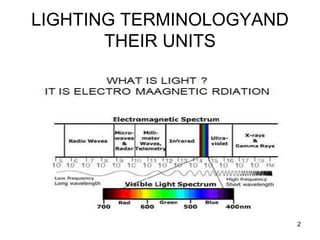
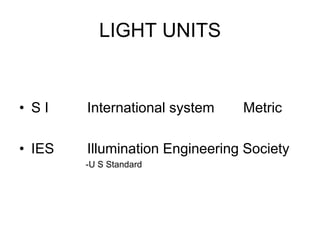
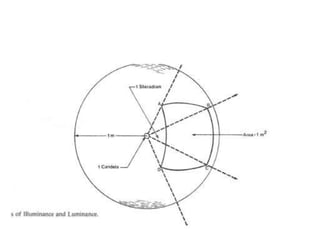
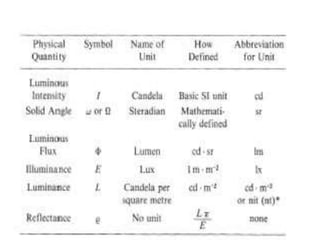
Lighting terminology and units can be complex, but essentially come down to three main concepts:
1) Luminous flux refers to the total amount of visible light emitted by a source, measured in lumens. 2) Illuminance refers to the amount of light falling on a surface, measured in lux. 3) Luminance refers to the amount of light emitted from or reflected off a surface, measured in candelas per square meter. Understanding these core photometric concepts and the related units like lumens, lux, and candelas is essential for working with lighting.