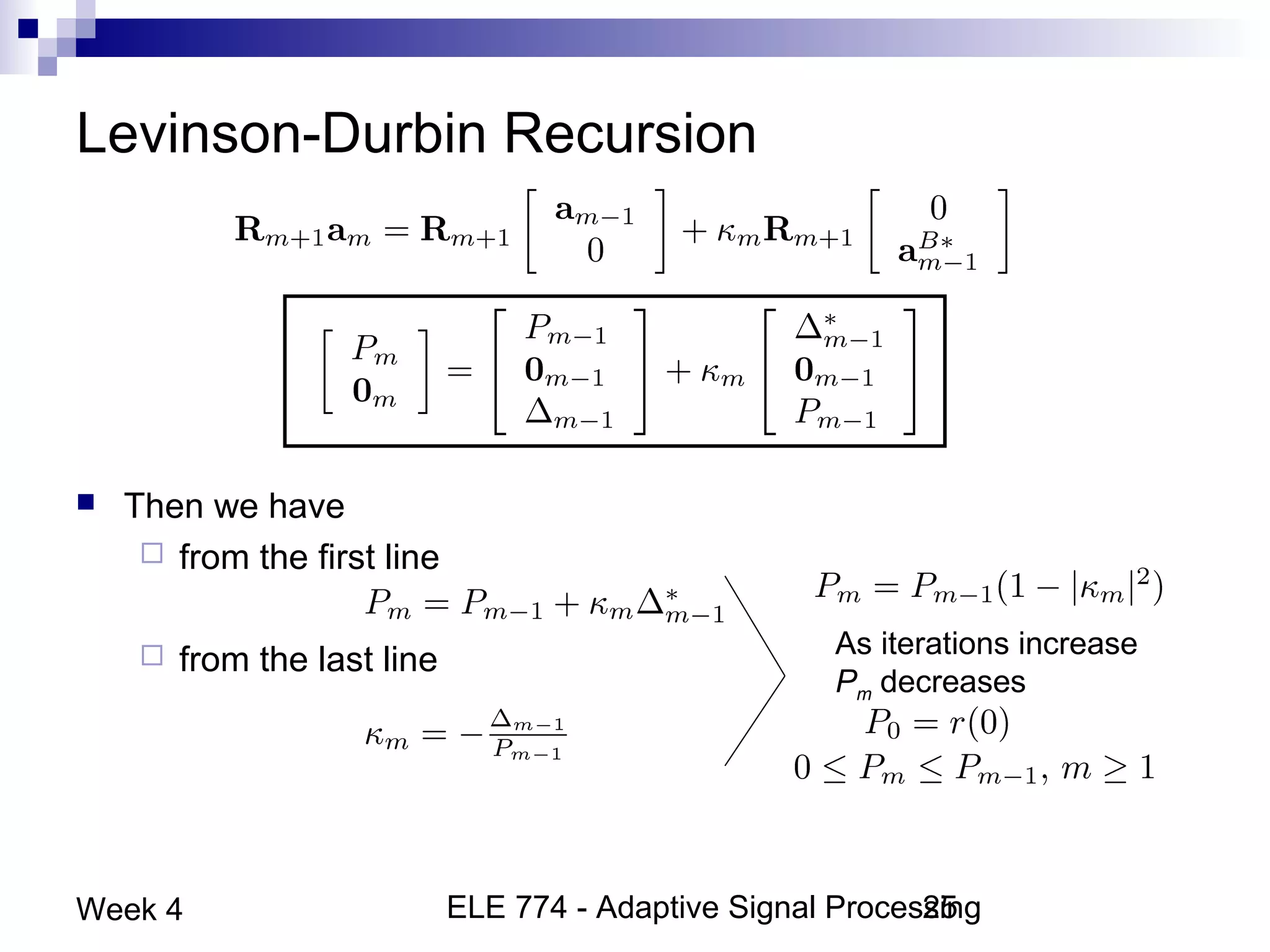
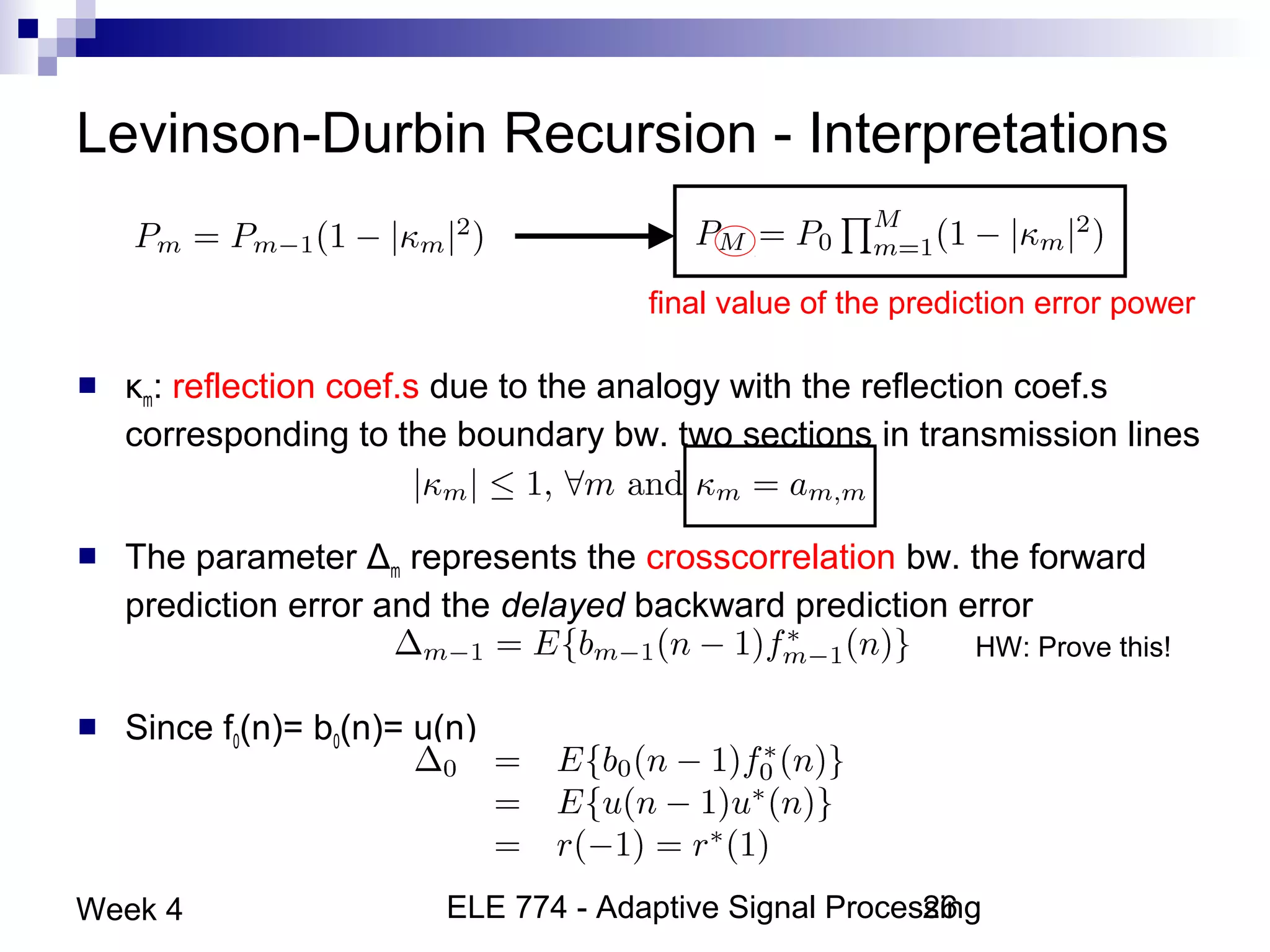
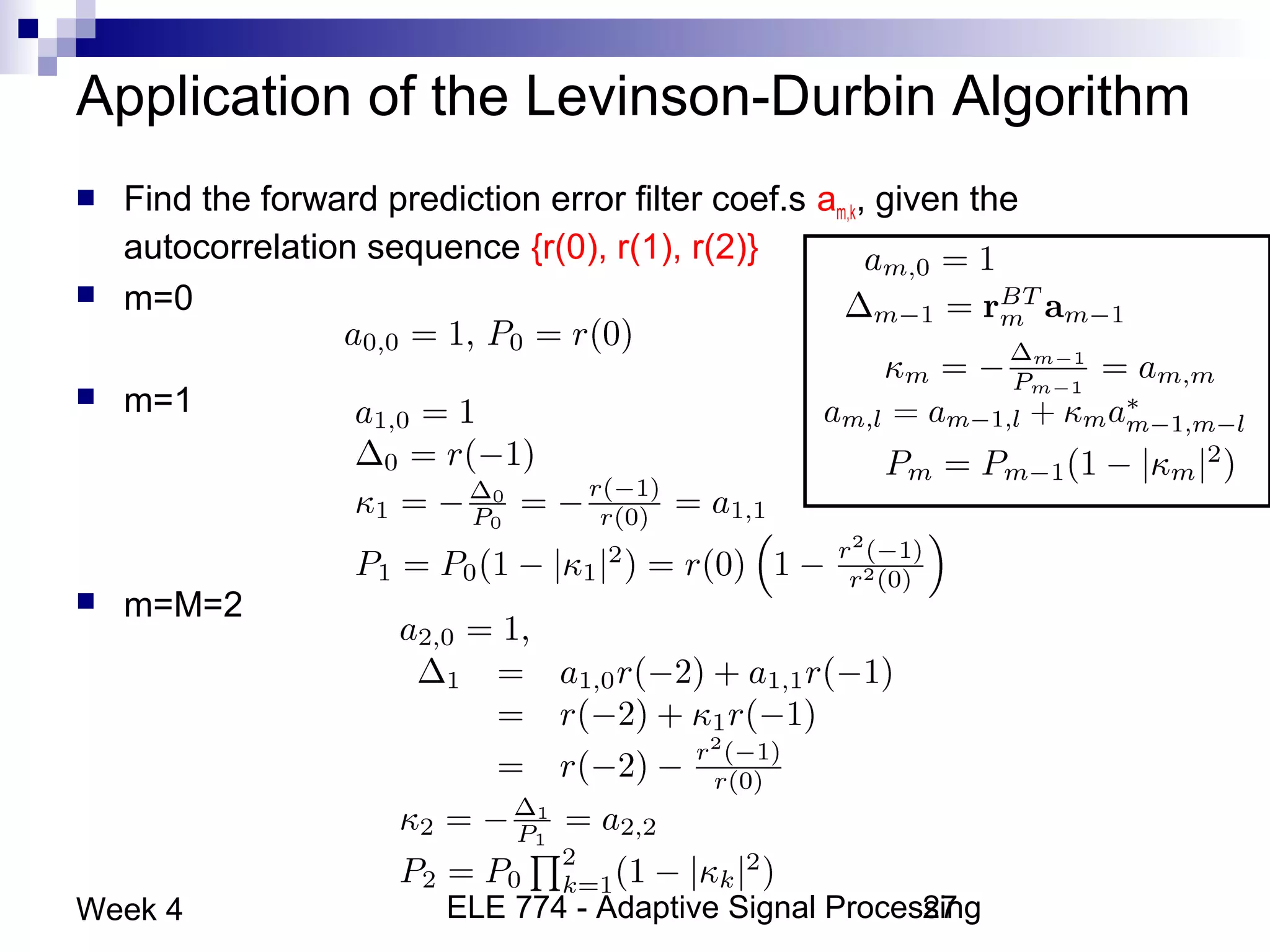
