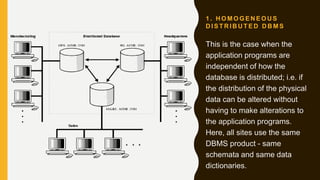
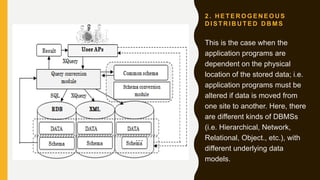
Distributed database management systems (DDBMS) allow data to be spread across multiple computer sites connected by a network. A DDBMS provides location transparency so users can access data without knowing its physical location. It also coordinates transactions that involve data stored at multiple sites. DDBMS architectures include transaction managers, data managers, and transaction coordinators to process transactions and subtransactions across distributed data.