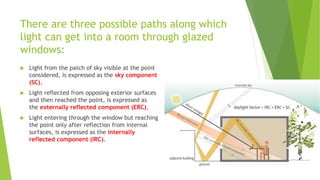
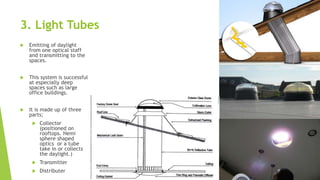
Daylight factor is defined as the ratio of indoor light level to outdoor light level, expressed as a percentage. There are three paths for light to enter a room: from the visible sky patch, from external reflections, and from internal reflections. Daylight is preferable to artificial light because it covers the full color spectrum, varies throughout the day, and can save energy. When providing daylight, issues like shading, glare, heat gain, and energy performance must be considered. Advanced daylight systems include light shelves, dynamic light shelves, light tubes, fiber optics, and anidolic systems, which increase daylight penetration without additional artificial lighting.