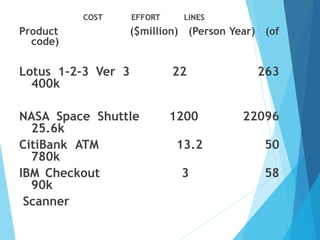
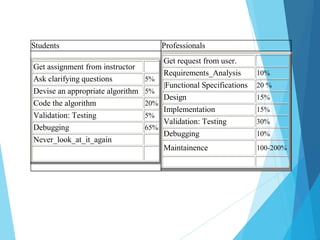
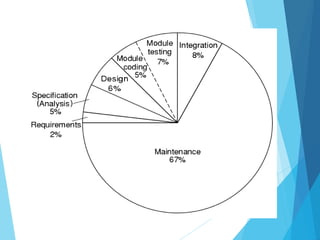
The document provides an overview of software engineering, defining it as the systematic approach to the development, operation, and maintenance of software to ensure high quality, cost-effective production. It discusses the evolution of software through different eras, highlighting challenges such as cost overruns, quality issues, and the increasing complexity of software projects. The document emphasizes the importance of adopting structured methods and tools in software engineering to address the ongoing 'software crisis' and meet user demands.