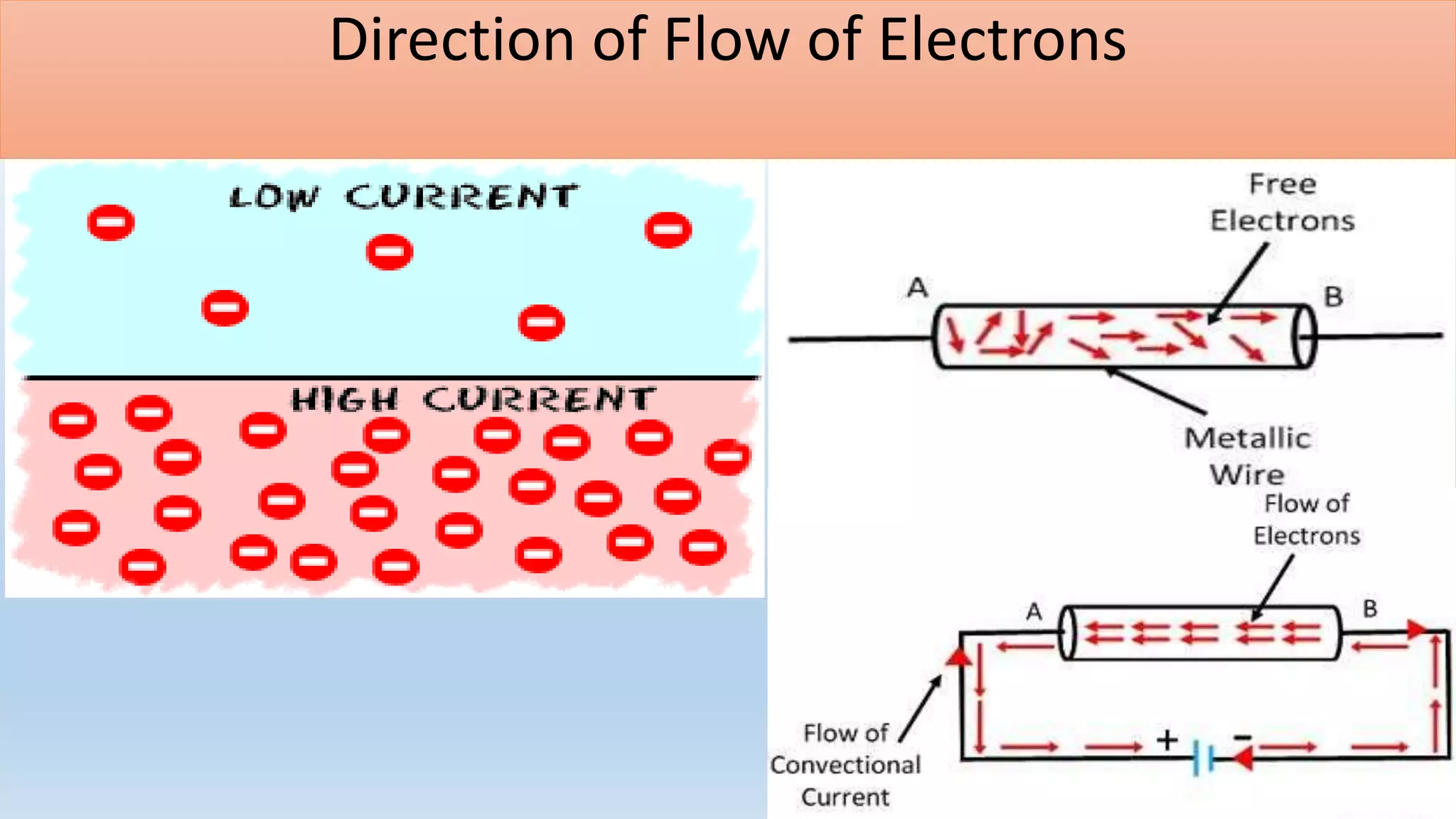
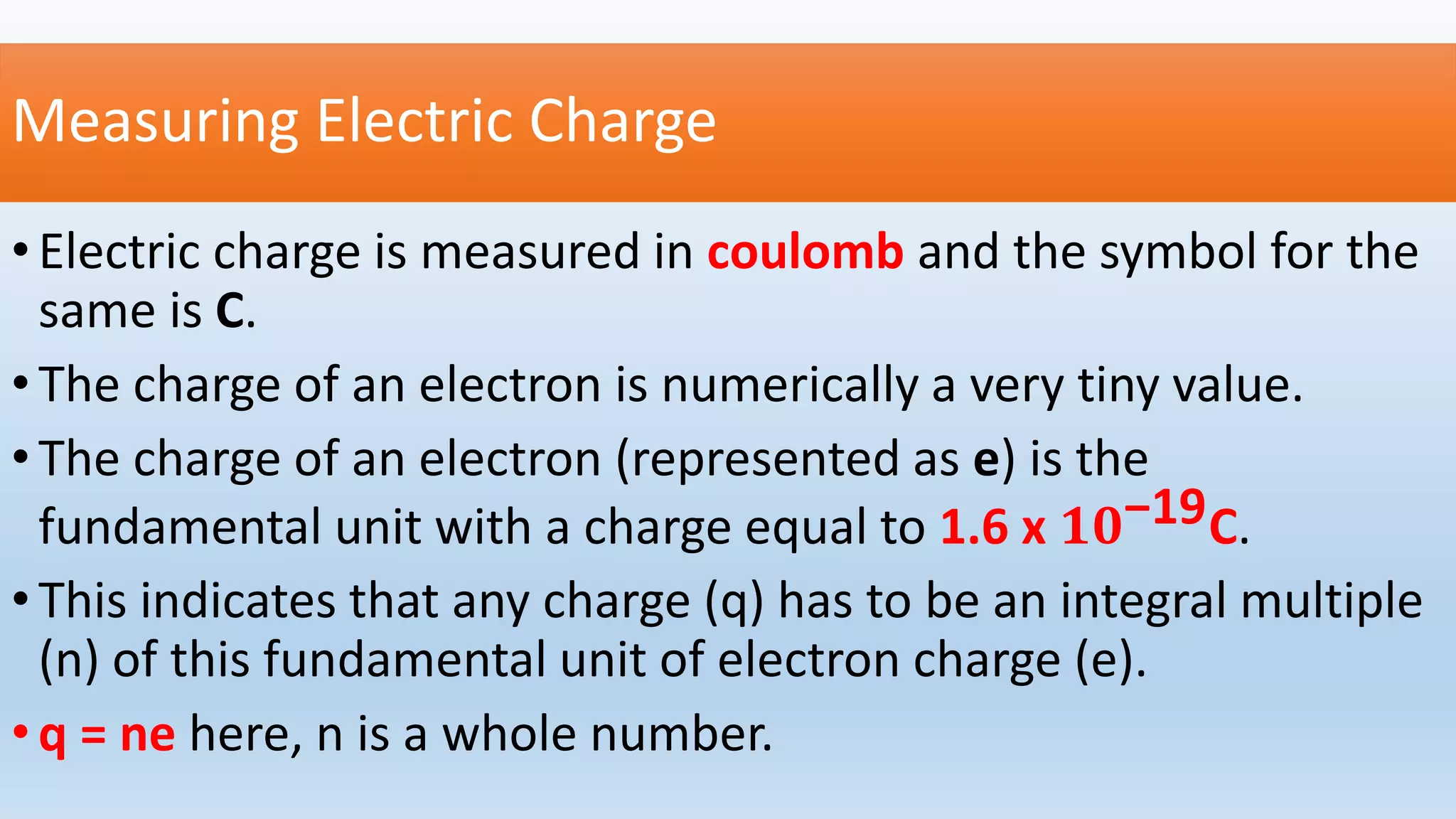
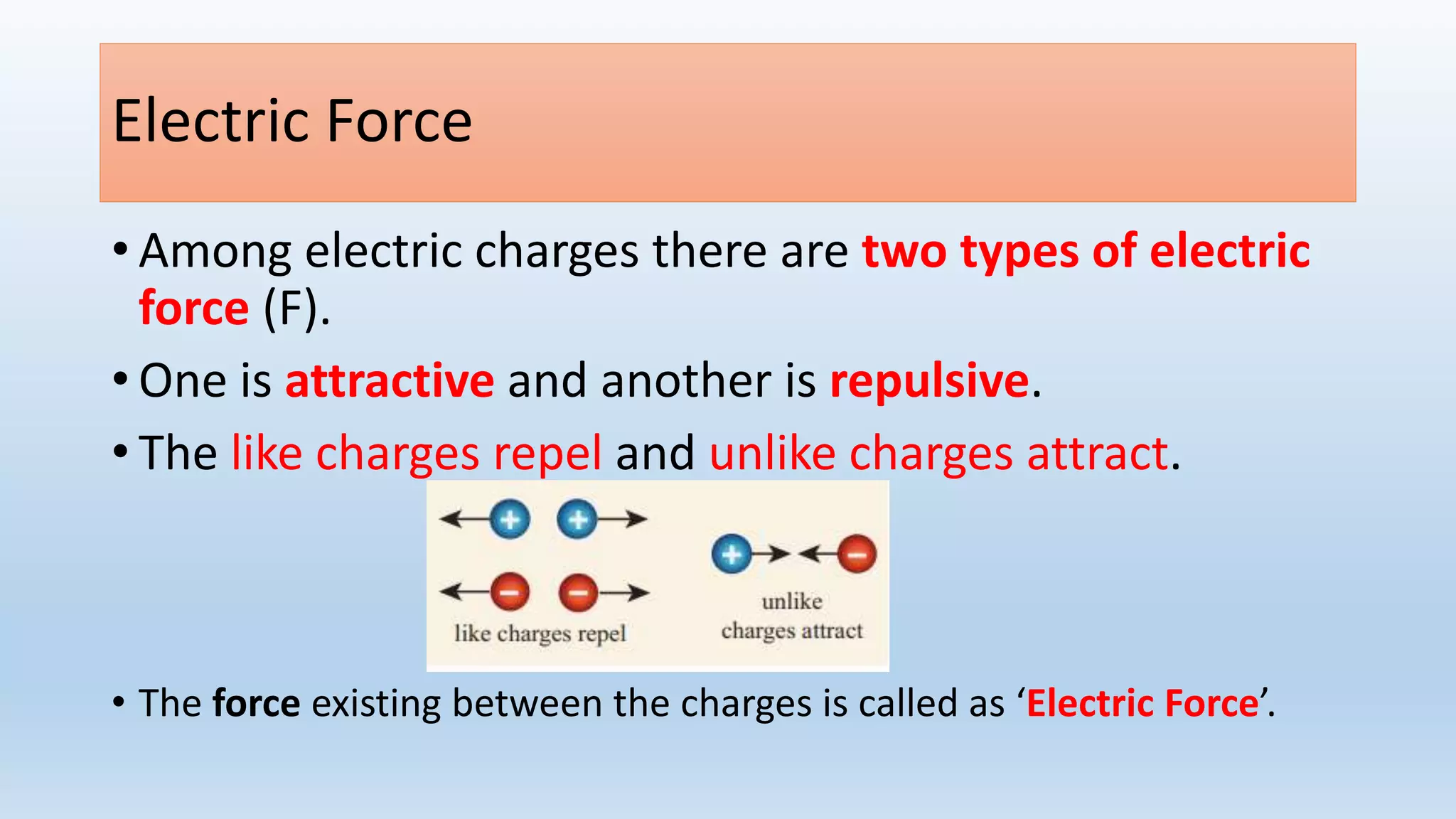
