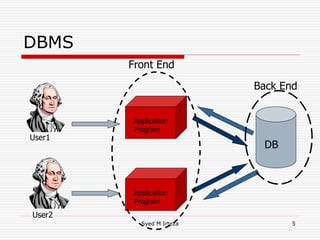
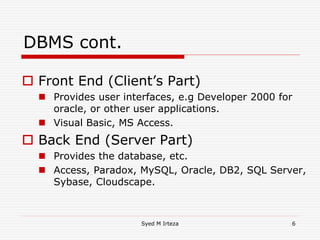
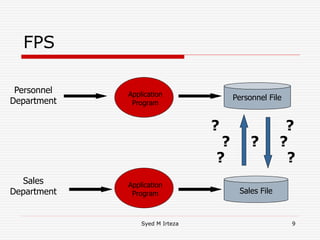
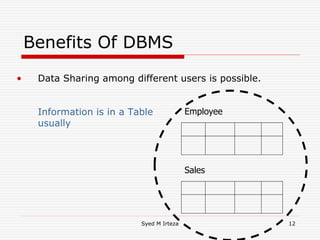
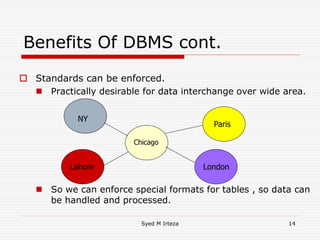
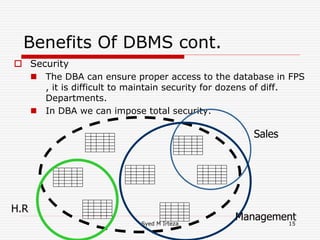
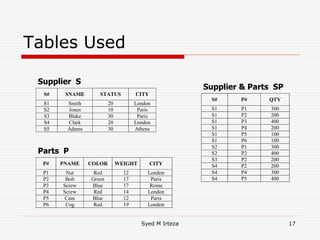
This document provides an introduction and overview of database management systems (DBMS). It begins by stating there are no prerequisites for the course. It then defines a DBMS as a computer system that stores, retrieves, and manipulates information efficiently and securely. A DBMS provides abstraction and control between data and users that is not possible with conventional file systems. The document contrasts DBMS with file processing systems, noting that DBMS provides centralized control under a database administrator, whereas file processing results in localized control and potential incompatibilities. It provides examples of tables that may be used in a DBMS and concludes with benefits of DBMS like data sharing, reduced redundancy, enforced standards, security, and transaction support.