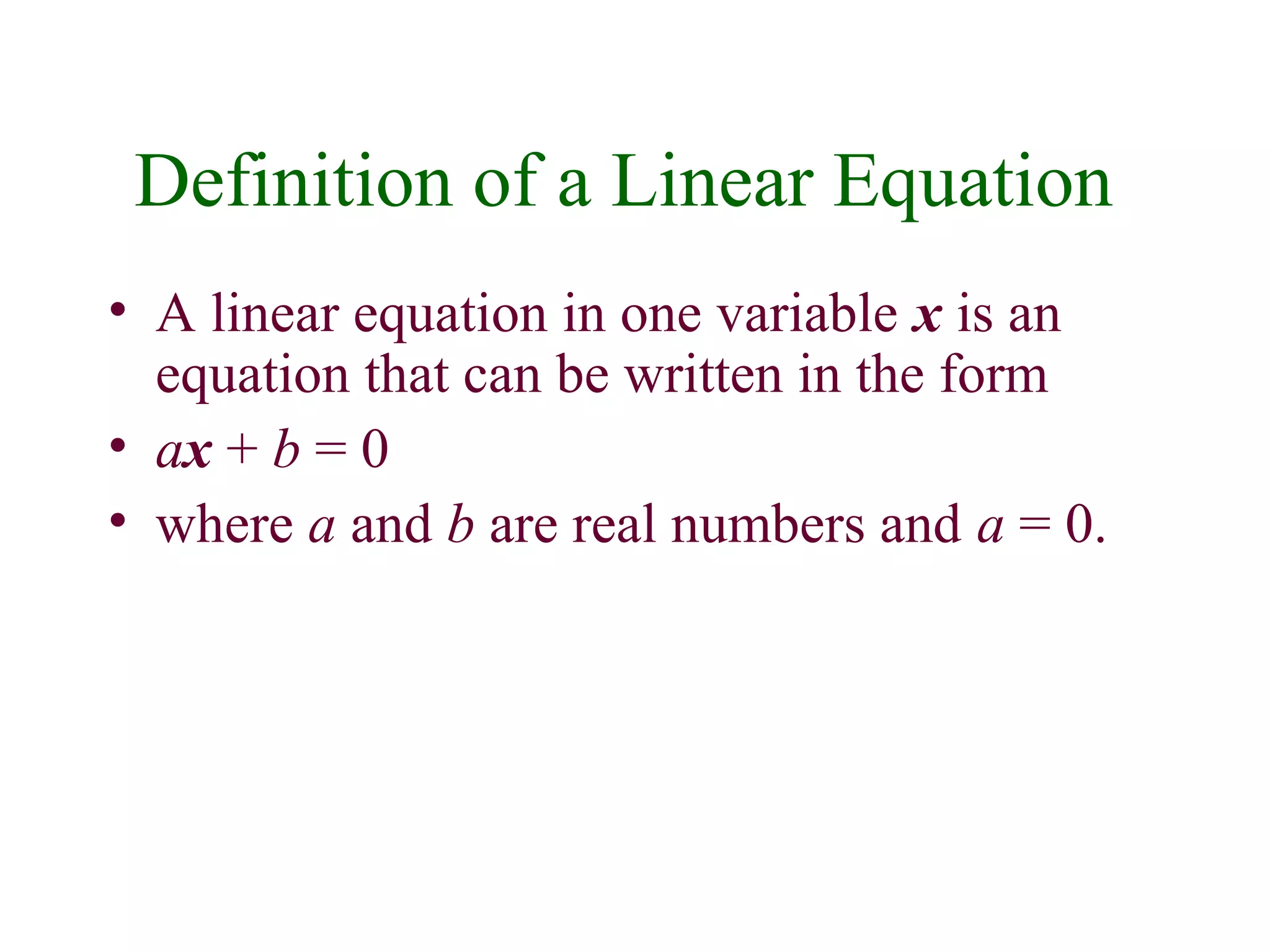
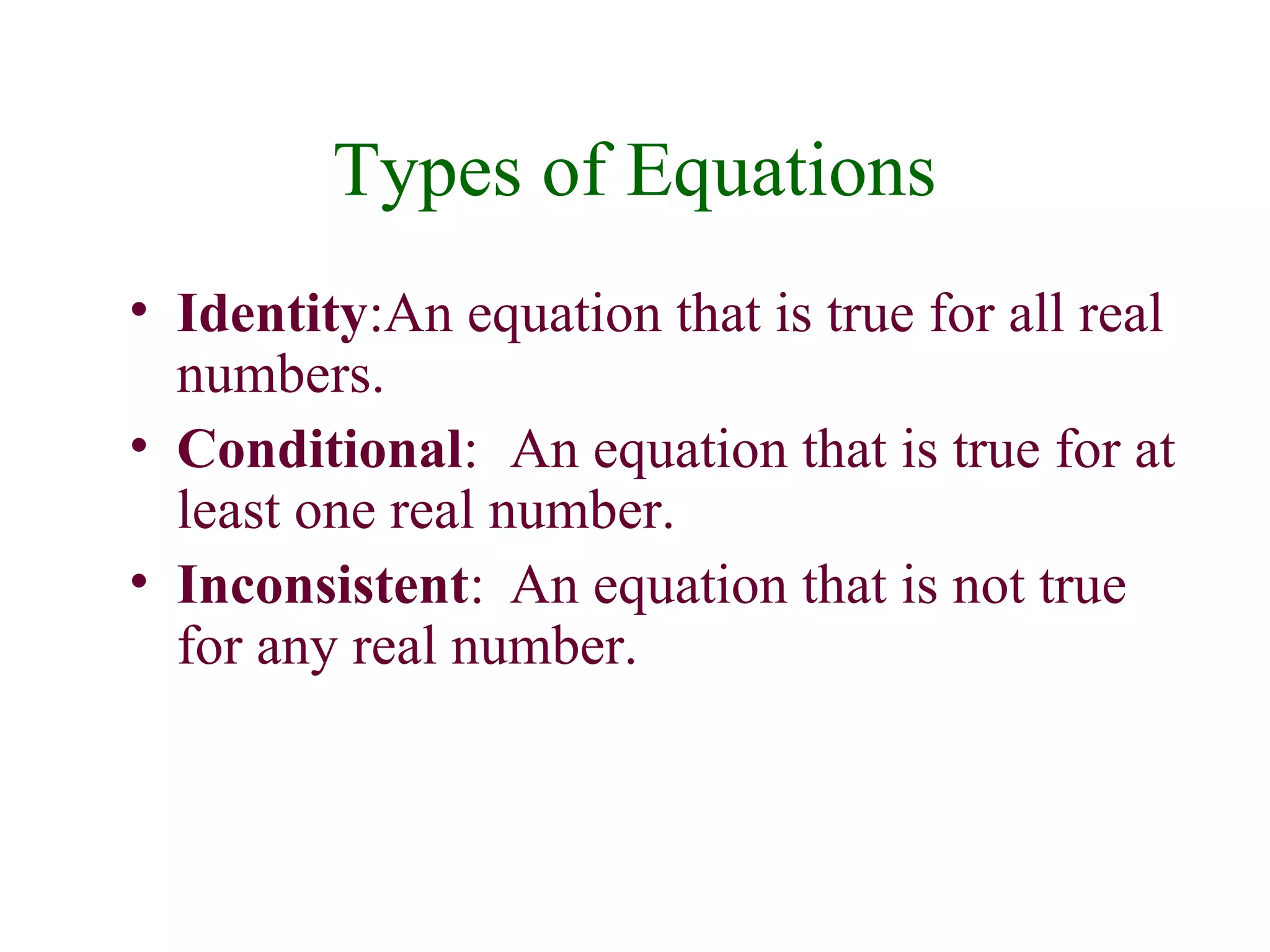
1) A linear equation can be written in the form ax + b = 0, where a and b are real numbers and a is not equal to 0.
