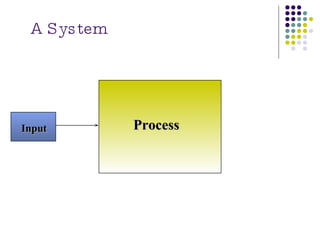
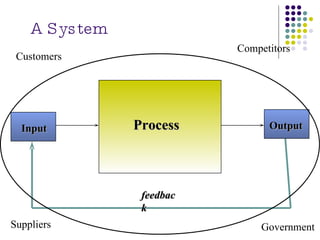
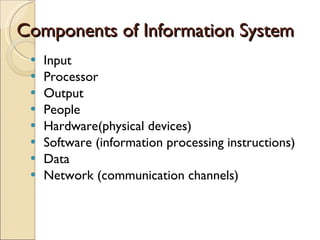
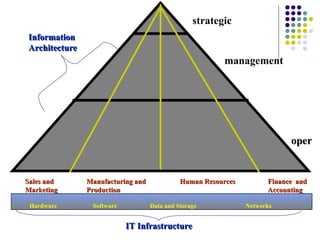
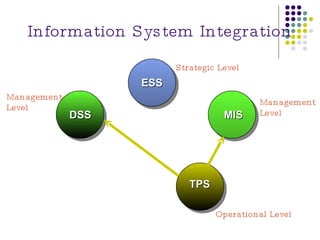
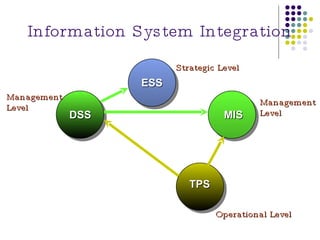
The document discusses management information systems and different types of information systems. It defines management information systems as integrated user-machine systems that provide information to support decision making, coordination, and control within an organization. It describes different levels of information systems, including transaction processing systems, management information systems, decision support systems, executive information systems, and expert systems. It also discusses the integration of different system types at strategic, management, and operational levels.