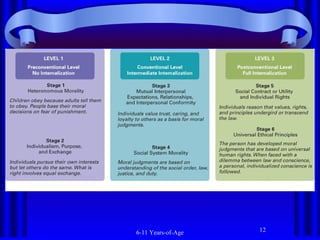
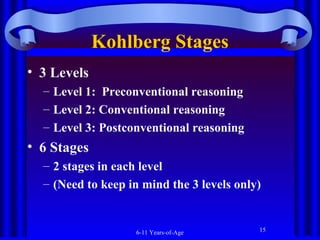
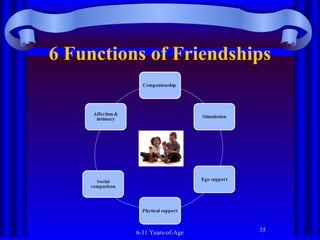
The document summarizes socioemotional development in middle and late childhood from ages 6 to 11. During this period, children develop a more complex understanding of themselves, including describing themselves using psychological traits. They also recognize social aspects of their identity and how they compare to others. Children's self-esteem and self-concept become more multidimensional as they evaluate themselves in different areas. They also develop increased ability to understand and manage their emotions, behavior, and thoughts through self-regulation. Gender differences emerge in areas like aggression, prosocial behavior, and physical and cognitive development during these years.