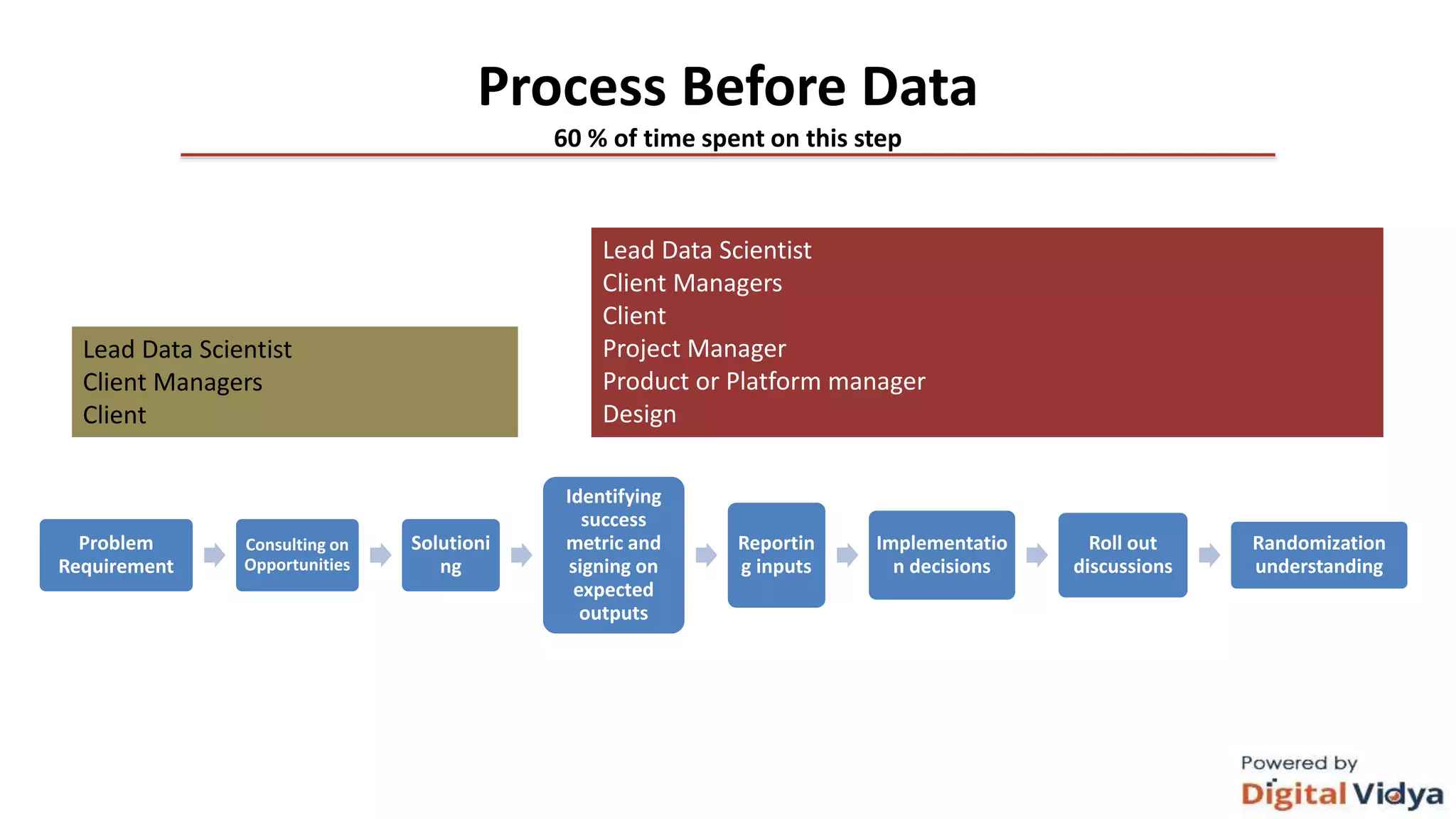
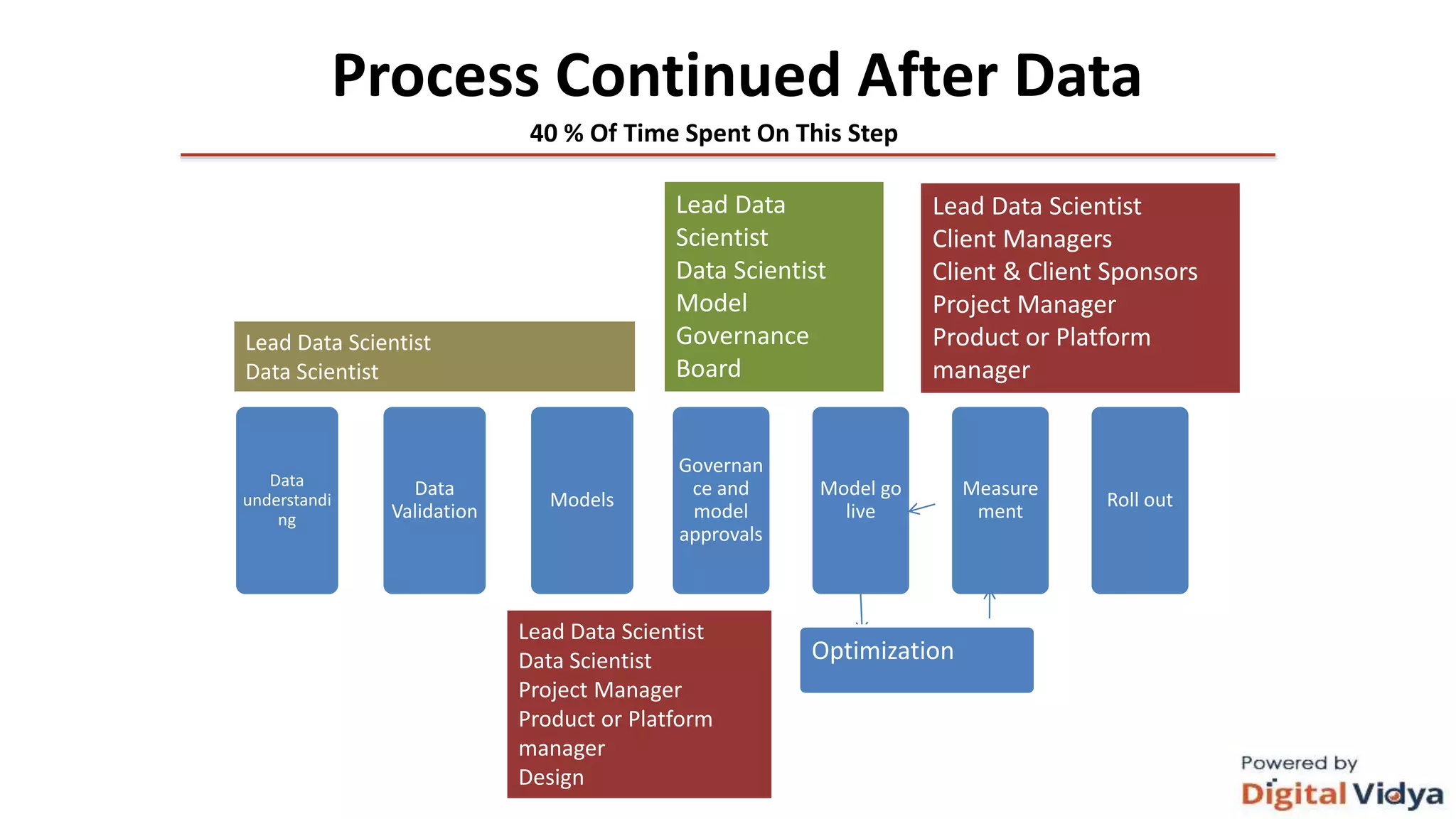
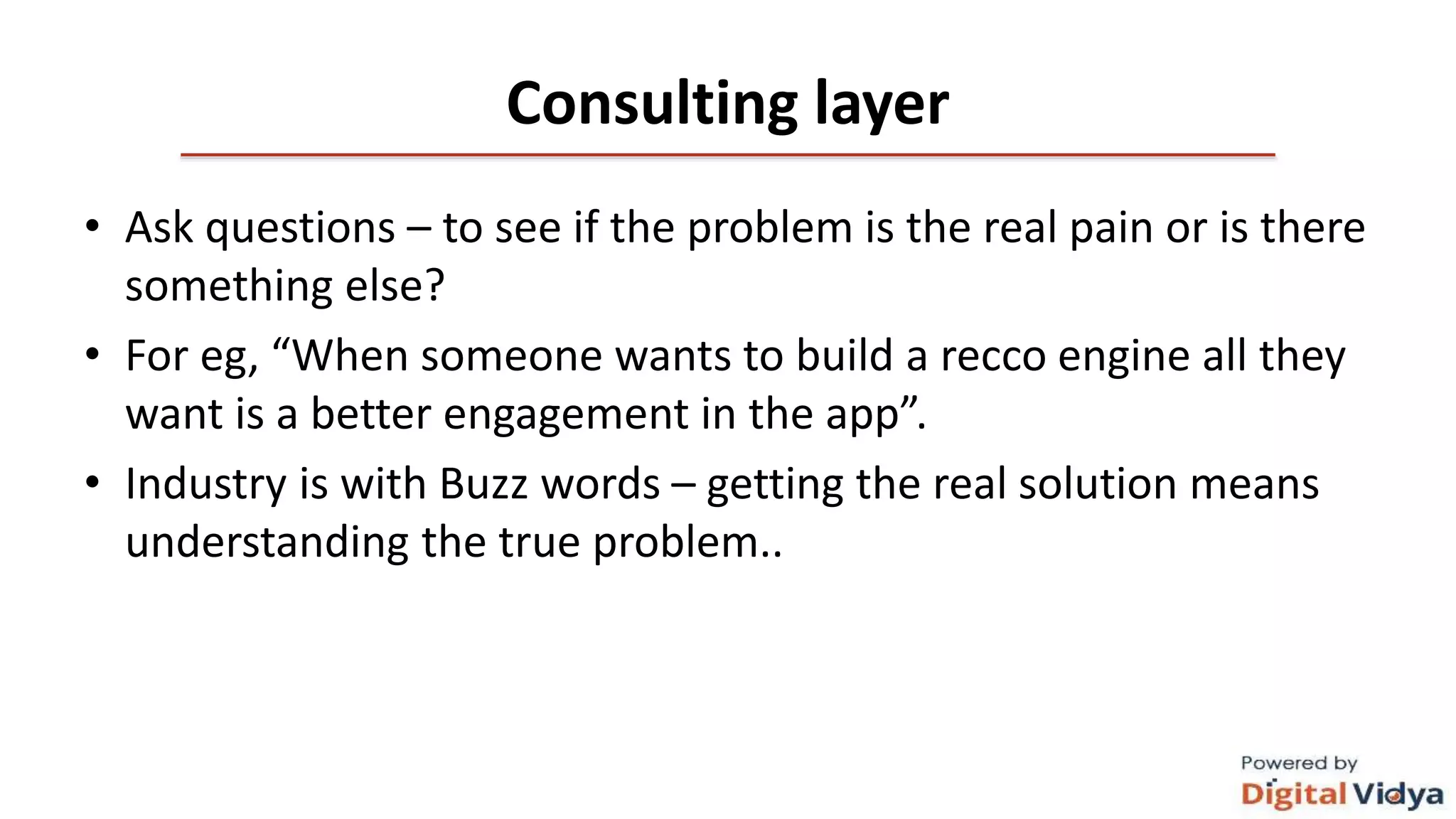
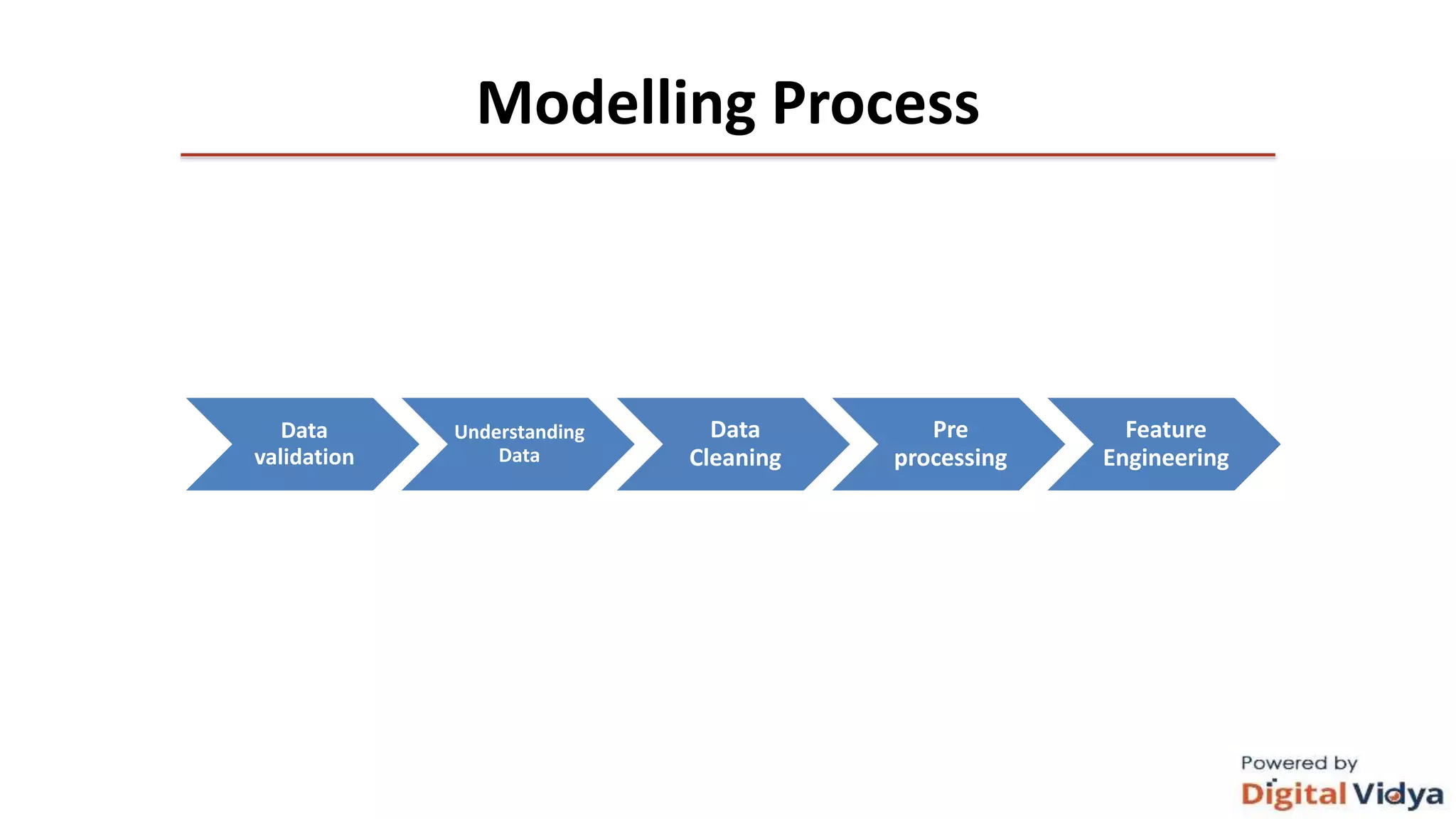
