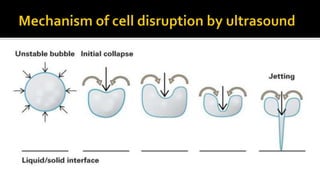
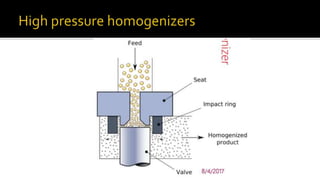
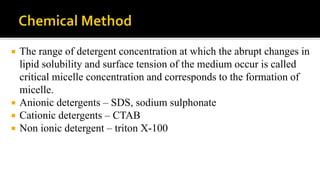
Cell disruption is a process used to break open cell walls to extract intracellular fluid and components. The goal is to break open the cells without damaging intracellular components. Various mechanical and non-mechanical methods can be used depending on the cell type, desired product, and scale of operation. Common mechanical methods include bead mills, ultrasonication, and French presses. Non-mechanical options include heat, osmotic shock, chemicals, and enzymes. Process parameters like temperature, pressure, and number of passes must be optimized for maximum disruption and minimal product damage.