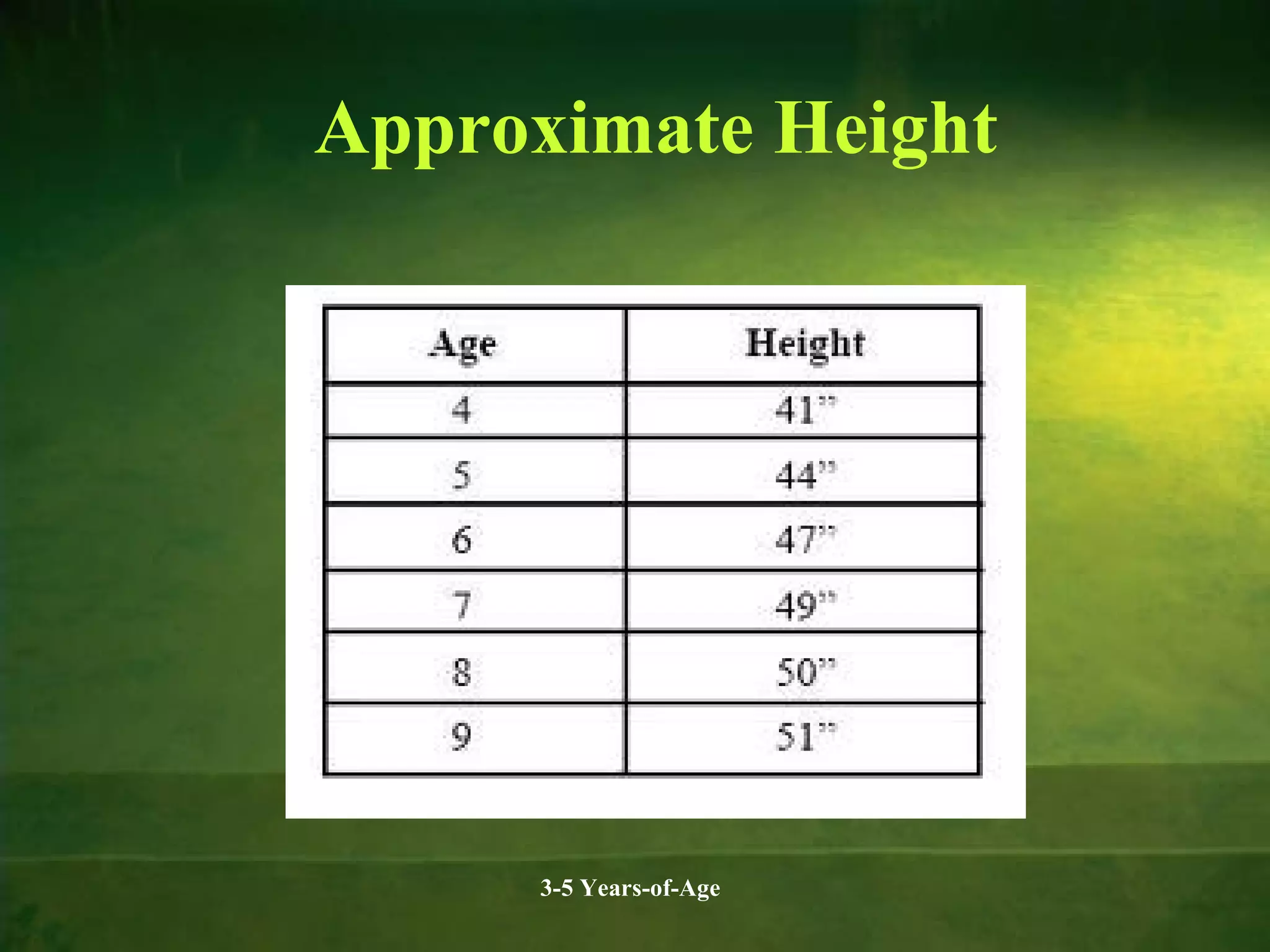
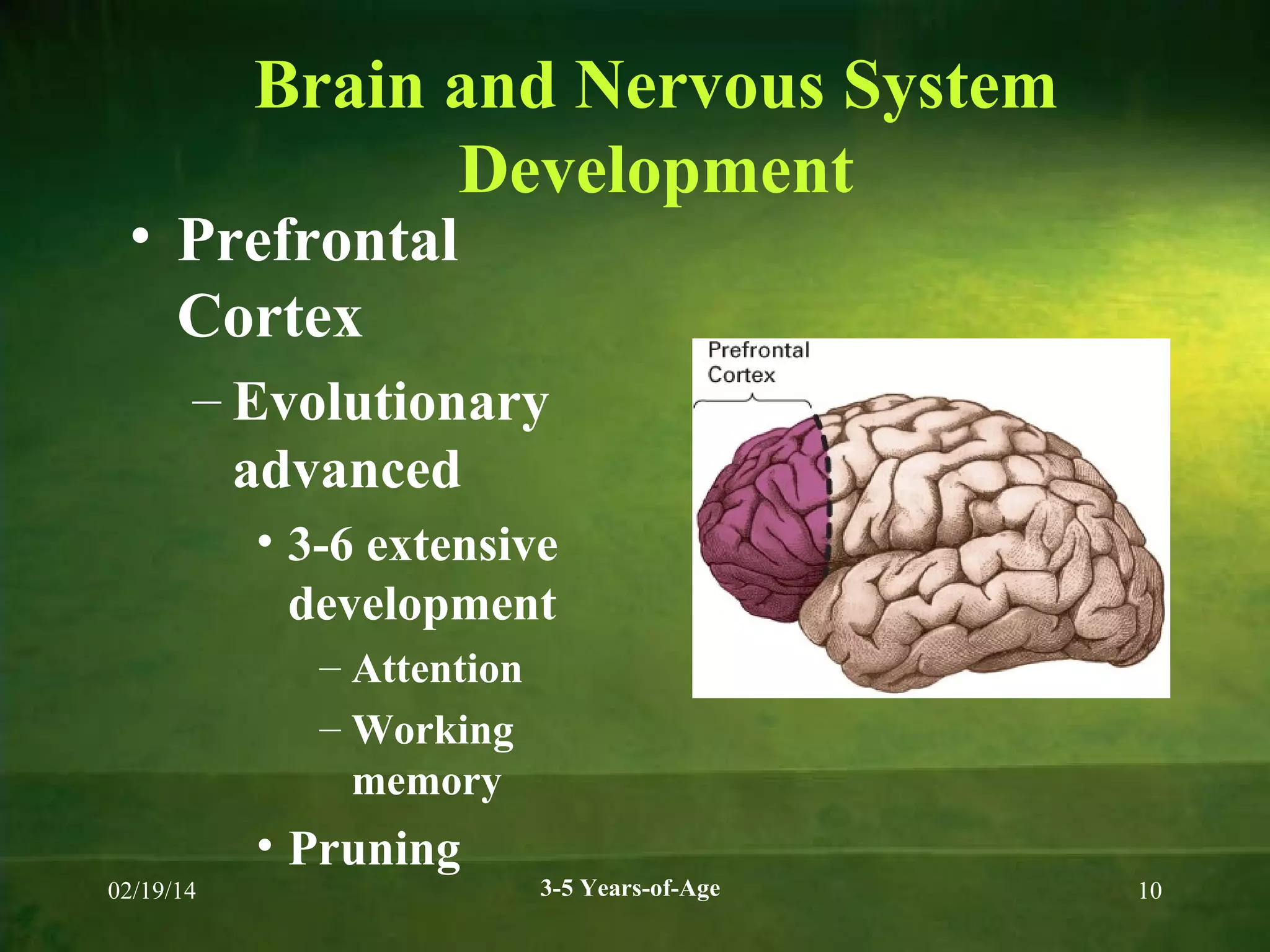
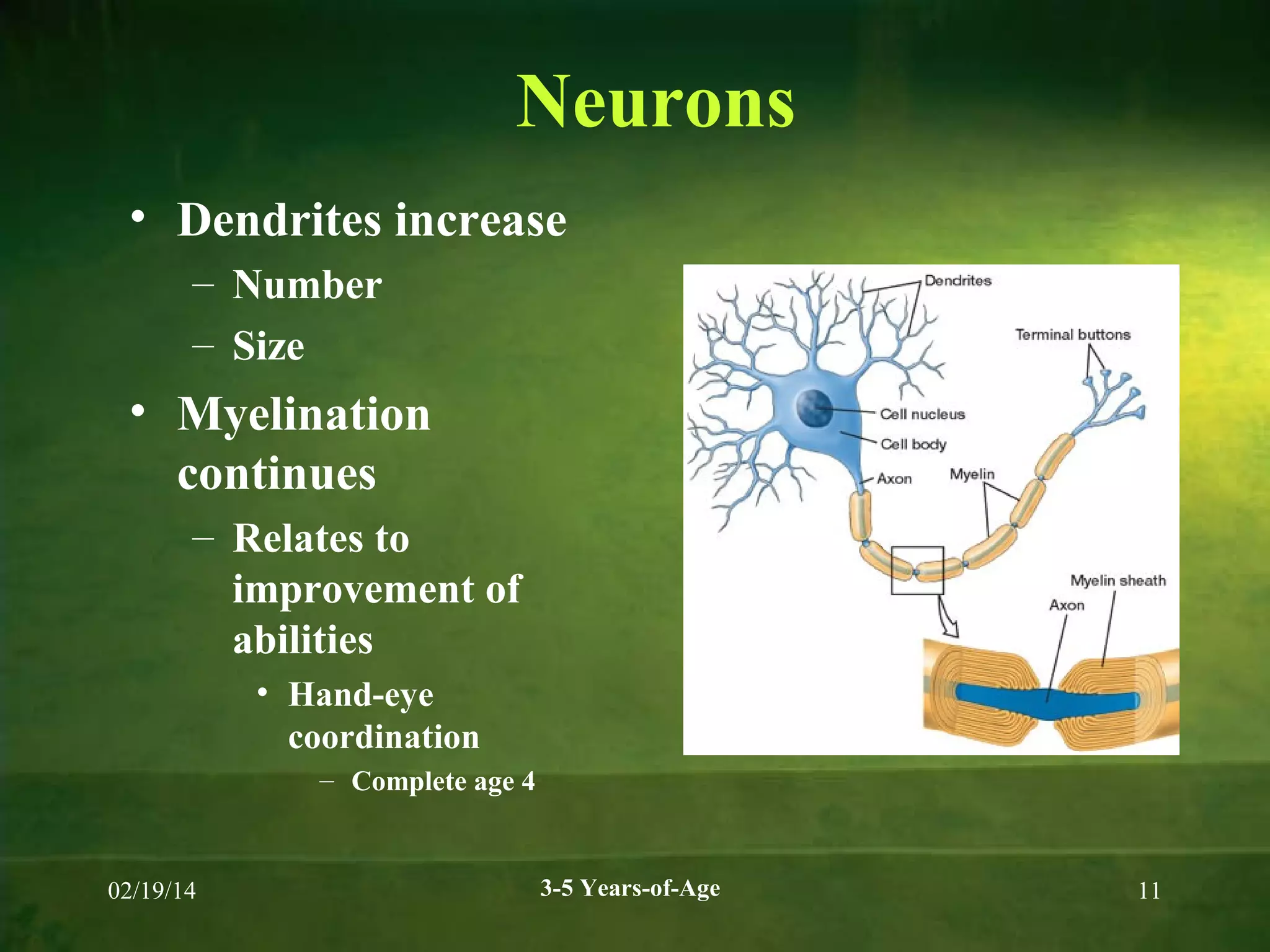
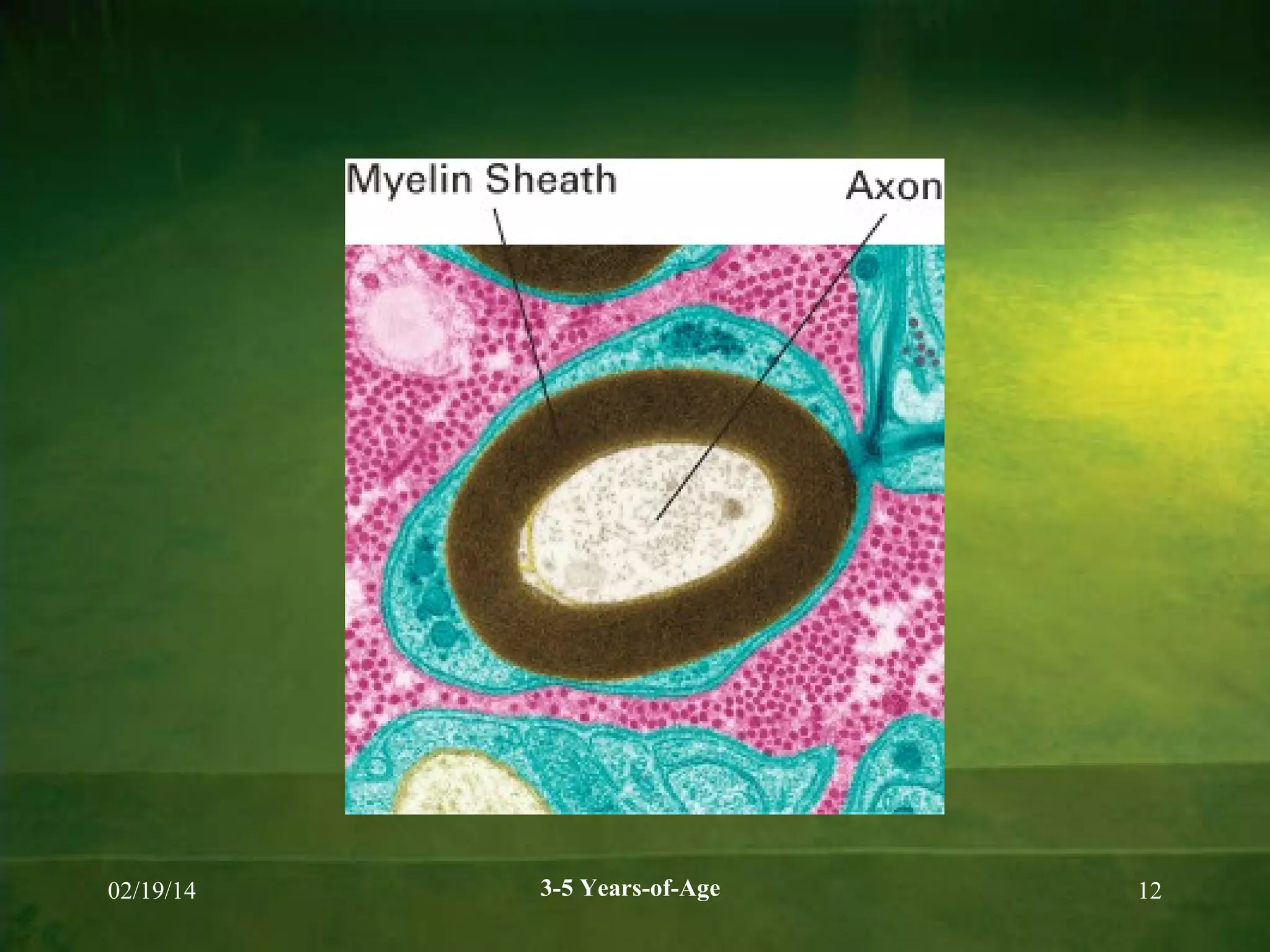