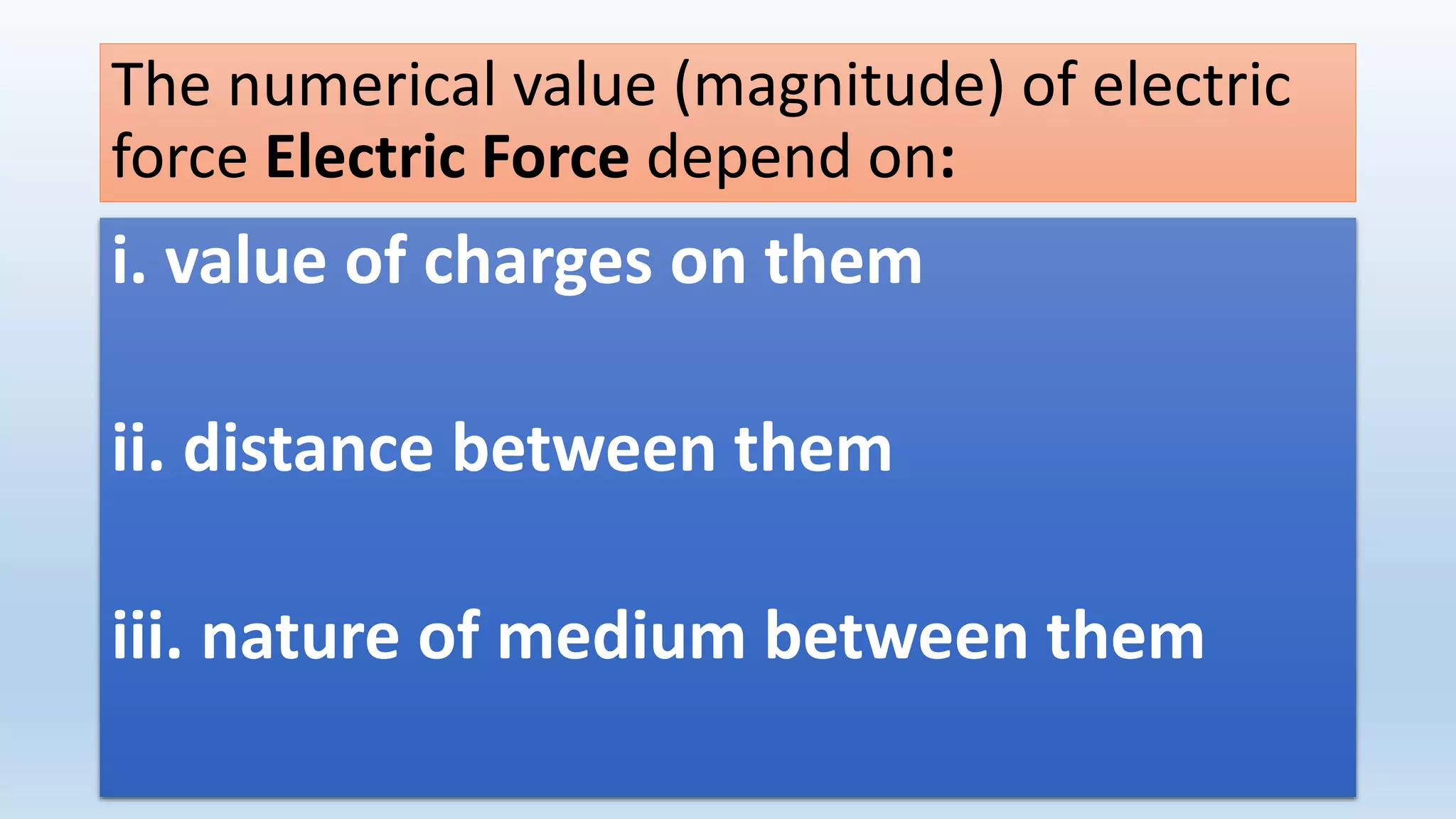
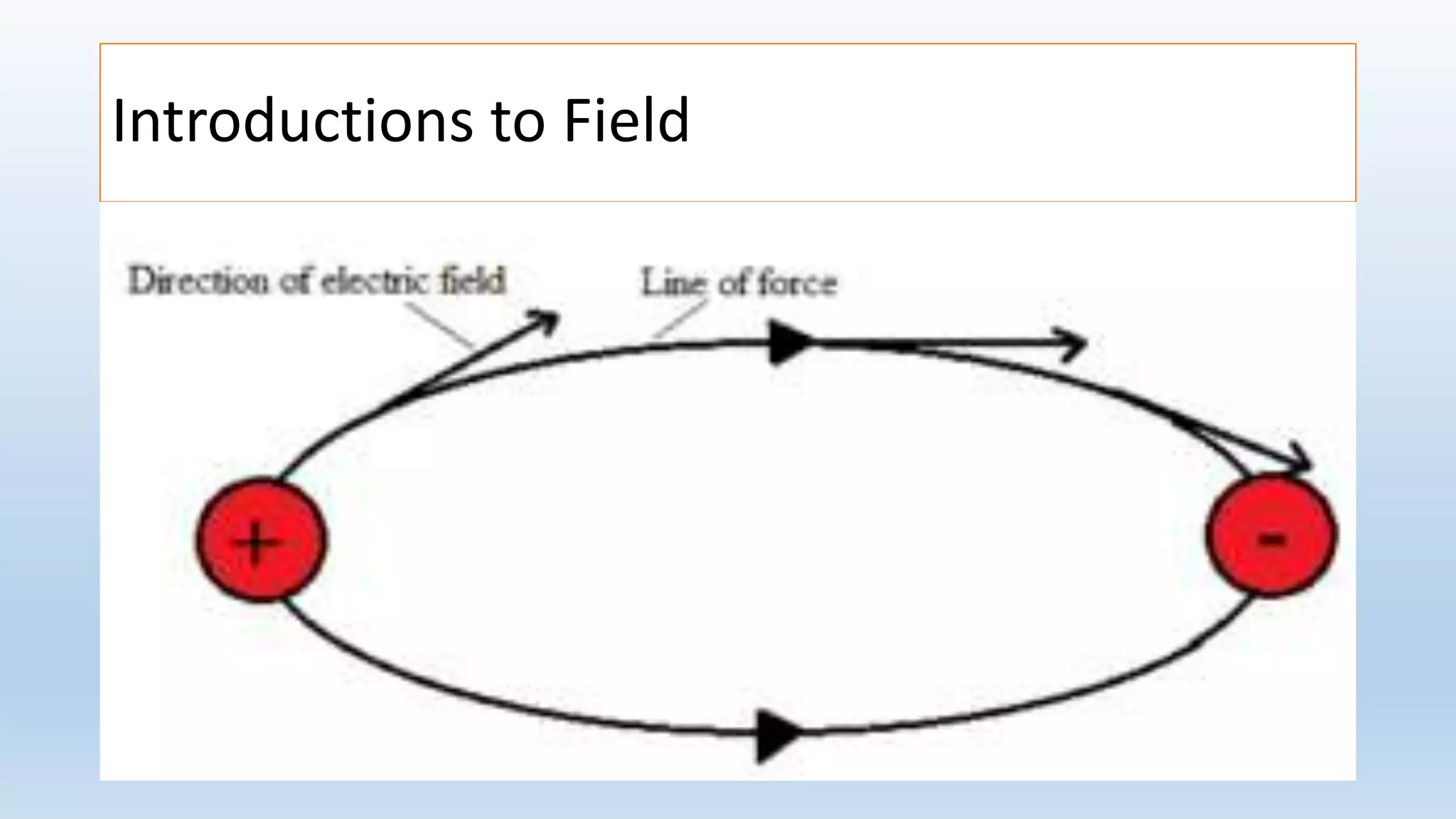
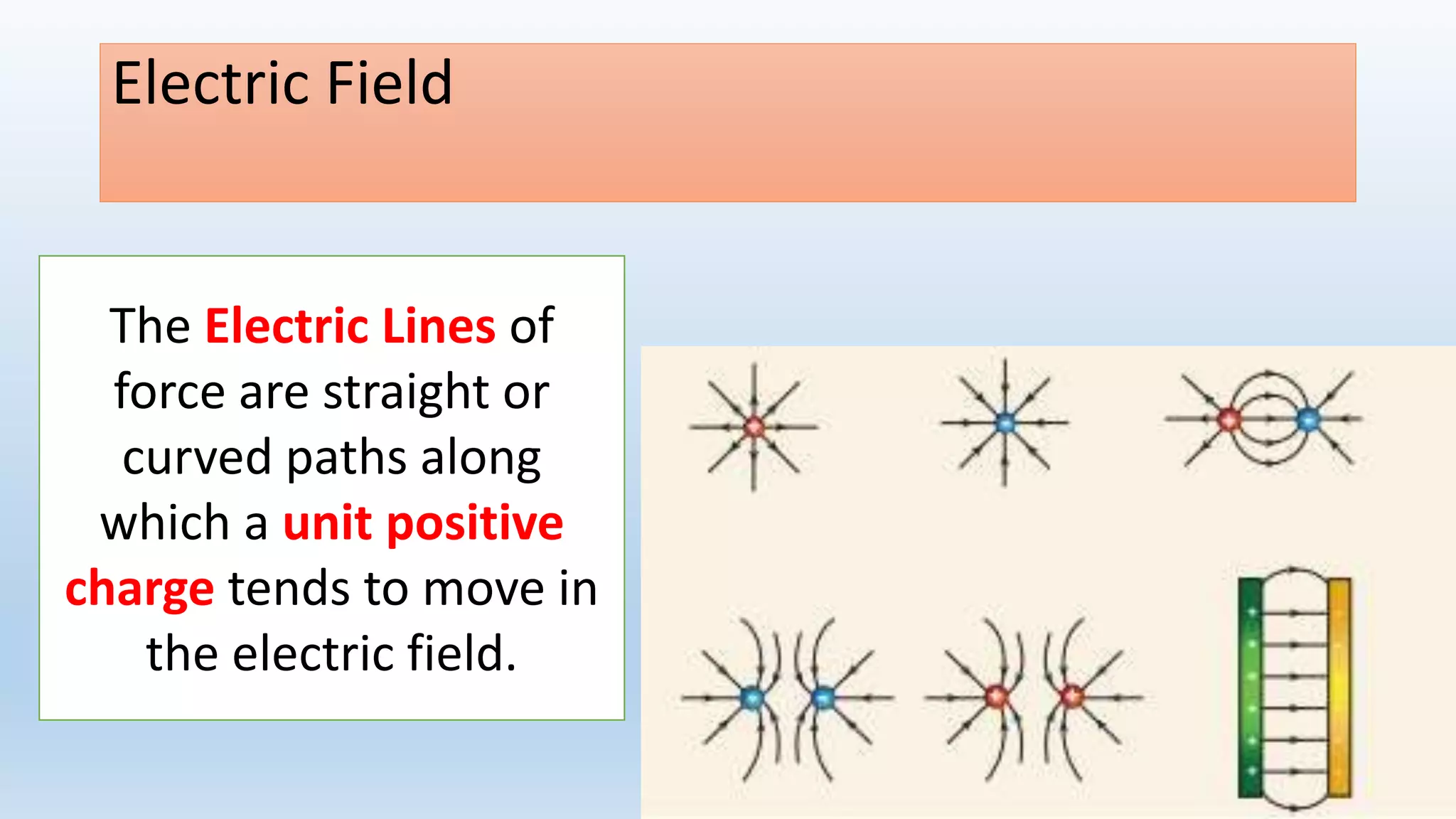