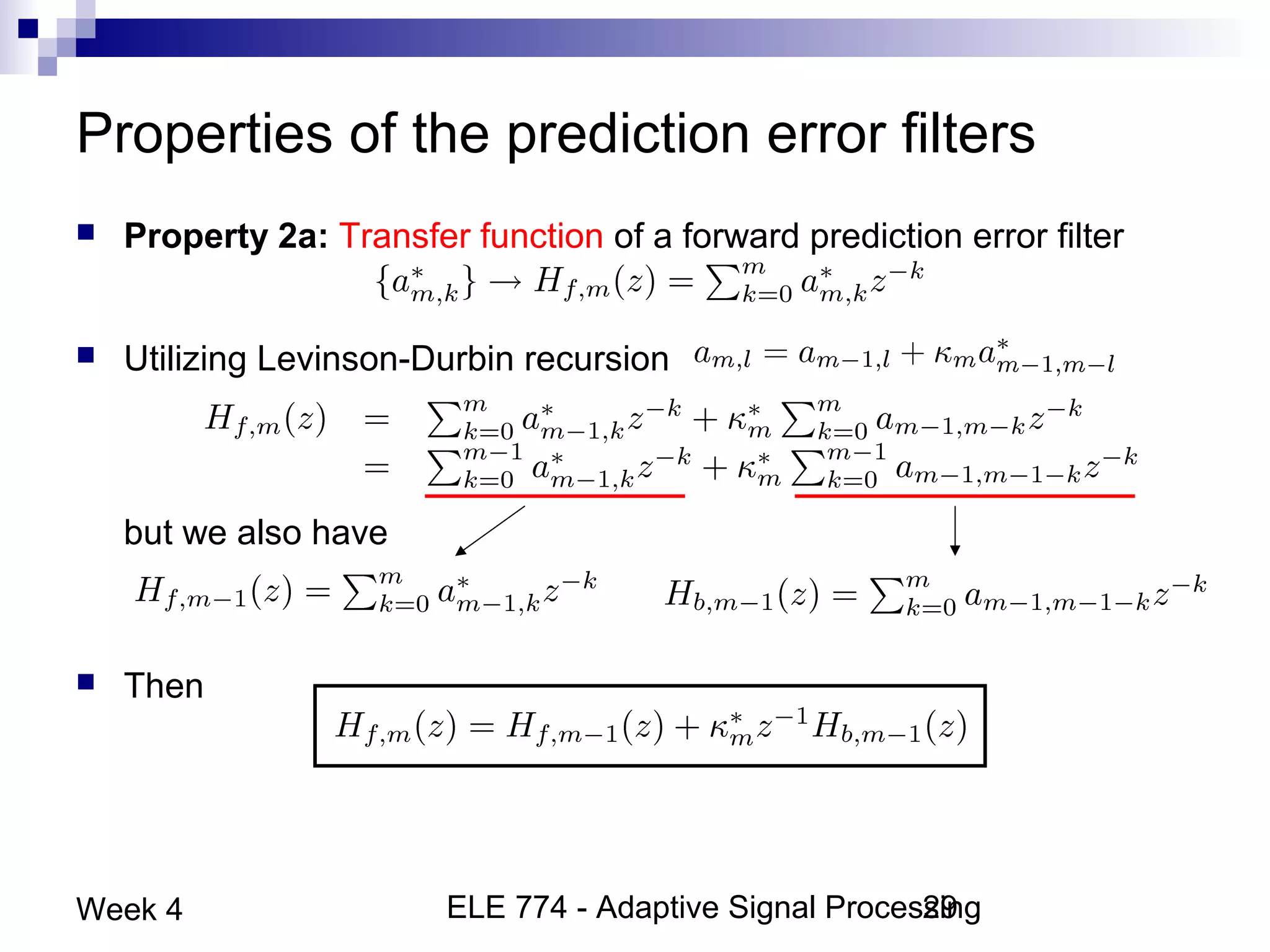
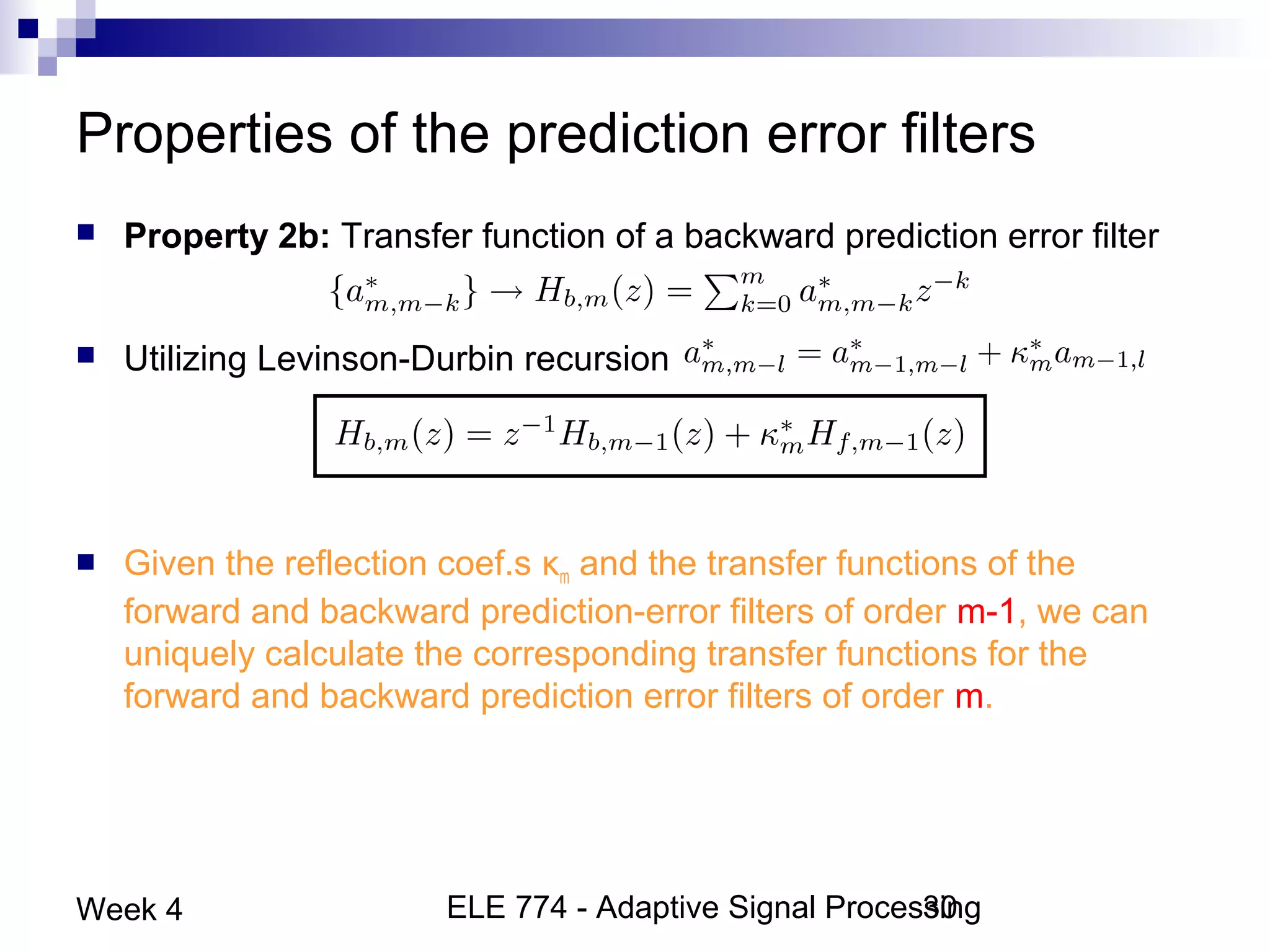
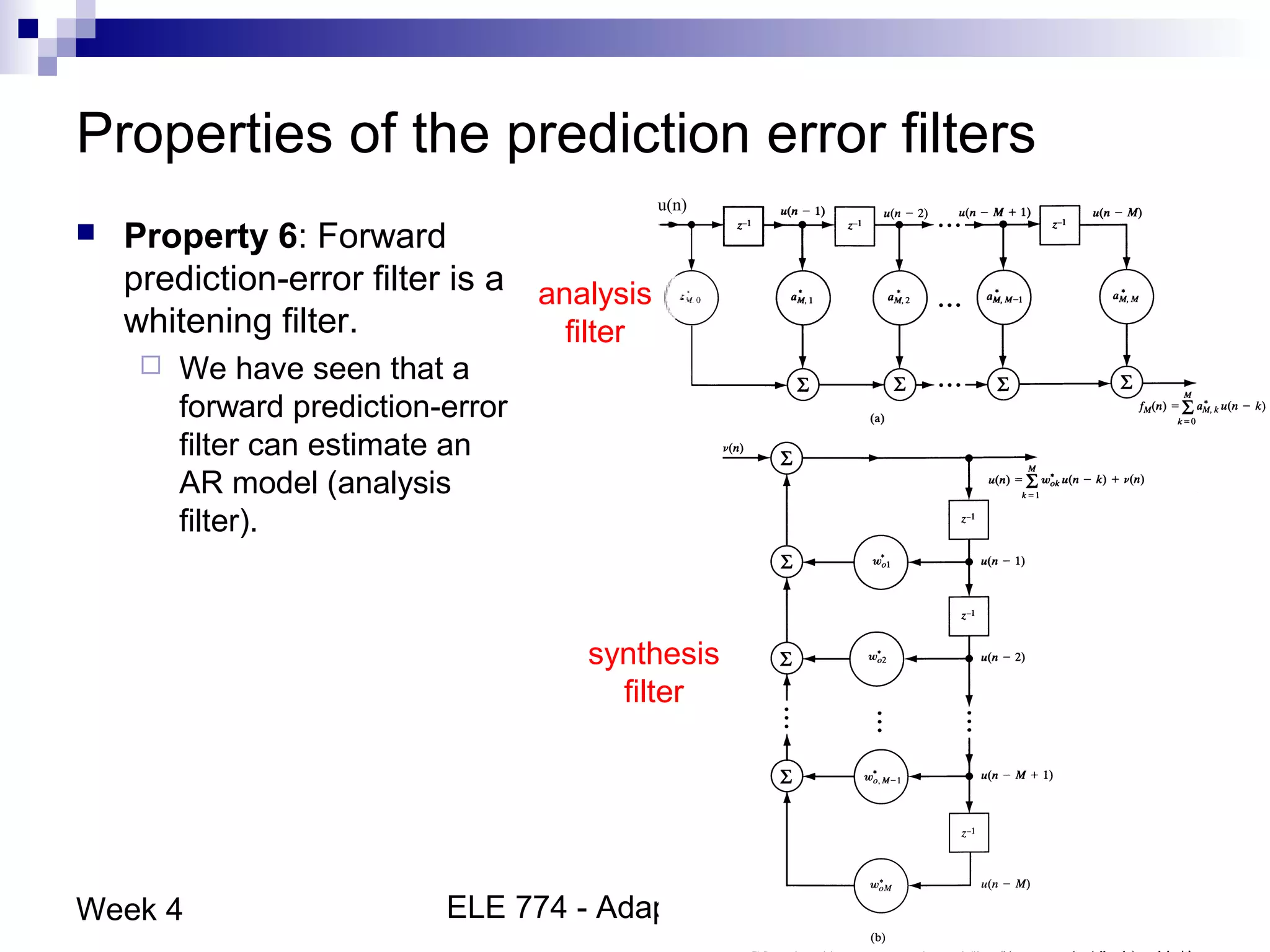
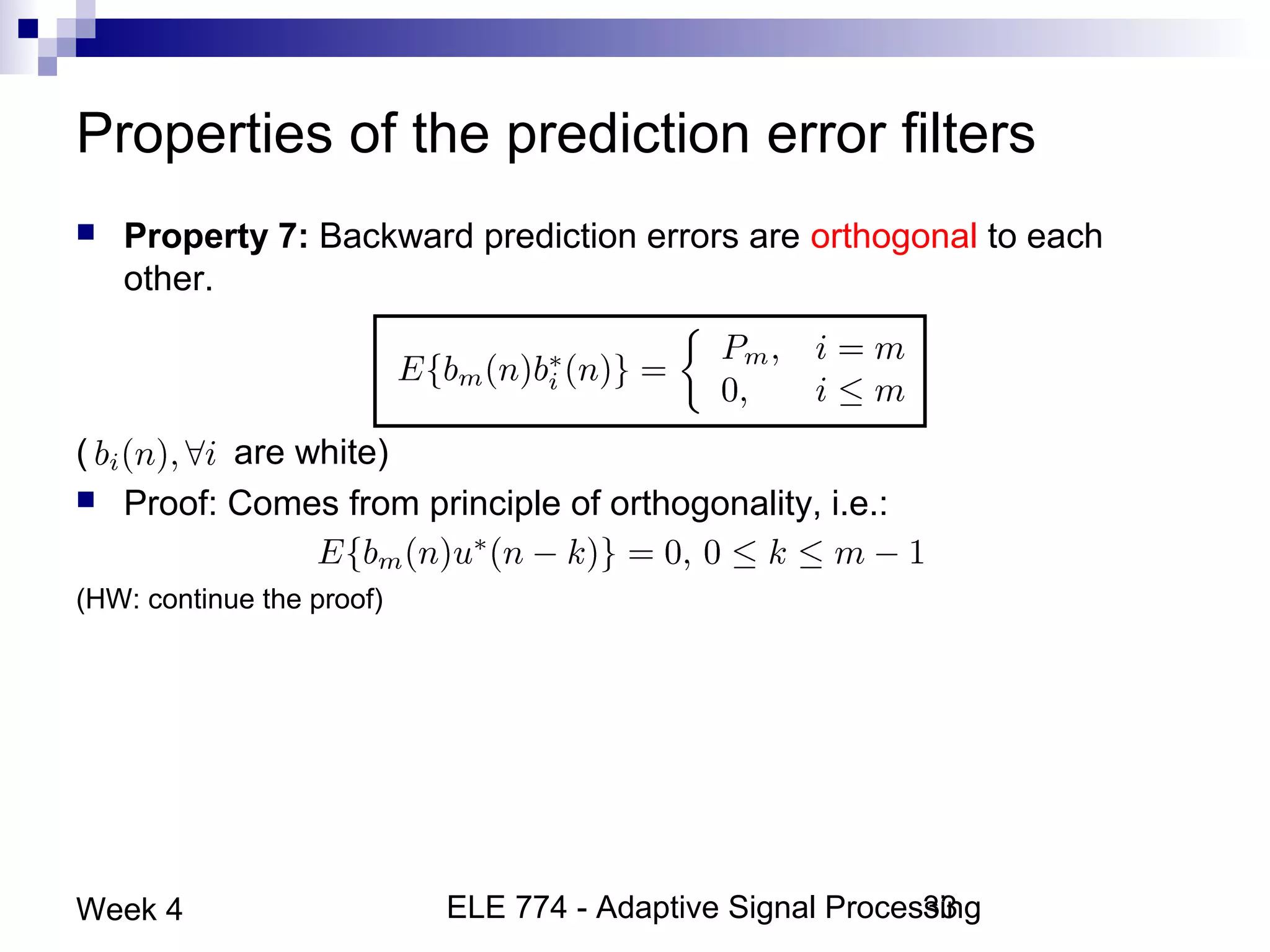
