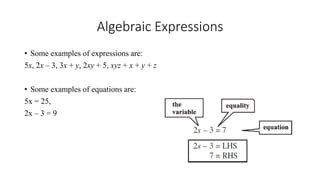
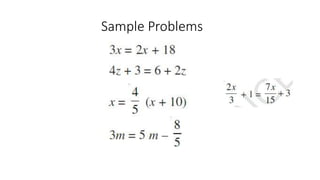
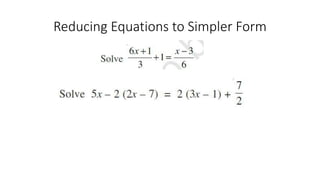
This document discusses linear equations in one variable. It defines expressions and equations, identifies one-variable linear equations, and explains how to simplify and solve one-variable linear equations. Specifically, it provides examples of algebraic expressions and equations, defines linear equations as having the highest power of the variable being 1, and demonstrates how to isolate the variable on one side of the equation and solve for its value using addition, subtraction, multiplication, or division.