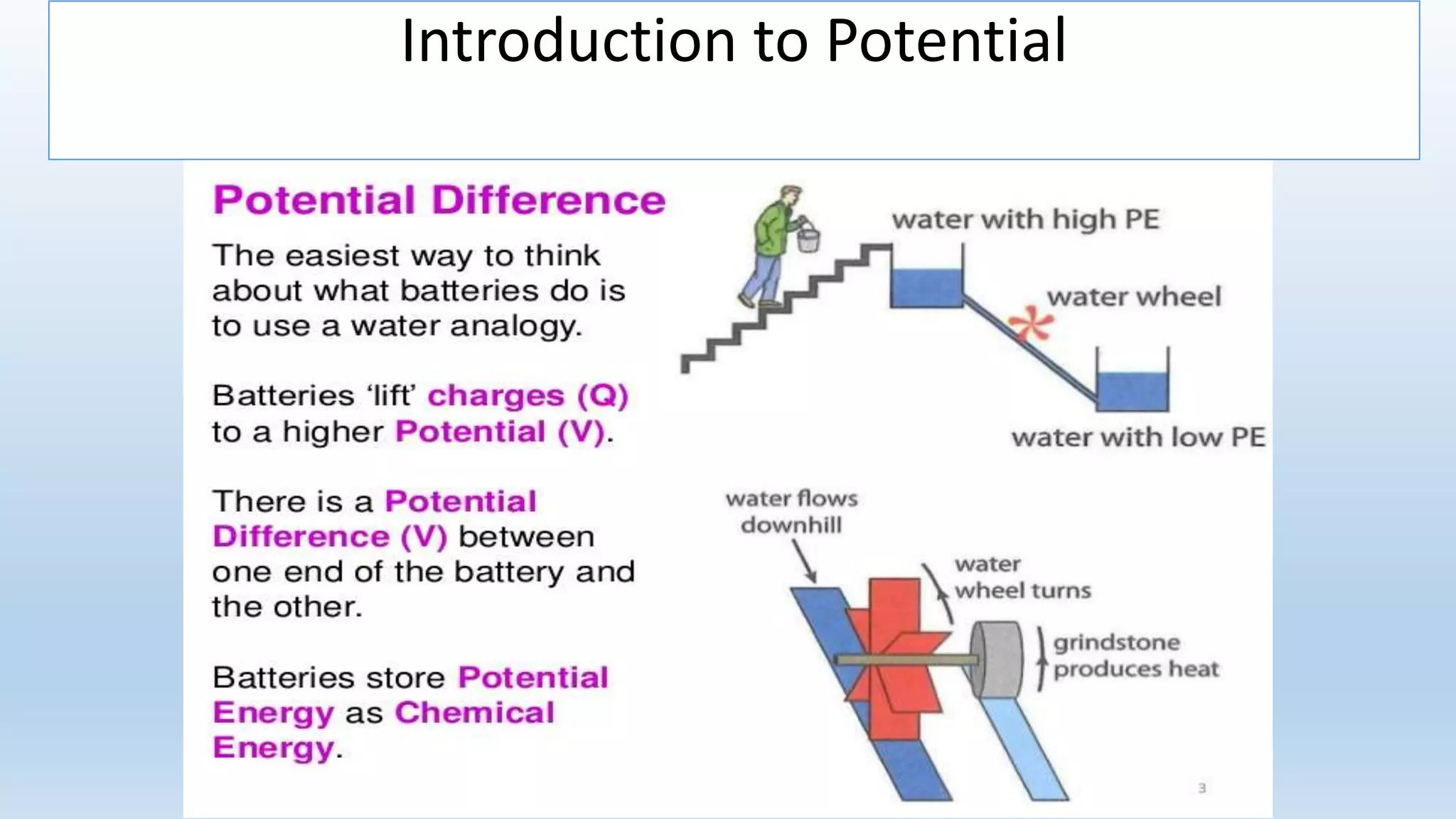
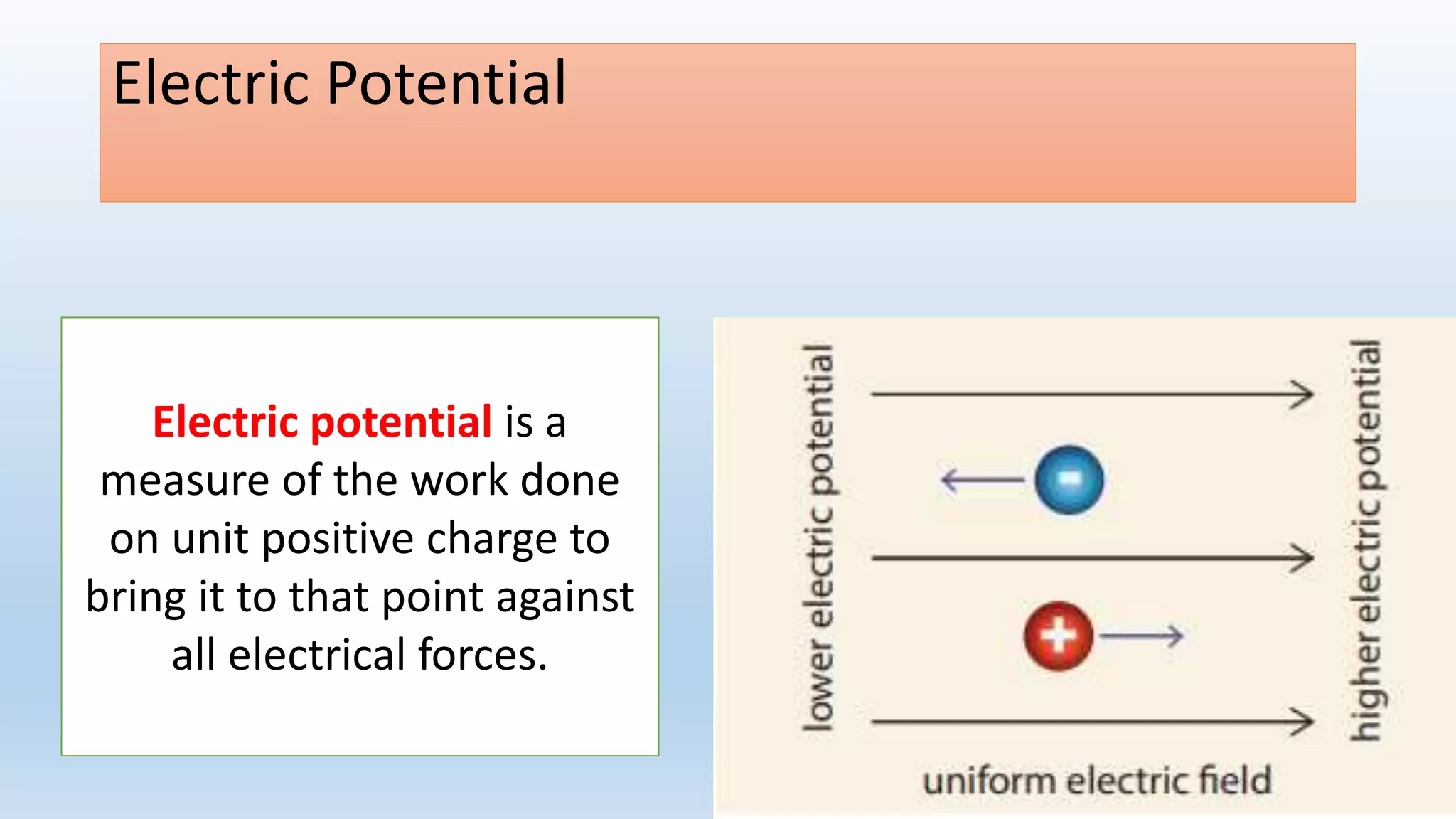
This lesson plan introduces various concepts of electricity including electronic charges, direction of electron flow, measuring electric charge, electric force, electric field, and electric potential. It aims to help students understand that electric charge is a fundamental property of matter, electrons determine whether an object is positively or negatively charged, and charge is measured in coulombs. The lesson will also explain that electric force depends on the charges and distance between them, as well as the medium, and that electric field lines show the direction of force. Finally, it will define electric potential as the work needed to bring a unit positive charge to a point against electric forces.