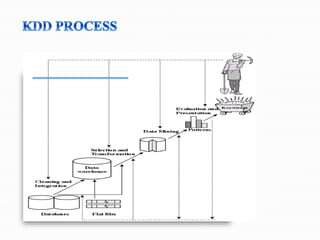
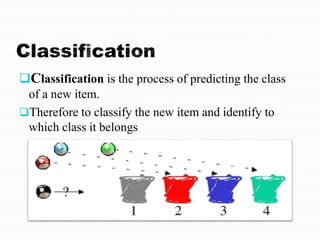
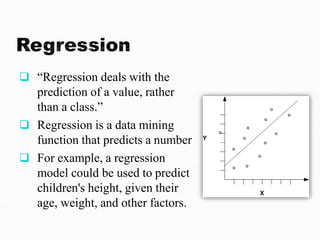
The document discusses data mining and its processes. It states that data mining involves extracting useful information and patterns from large amounts of data through processes like data cleaning, integration, transformation, mining, and presentation. This extracted knowledge can then be applied to various domains such as fraud detection, market analysis, and science exploration.