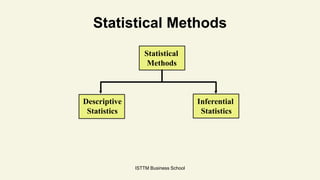
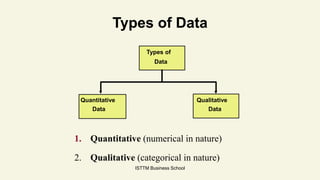
Statistics is the science of data. It involves collecting, presenting, and characterizing data. It plays an important role in fields like industry, commerce, economics, and more by analyzing data. There are two main types of statistics: descriptive statistics which describes data through measures like average, and inferential statistics which makes decisions about population characteristics through estimation and hypothesis testing. Statistics helps answer questions about whether certain factors increase outcomes and helps predict things like election results. It is an essential tool in data science.