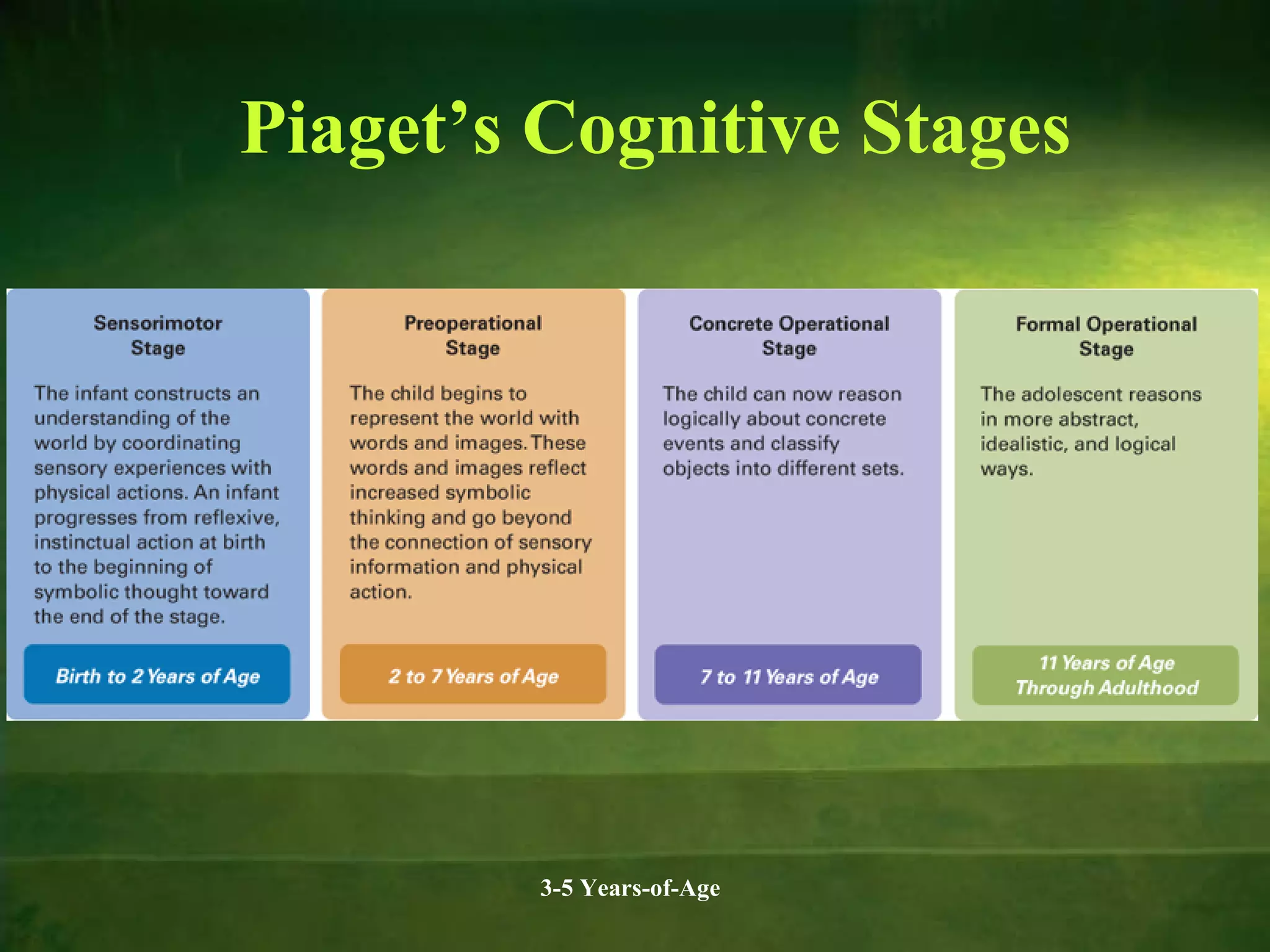
Physical and cognitive development occurs rapidly in early childhood between ages 3-5. Children experience steady growth and development in their bodies, brains, motor skills, health, cognition, memory, language and theory of mind during this period. Key developments include continued brain growth, improved fine motor skills, emerging abilities in logical thinking and reasoning, longer attention spans, and understanding that others may have different beliefs or perspectives. Proper nutrition is important for supporting physical, cognitive and behavioral development during the preschool years.