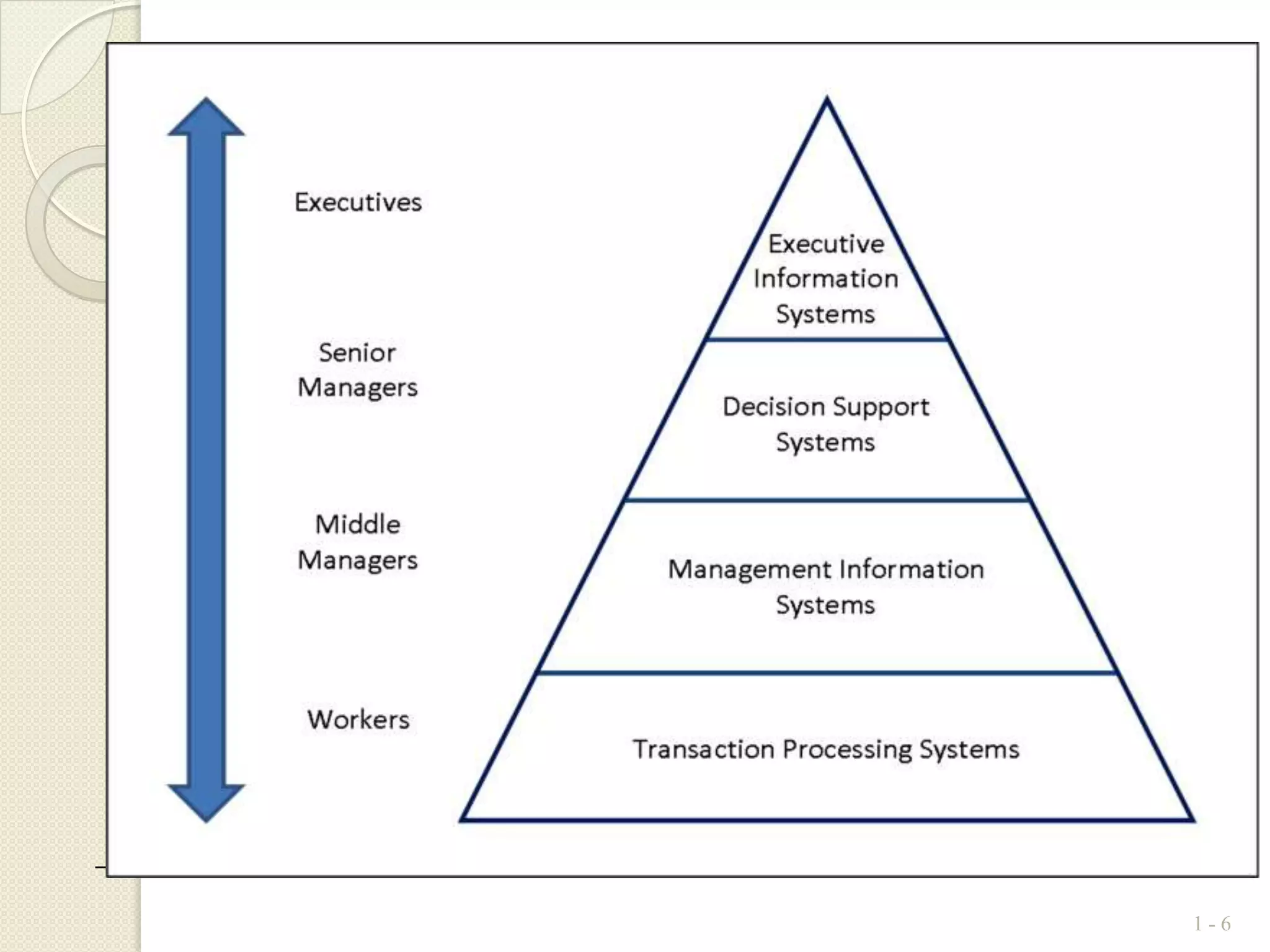
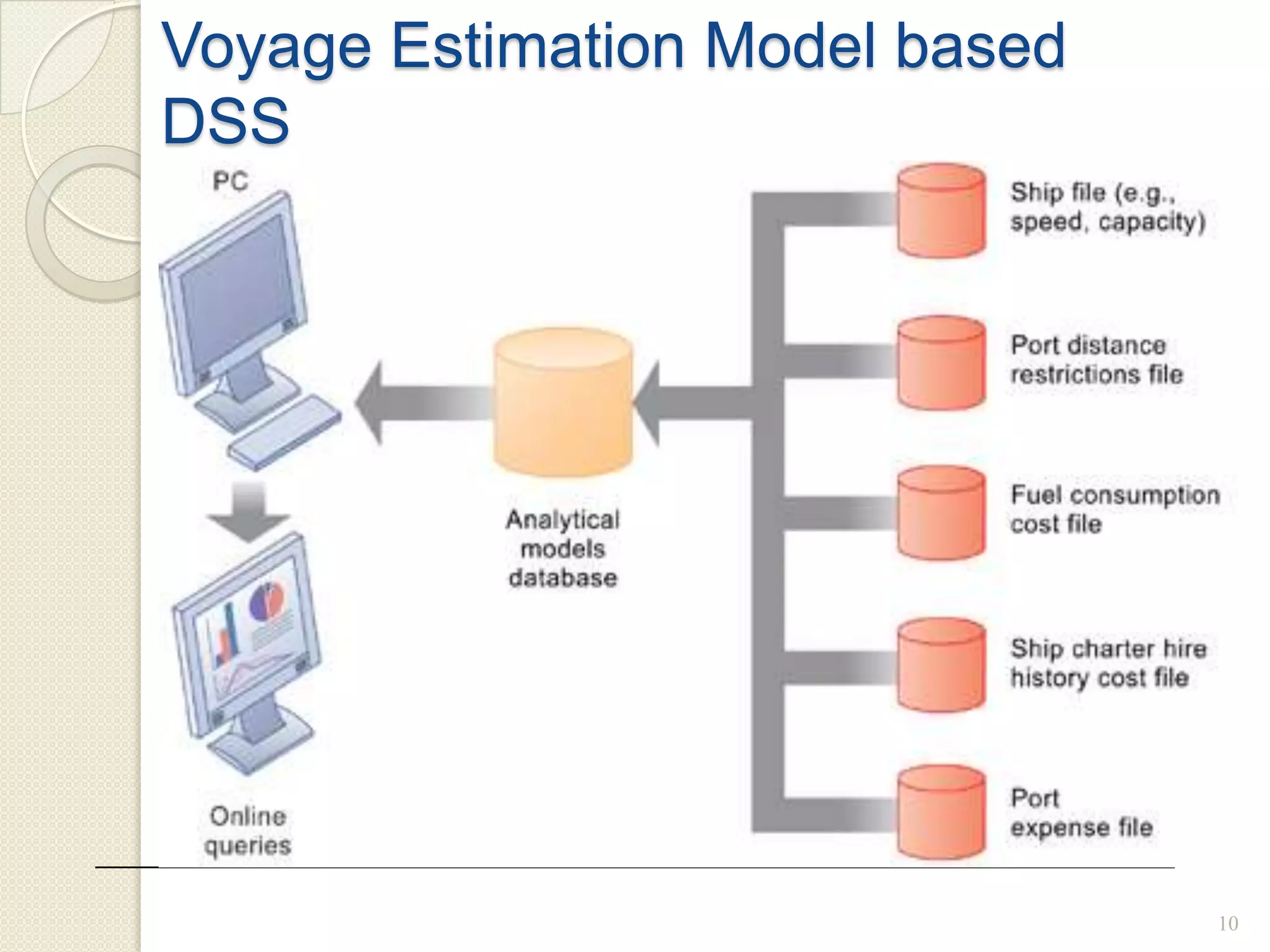
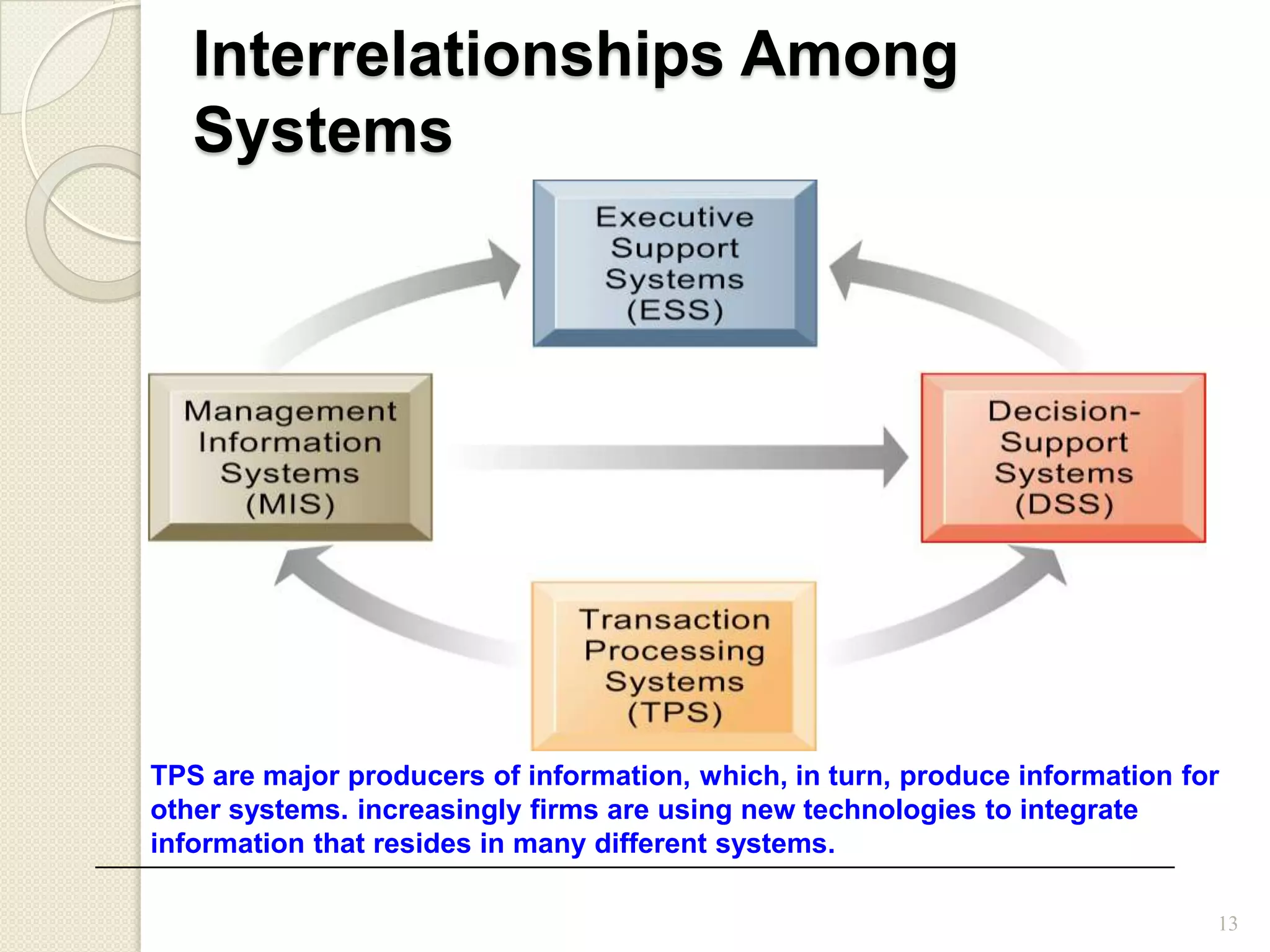
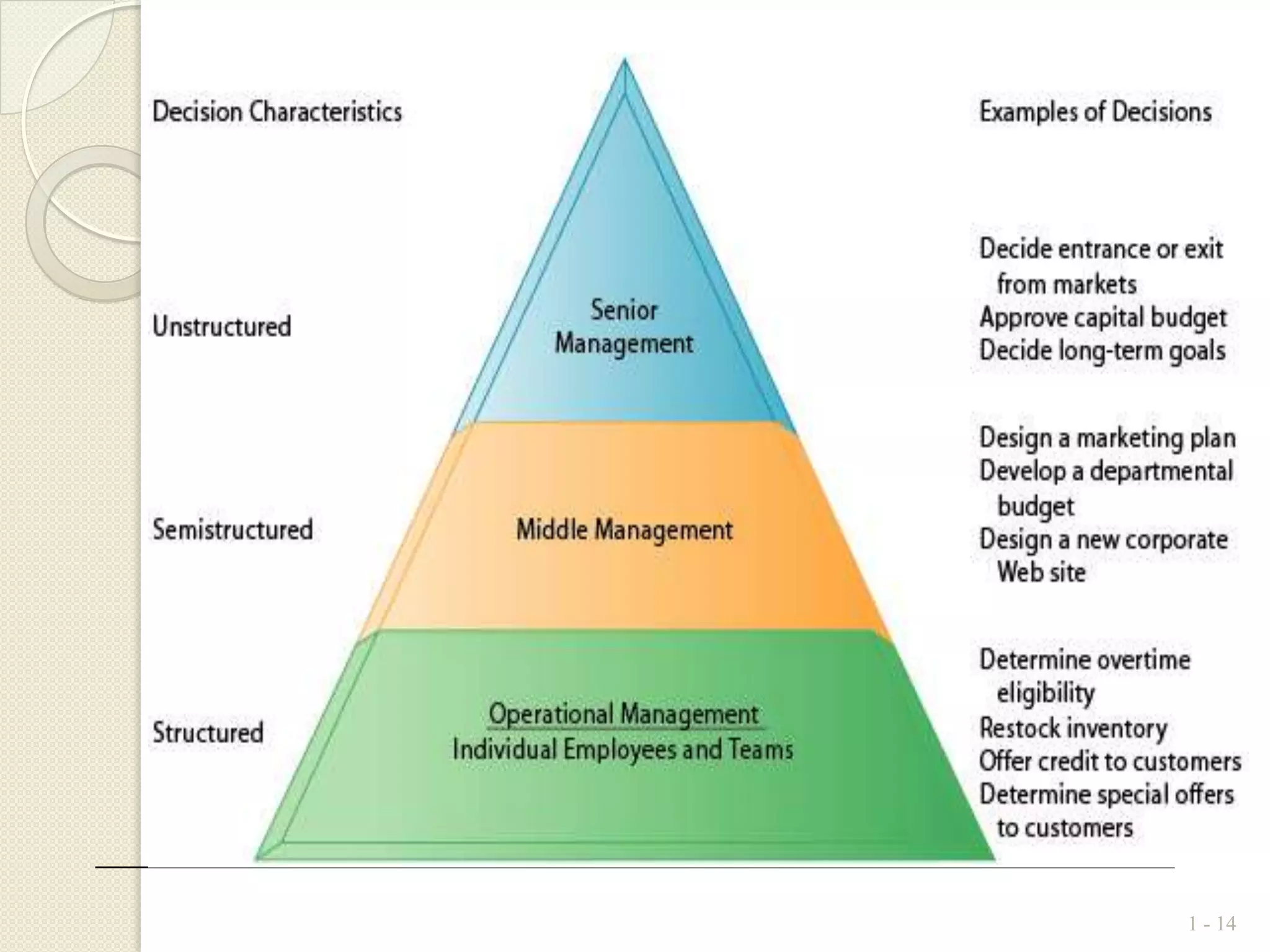
There are different types of information systems that can be used for various organizational functions and management levels. Major functional subsystems include marketing, manufacturing, logistics, personnel, finance and accounting, and information processing. These systems support different activities along the value chain such as transaction processing, operational control, management control, and strategic planning. Information systems also differ in terms of time scales, level of detail, source of data, and frequency of use depending on whether they are used for operational, tactical, or strategic management. Transaction processing systems provide data to decision support systems and executive information systems which are used to support non-routine decisions at middle and senior management levels respectively.