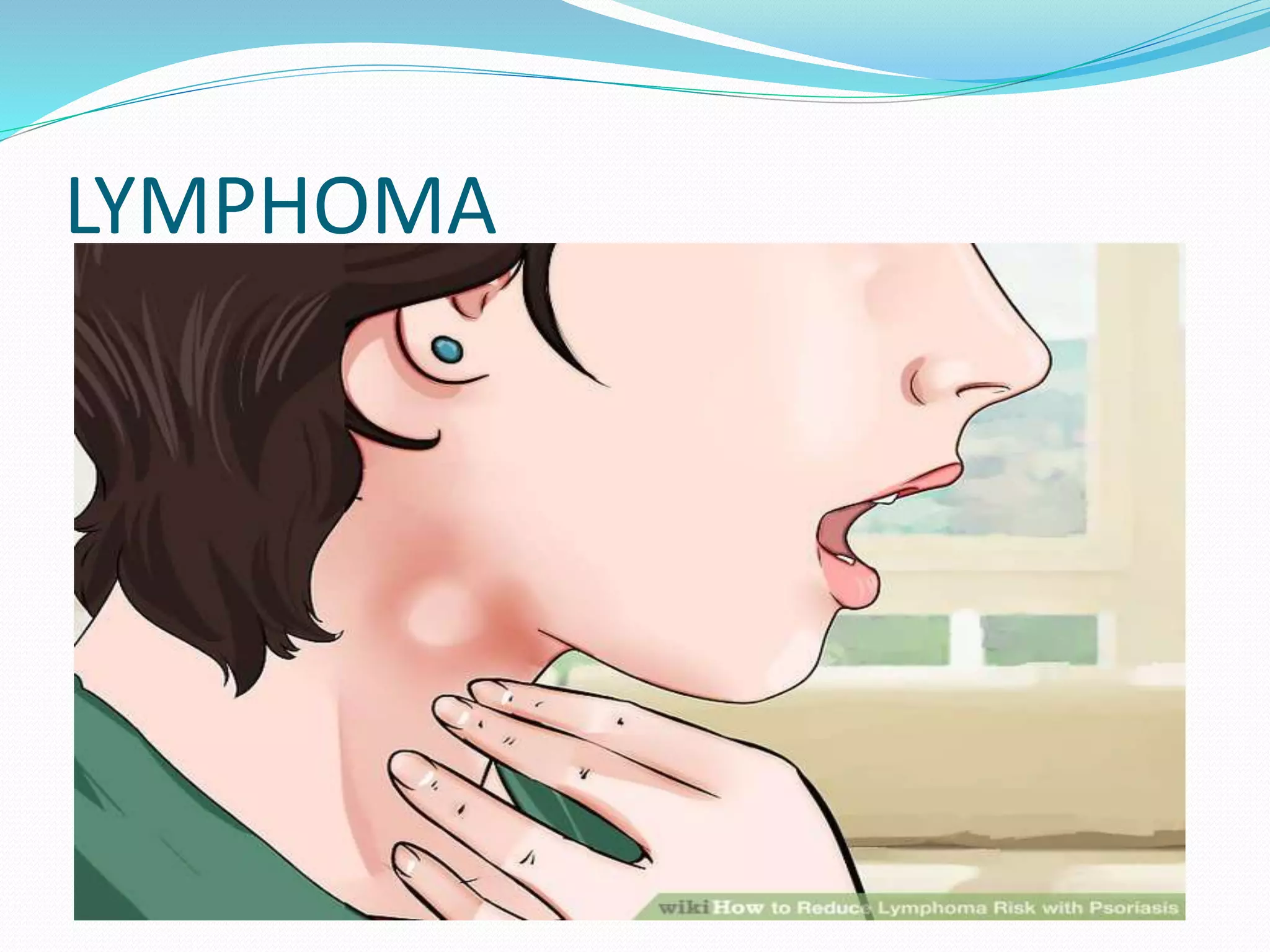
The document provides an overview of leukemia and lymphoma, detailing types, symptoms, causes, risk factors, diagnostic methods, and treatments. Leukemia is classified into acute and chronic forms based on the maturity of white blood cells involved, while lymphoma includes Hodgkin's and non-Hodgkin's variants. Treatment options vary but commonly include chemotherapy, radiation, and targeted therapies, with specific management strategies based on the leukemia or lymphoma type.