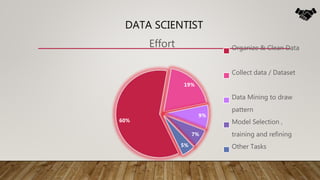
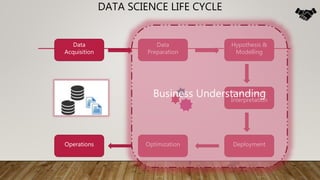
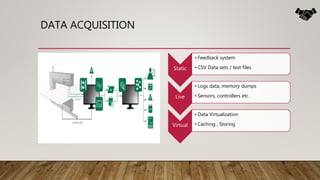
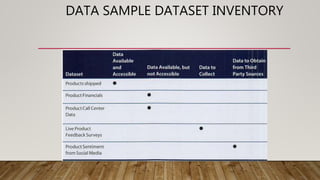
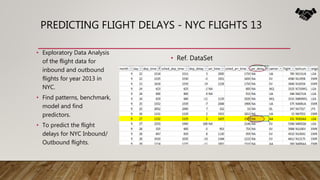
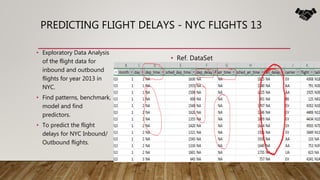
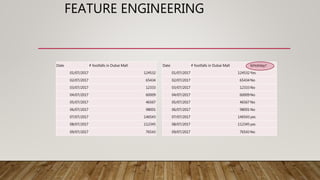
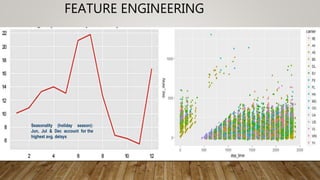
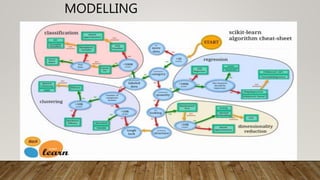
The document outlines the data science lifecycle, emphasizing the importance of data preparation, model selection, and evaluation in predictive analytics. It highlights the need for robust data cleansing and preprocessing to enhance accuracy, as well as explores various tools and methodologies for modeling flight delays using historical data. Additionally, it discusses the iterative nature of the data preparation phase, which can take up to 60% of the overall project time.