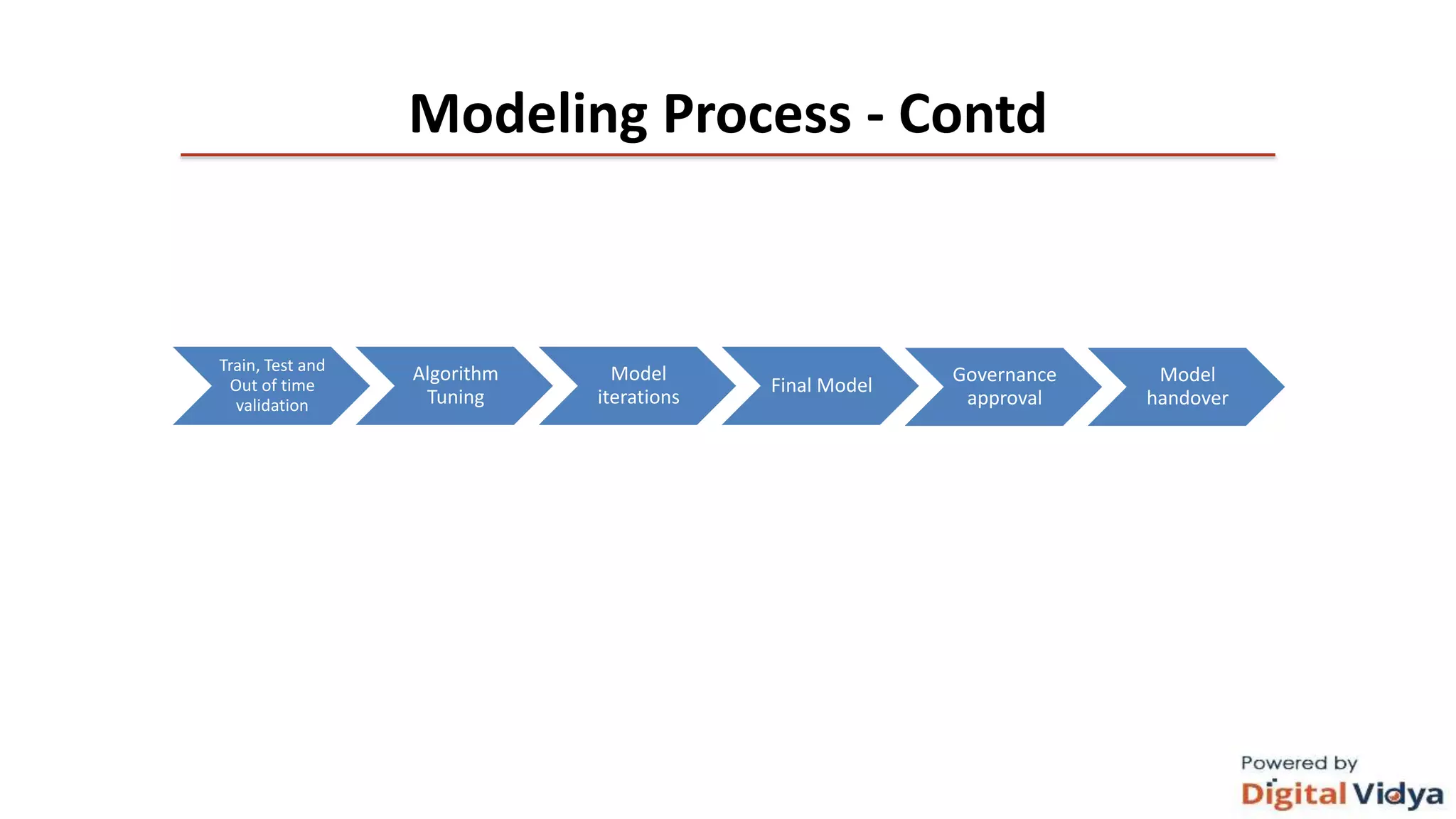
The document outlines the data science life cycle and its application across different types of organizations, distinguishing between product and service-oriented approaches. It describes the roles of various team members, the consultation processes for understanding problem requirements, and the steps involved in implementing data science solutions, including data validation, modeling, and optimization. Additionally, it highlights the importance of stakeholder engagement, attribution challenges, model governance, and intellectual property generation throughout the project.