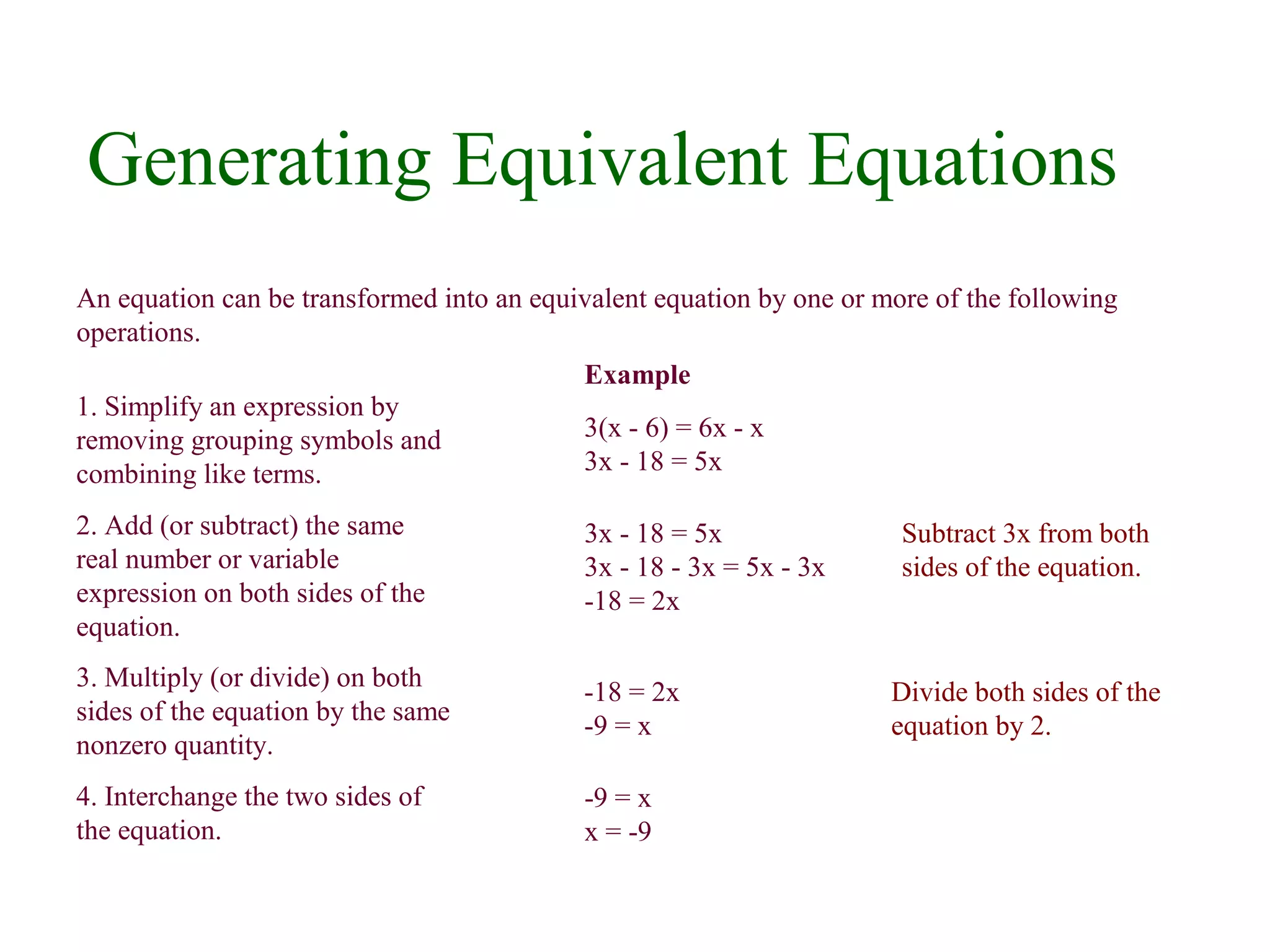
2) Equivalent linear equations can be generated through operations like combining like terms, adding/subtracting the same quantity to both sides, and multiplying/dividing both sides by the same nonzero number.