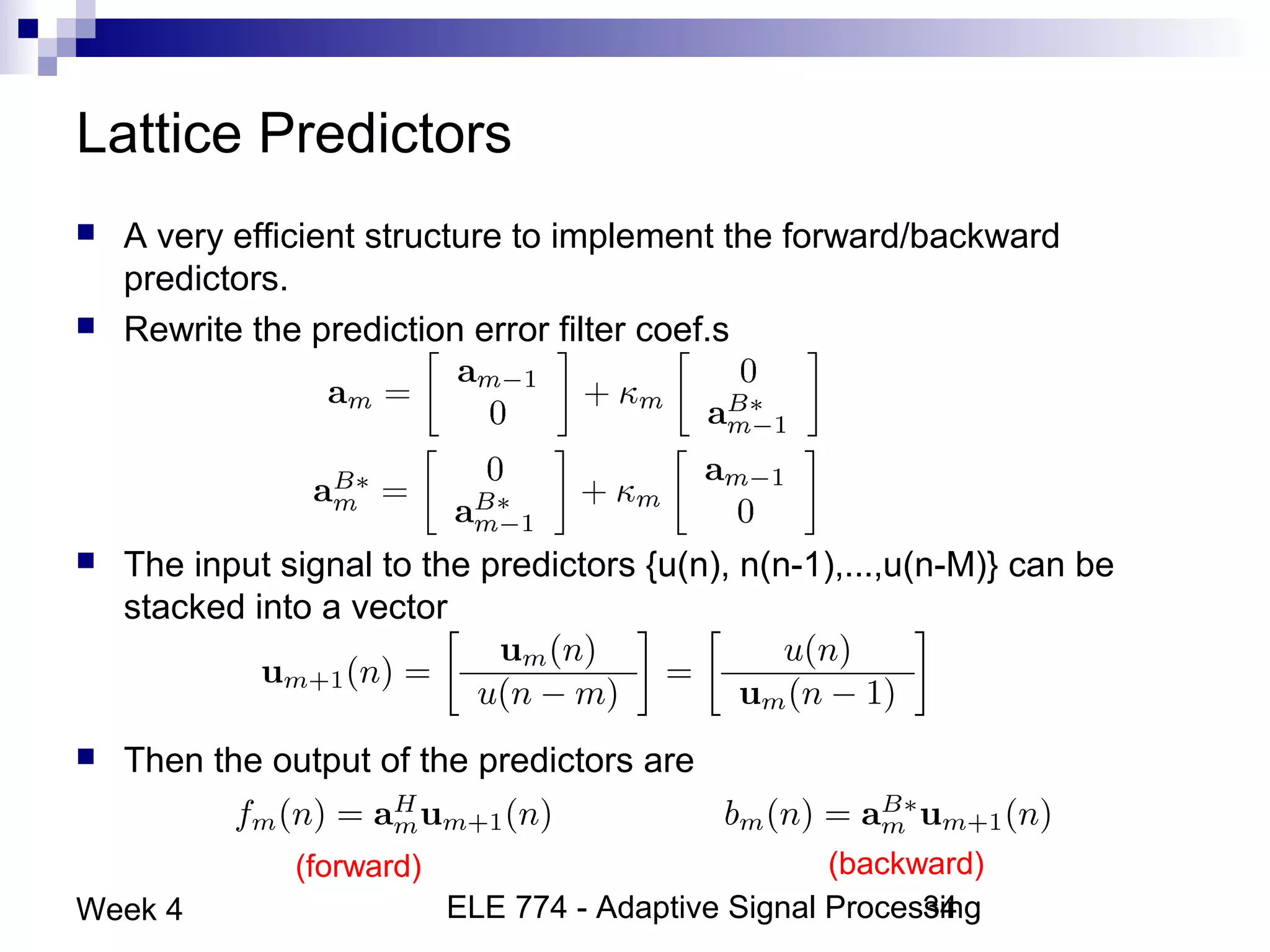
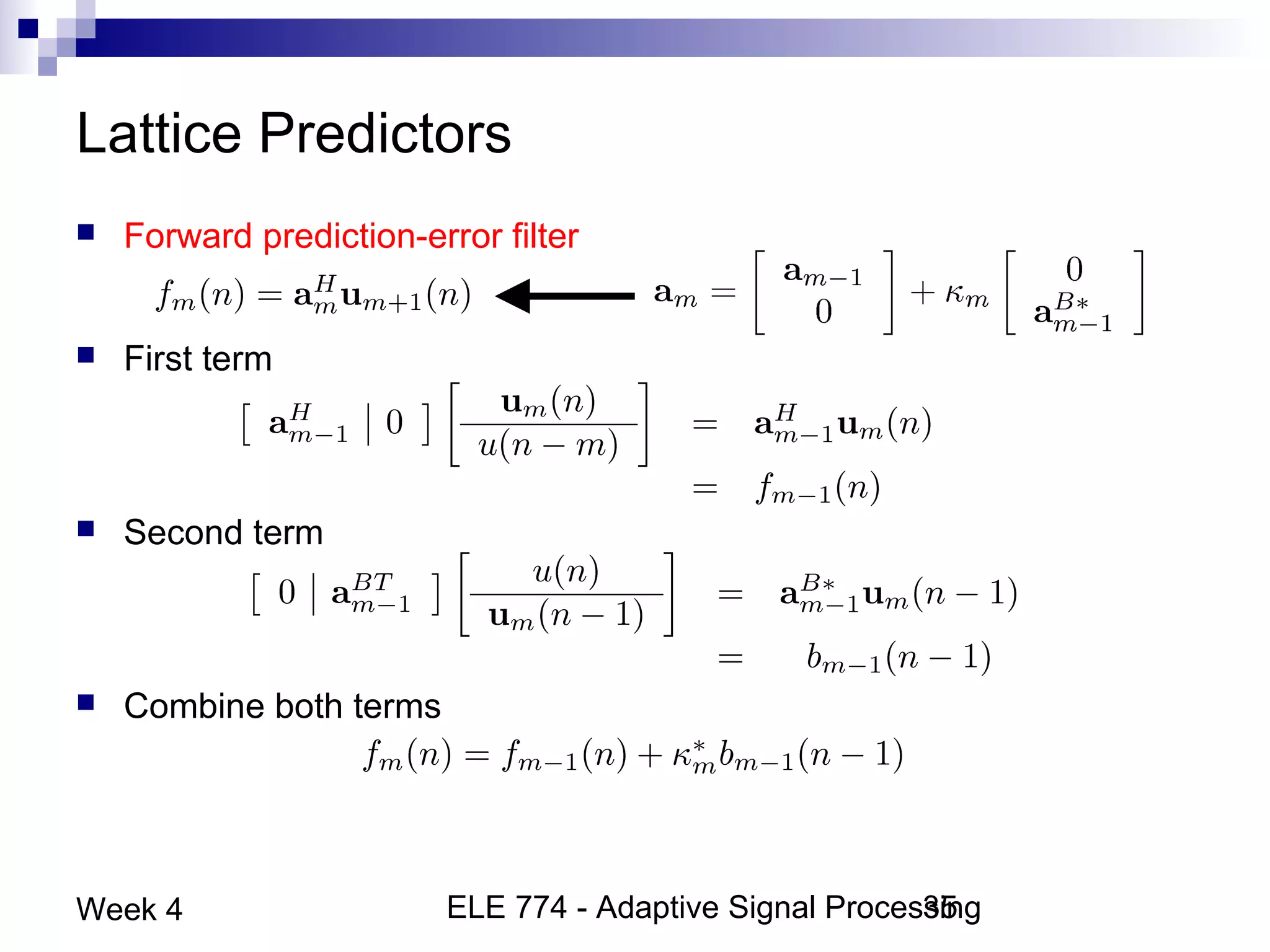
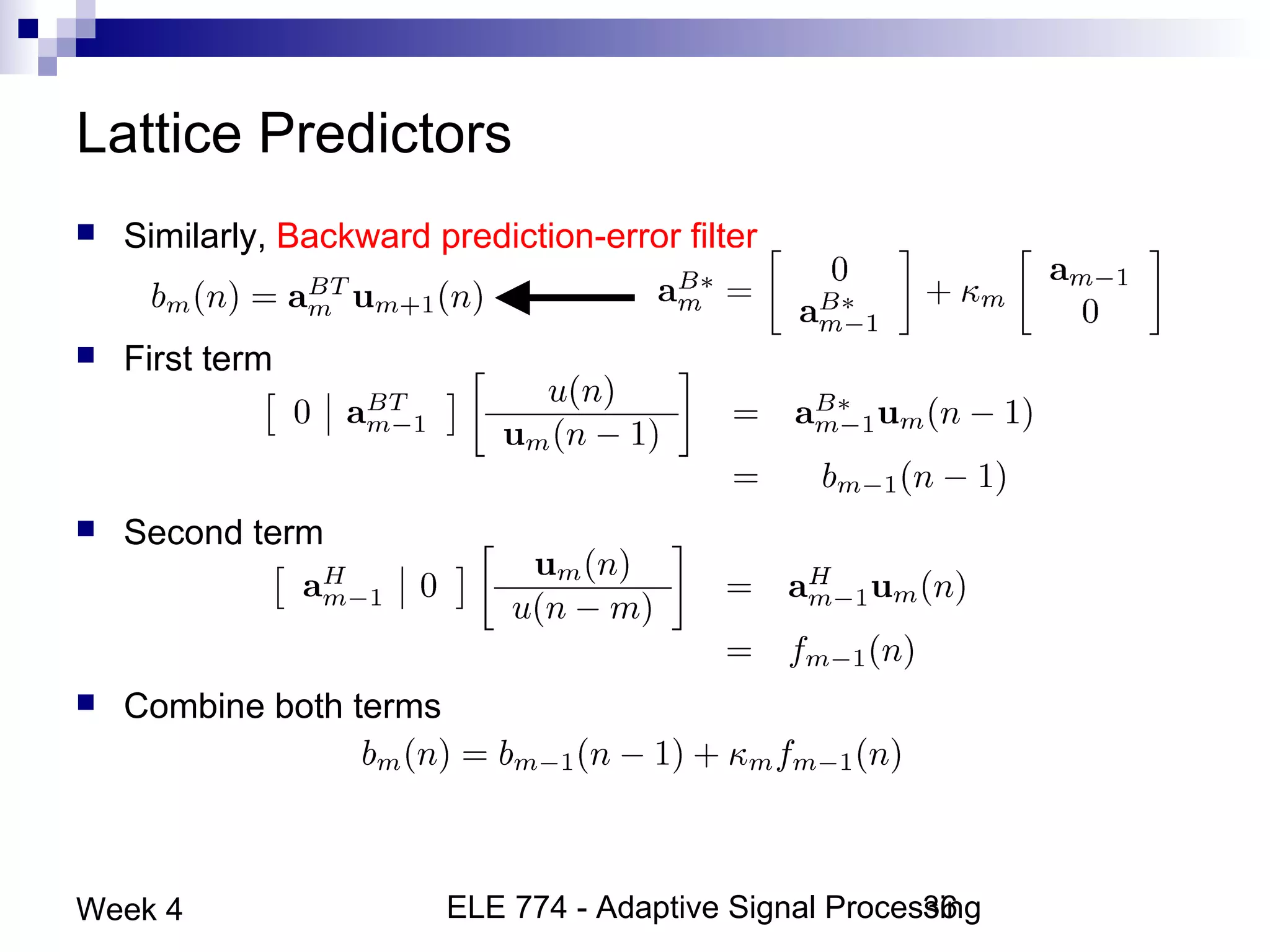
