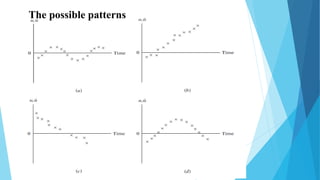
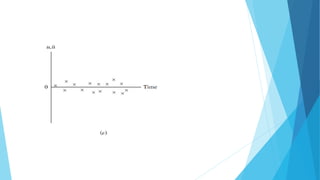
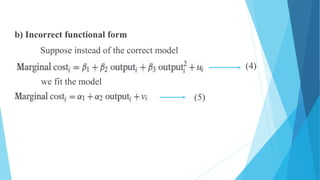
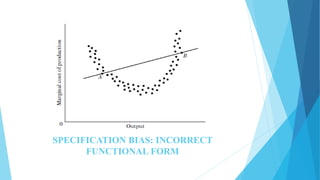
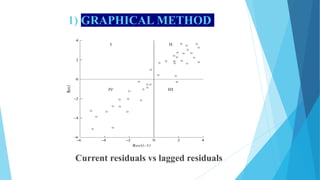
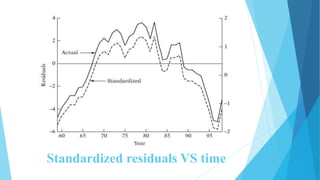
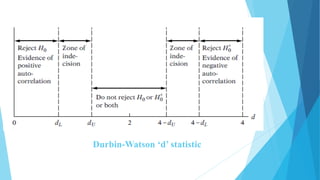
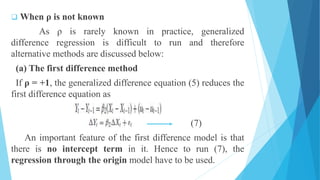
This document discusses autocorrelation in the context of time series regression analysis. It begins by defining autocorrelation as correlation between observations in a time series. When autocorrelation is present, the assumptions of the classical linear regression model are violated. The document then discusses some potential causes of autocorrelation, including omitted variables, incorrect functional form, and exclusion of lagged variables. It proceeds to describe several tests to detect autocorrelation, including graphical tests, the runs test, Durbin-Watson test, and Breusch-Godfrey test. The document concludes by outlining some remedial measures that can be taken if autocorrelation is present, such as generalized least squares and first differencing transformations.

![AUTOCORRELATION
The term autocorrelation may be defined as “correlation
between members of series of observations ordered in time [as
in time series data]”.
In the regression context, the classical linear regression model
assumes that such autocorrelation does not exist in the
disturbances ui. Symbolically,
E(ui, uj ) = 0, i ≠ j (or)
Cov(ui, uj / xi, xj) = 0, means the disturbance ui and uj are
uncorrelated.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/autocorrelation-231030151706-f4e8f398/85/autocorrelation-pptx-2-320.jpg)