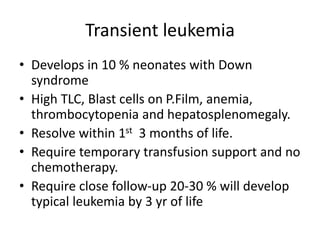
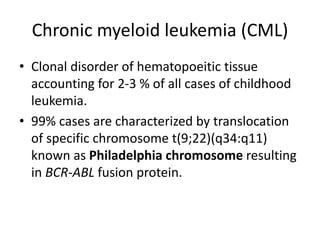
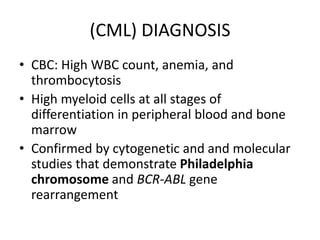
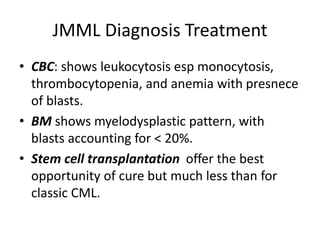
This document provides an overview of various types of leukemia, including acute myeloid leukemia (AML), chronic myeloid leukemia (CML), and infantile leukemia. It discusses the classification, signs and symptoms, diagnosis, and management of these leukemias. Specific hematologic emergencies that can occur in leukemia patients are also reviewed, such as leukostasis, tumor lysis syndrome, spinal cord compression, and respiratory distress syndrome.









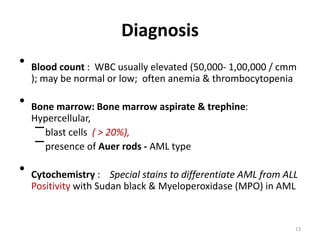
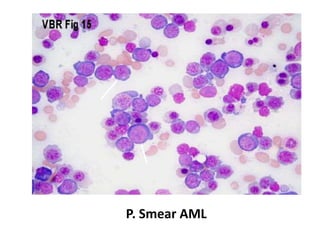
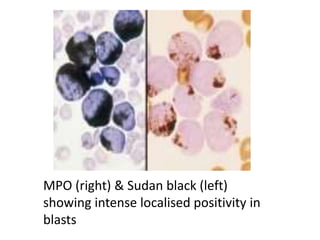



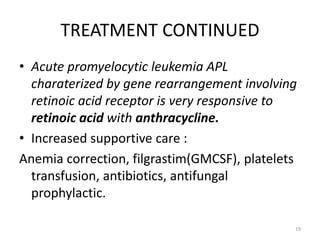









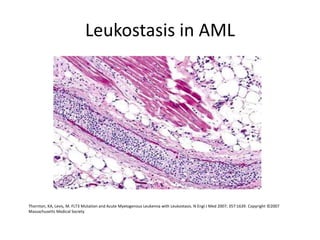







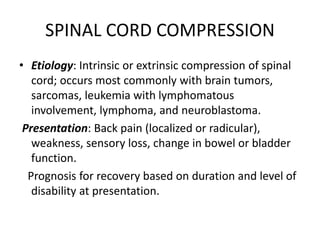
![DIAGNOSIS
• Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI [preferred])
or computed tomography (CT) scan of spine.
• A plain film of spine has good specificity but
detects only two thirds of abnormalities](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/leukemiaii-160308182621/85/Leukemia-ii-42-320.jpg)






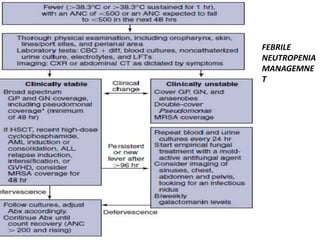
![PRESNTATION AND DIGNOSIS
Presentation: Fever, fatigue, chills, rigors,
listlessness, lethargy, tachypnea,tachycardia,
localized pain.
Diagnosis: Fever (temperature [T] > 38.3°C or T
> 38.0°C for >1 hour) in the setting of
neutropenia (ANC < 500 cells/μL, or < 1000
cells but expected to drop to <500 in the next
48 hours).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/leukemiaii-160308182621/85/Leukemia-ii-49-320.jpg)