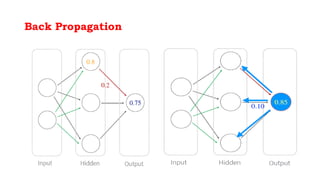
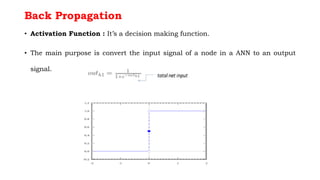
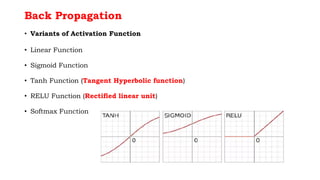
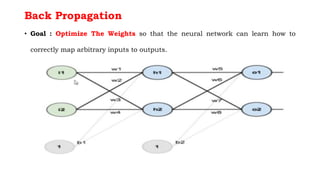
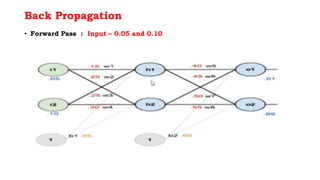
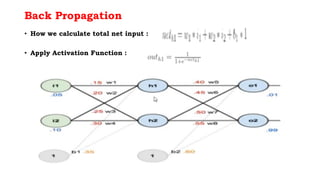
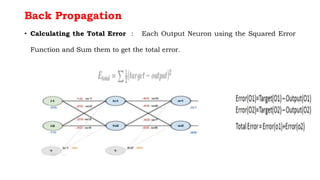
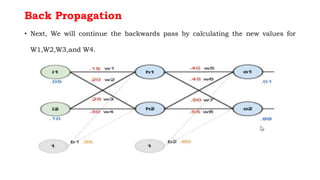
Back propagation is a supervised learning technique that calculates the gradient of the cost function to adjust the weights of neurons in a neural network. It propagates the error backwards from the output to the input layers to optimize the weights so the network can correctly map inputs to outputs. The forward pass involves calculating the total net input and activation at each node, while the backward pass calculates the error at each output neuron to determine how much to change each weight in order to minimize the total error.