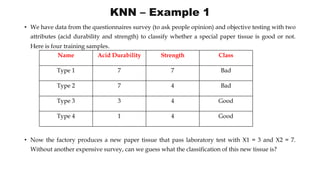
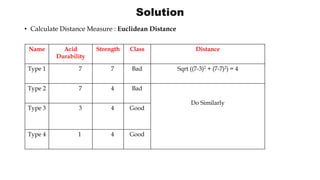
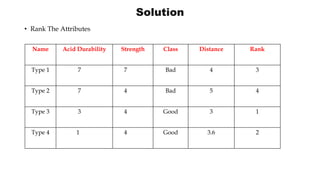
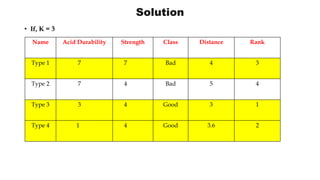
K-Nearest Neighbor (KNN) is a supervised machine learning algorithm that can be used for classification and prediction. It finds the K closest training examples to a new data point and assigns the most common class among those K examples to the new data point. Euclidean distance is often used to calculate the distance between points. An example is provided of classifying a new paper sample as good or bad based on acid durability and strength attributes by finding its 3 nearest neighbors and assigning it the majority class.