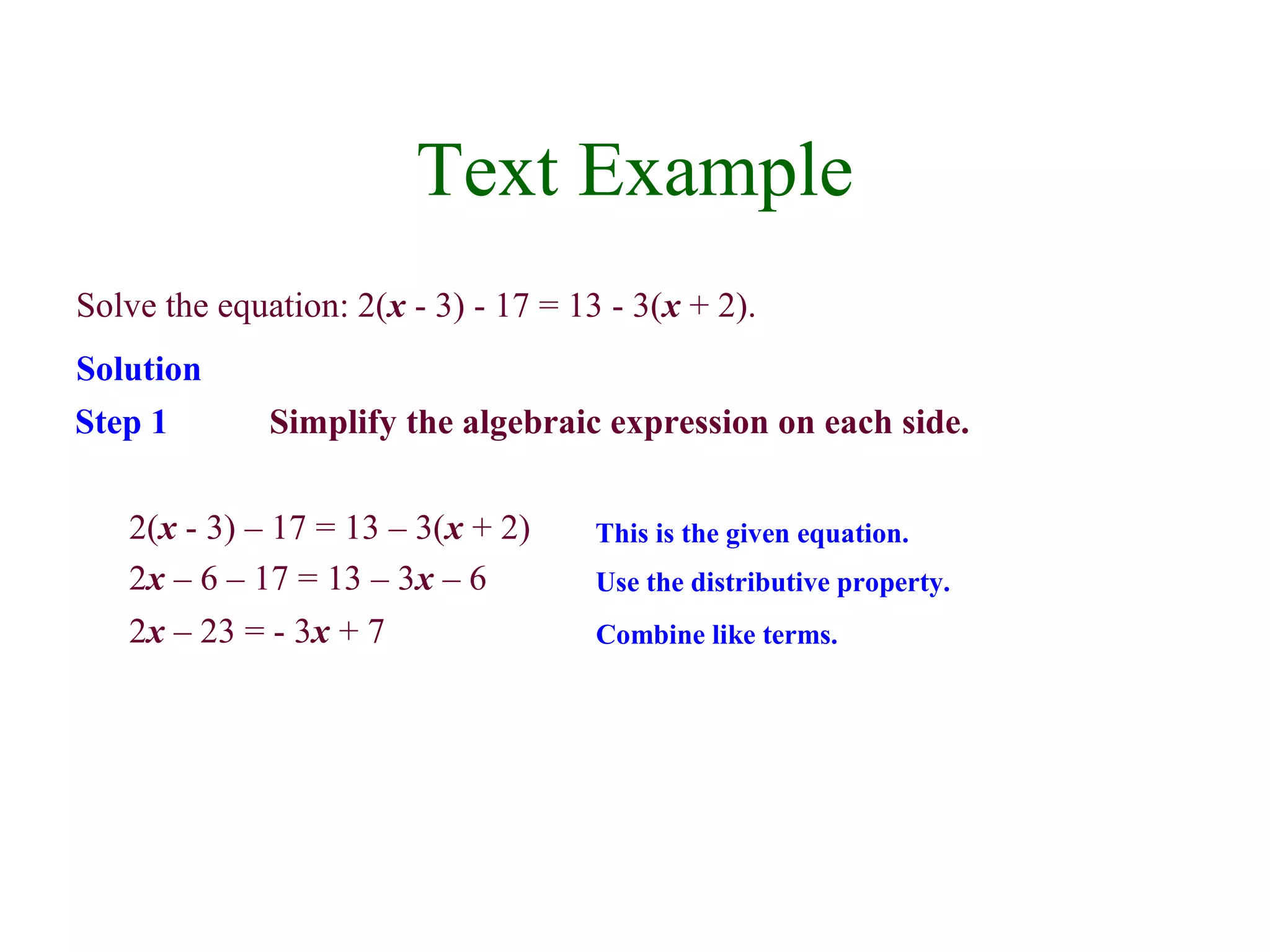
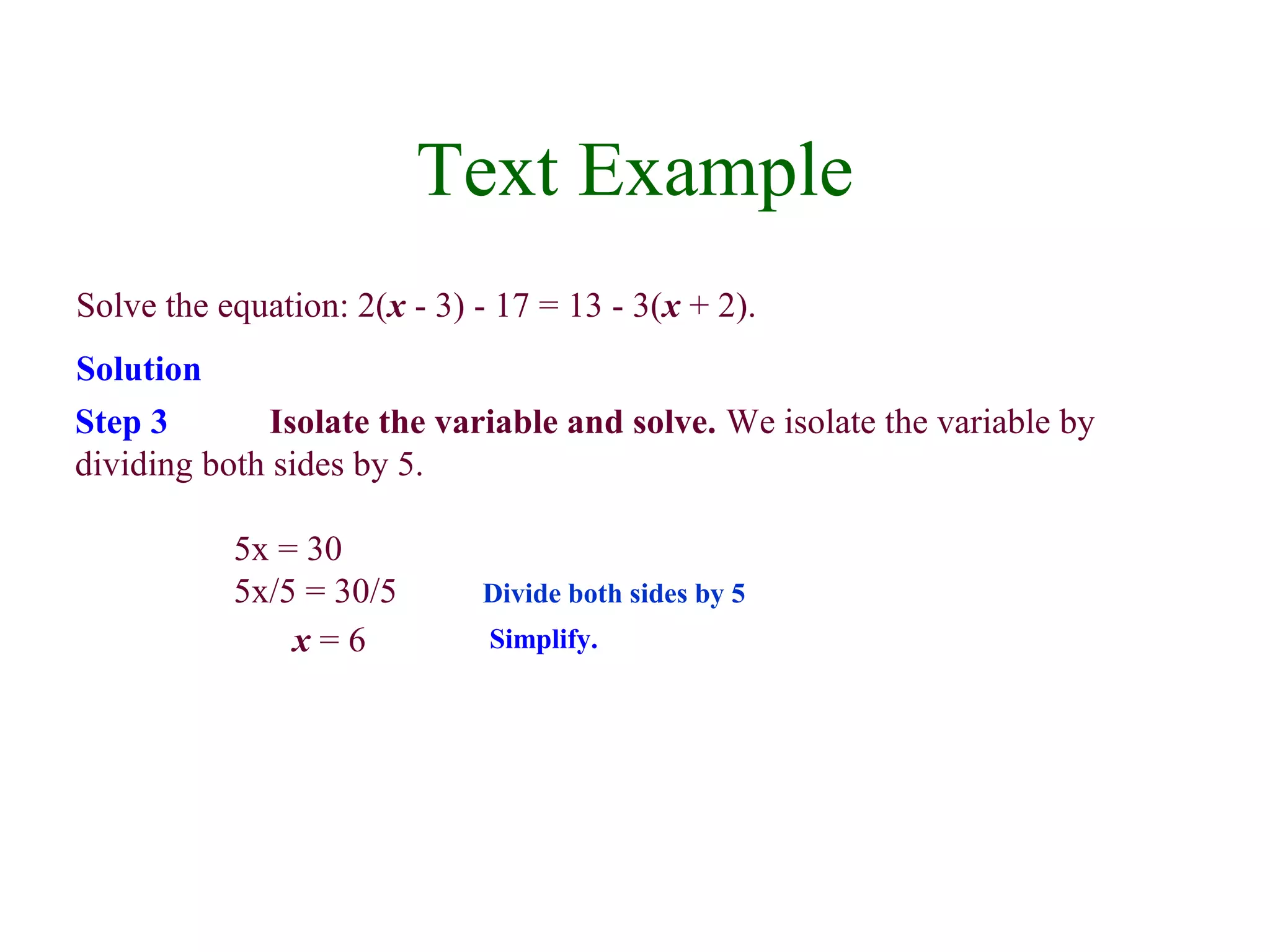
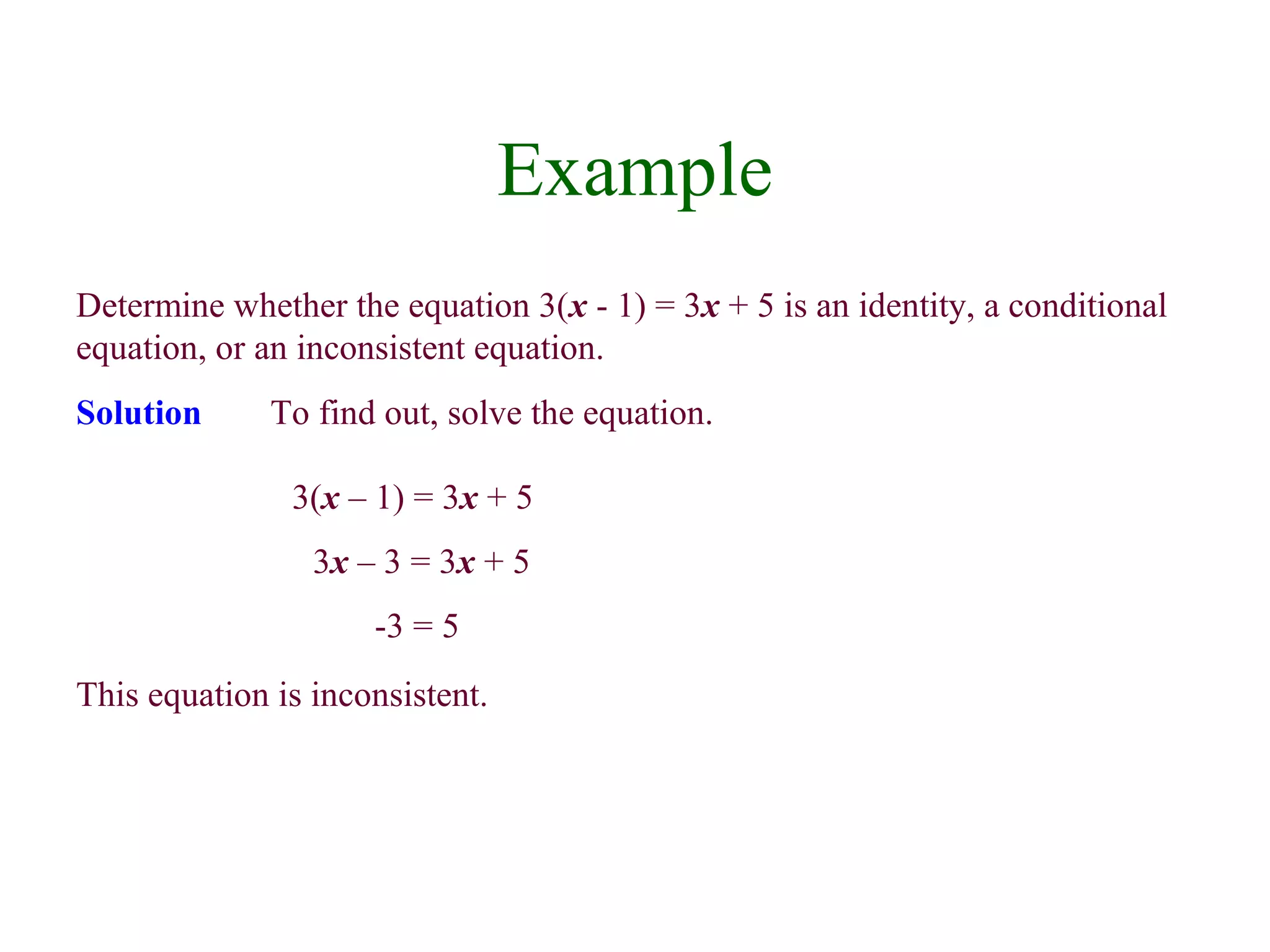
3) To solve a linear equation, simplify expressions, collect variable terms on one side and constants on the other, isolate the variable, and check the solution in the original equation.