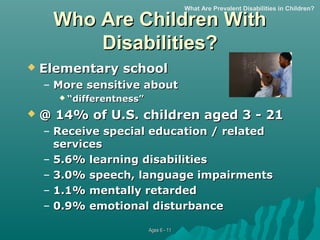
This document summarizes physical, cognitive, and social development during middle and late childhood between ages 6-11. It discusses growth in brain development and the prefrontal cortex. Children develop better motor skills, coordination, and the ability to think logically during concrete operations. A variety of disabilities that may impact development are also reviewed, including learning disabilities, ADHD, and intellectual assessments. Intelligence is discussed as being influenced by both genetics and environment and manifesting in different forms.