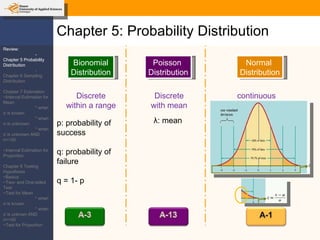
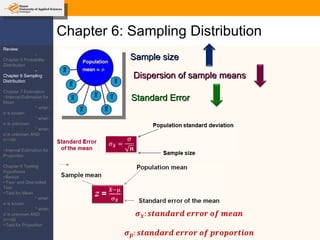
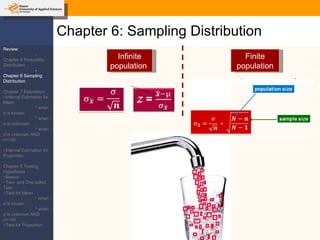
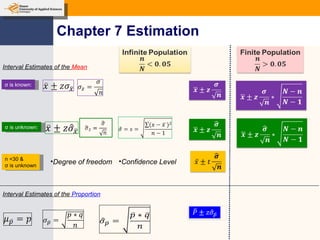
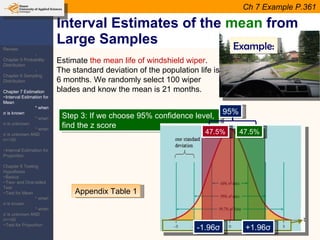
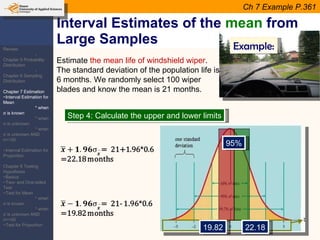
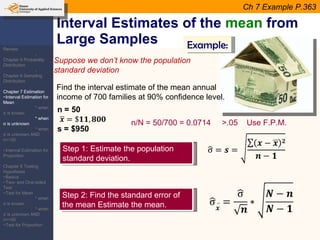
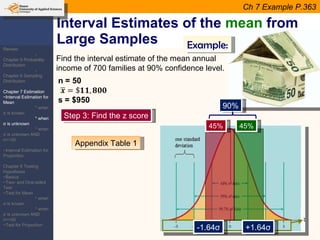
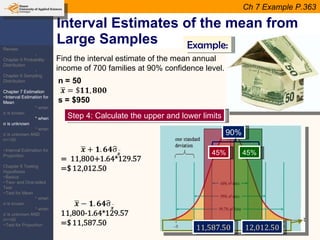
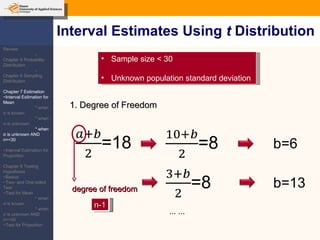
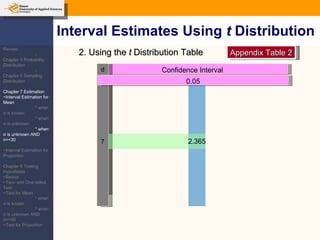
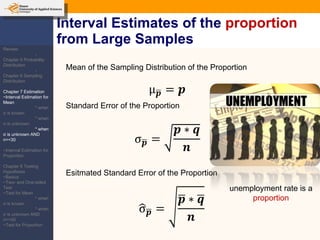
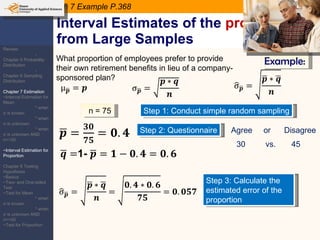
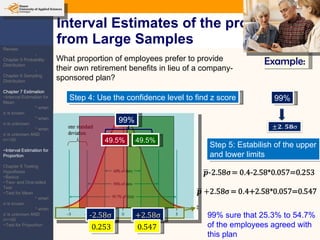
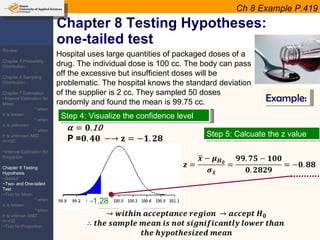
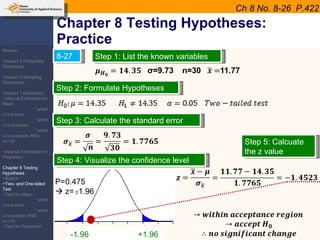
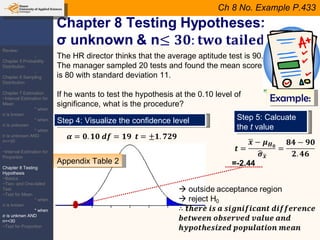
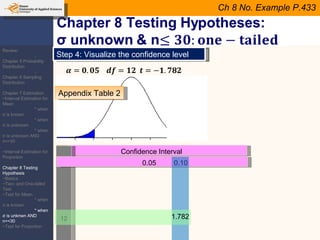
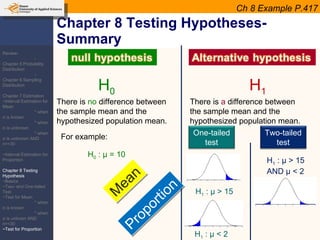
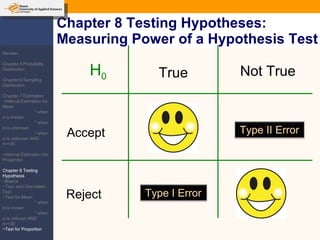
This document provides an outline and overview of topics covered in a course on inductive statistics, including probability distributions, sampling distributions, estimation, and hypothesis testing. Key topics discussed include interval estimation for means and proportions, using t-distributions when sample sizes are small and variances are unknown, and the basics of hypothesis testing such as null and alternative hypotheses. Examples are provided to illustrate concepts like confidence intervals for means, proportions, and hypothesis testing.
![Inductive Statistics Dr. Ning DING [email_address] I.007 IBS, Hanze You’d better use the full-screen mode to view this PPT file.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lesson04chapter7estimation-111009140027-phpapp02/85/Lesson-04-chapter-7-estimation-1-320.jpg)