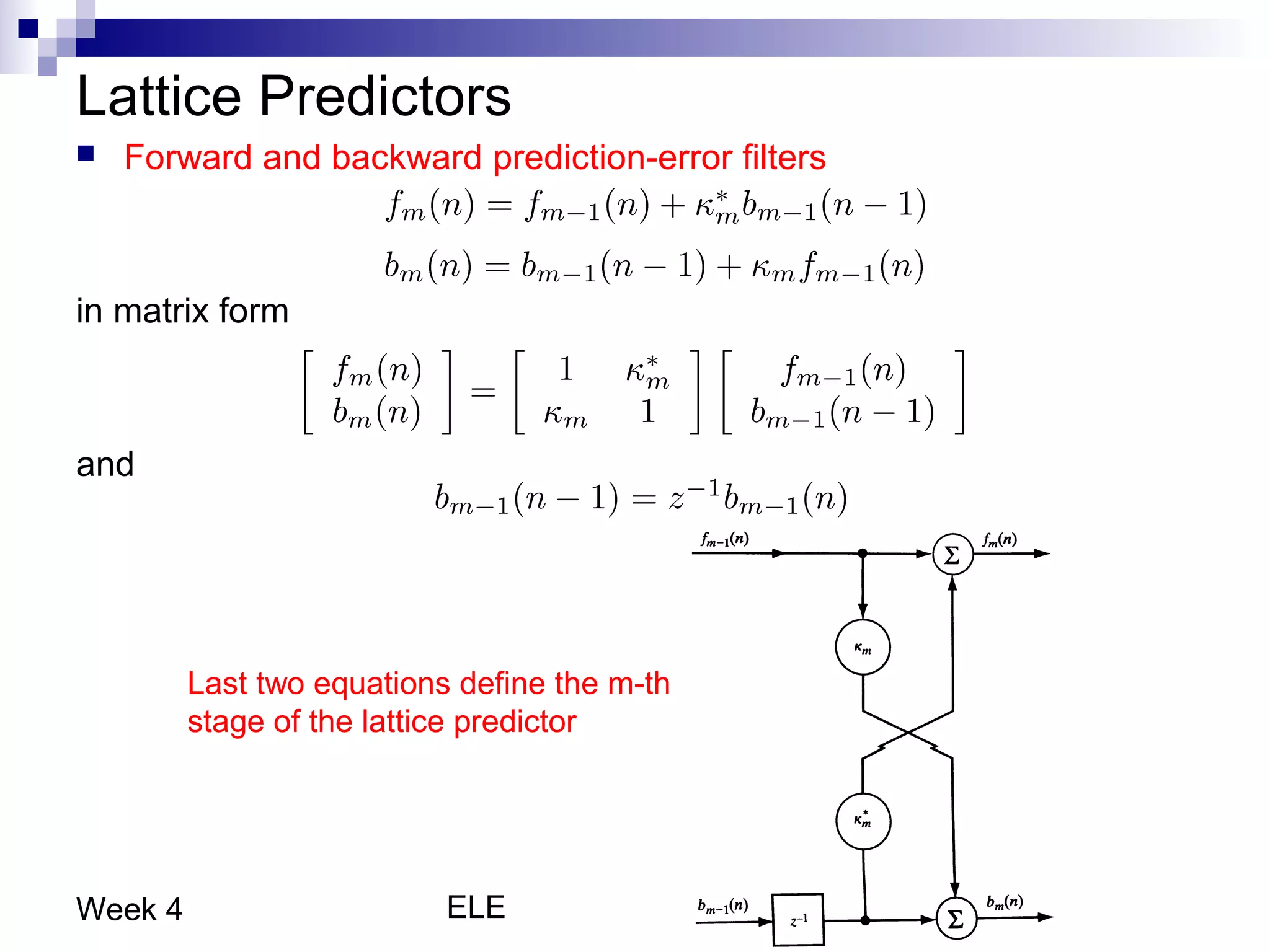
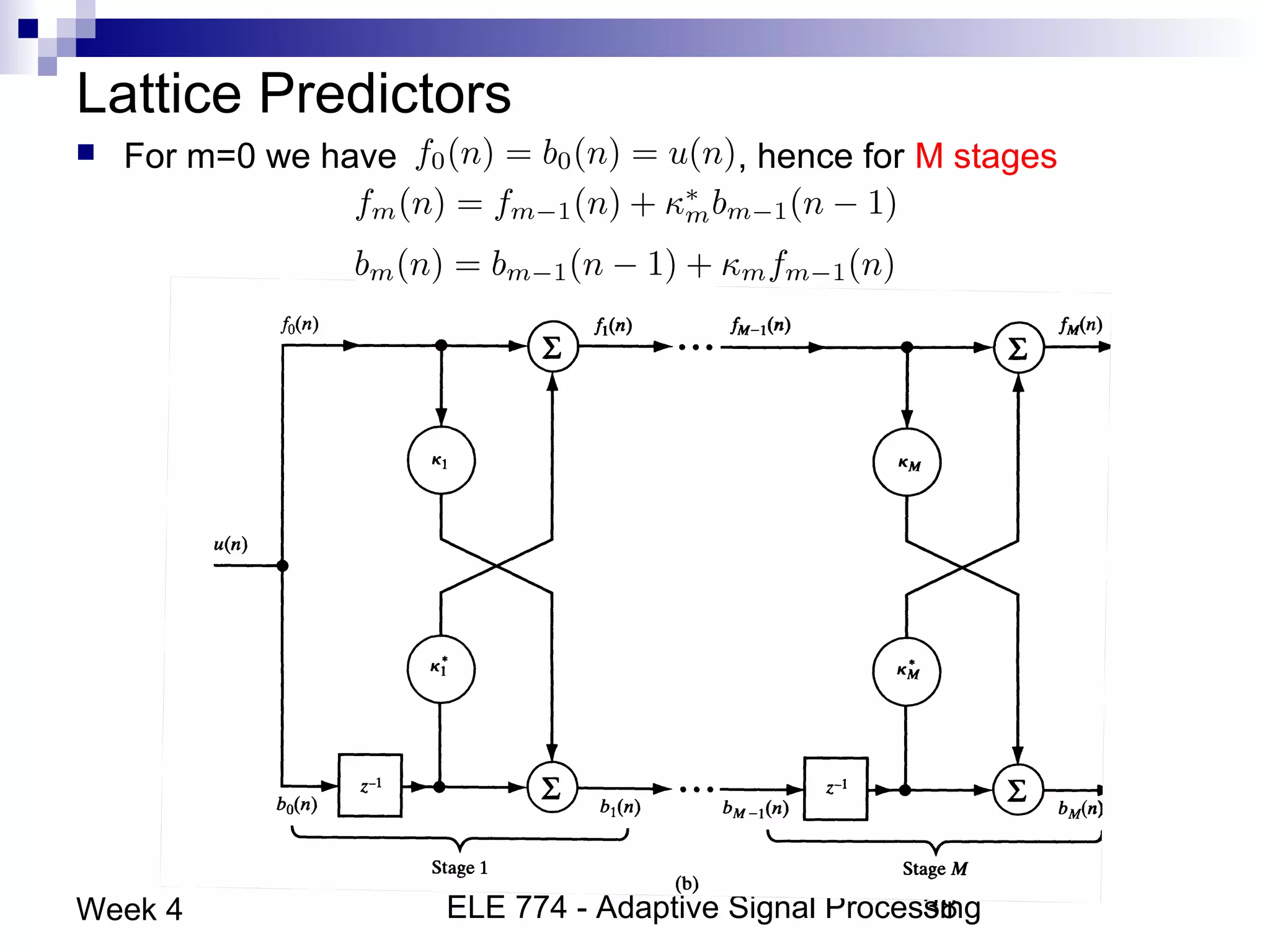
This document discusses linear prediction techniques including forward and backward prediction. It describes how to calculate the predictor filter coefficients using the Wiener-Hopf equations and how to solve them recursively using the Levinson-Durbin algorithm. This allows computing high-order predictor filters with low computational complexity. The properties of forward and backward prediction error filters are also covered, showing their relationship to autoregressive modeling and whitening filters. Lattice predictors are introduced as an efficient implementation of linear prediction filters.