The document discusses various topics relating to birth and infant care, including:
1. Birthing practices vary widely across cultures, from hospital births with physicians in the US to home births with midwives in other areas. Water birth and natural childbirth techniques aim to reduce pain.
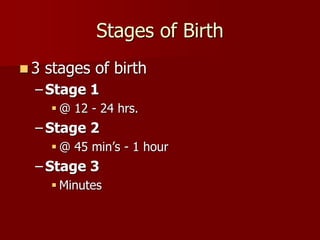
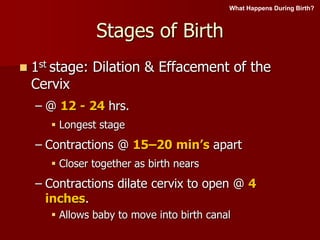
2. Birth occurs in three stages - dilation of the cervix, delivery of the baby, and delivery of the placenta. Newborns are assessed using the Apgar scale.
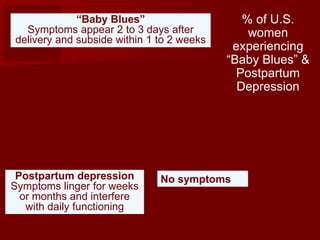
3. Preterm and low birth weight babies face greater health risks and bonding with parents is important for infant development, as is avoiding risks like SIDS through practices like having babies sleep on their backs.