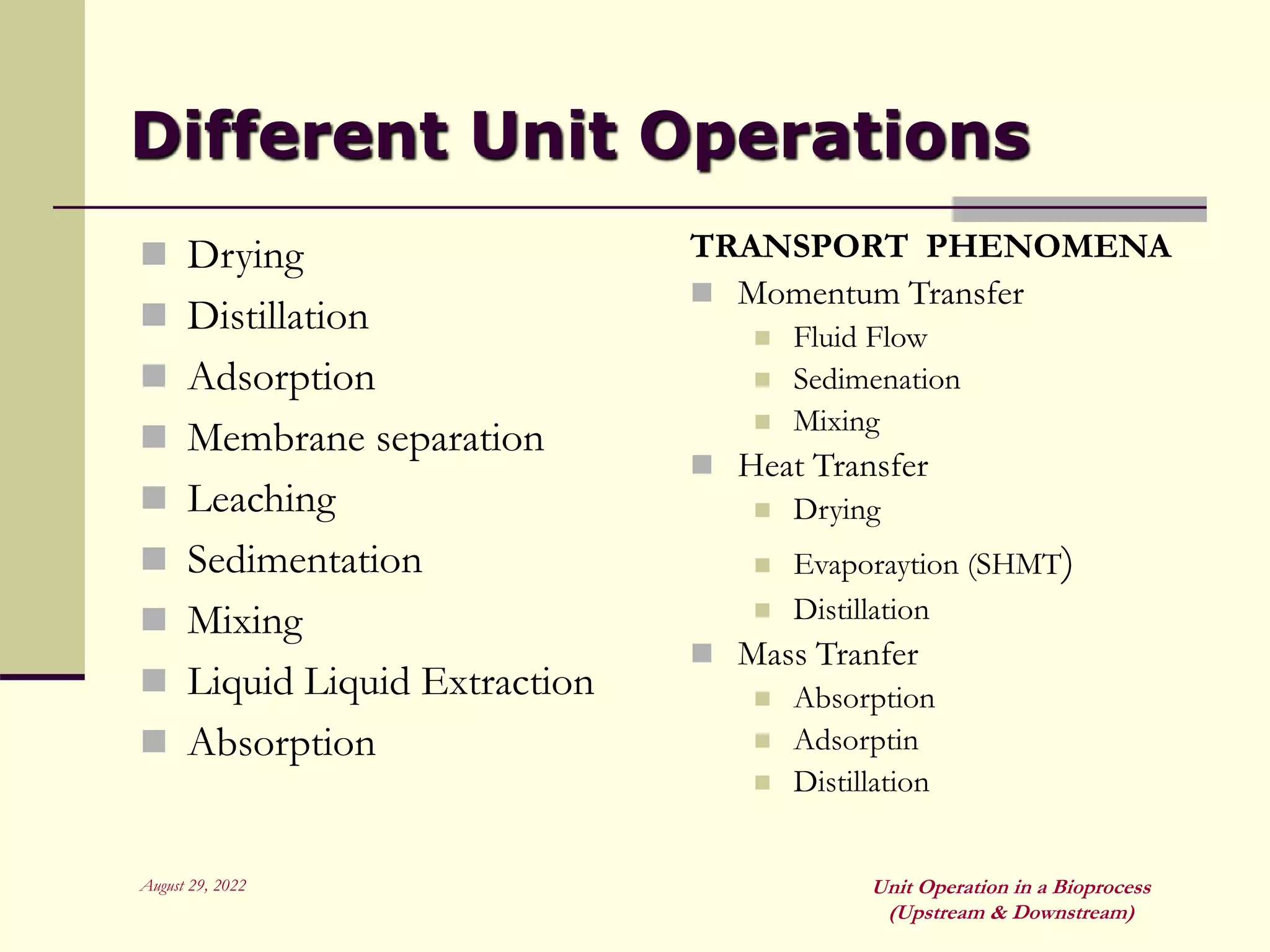
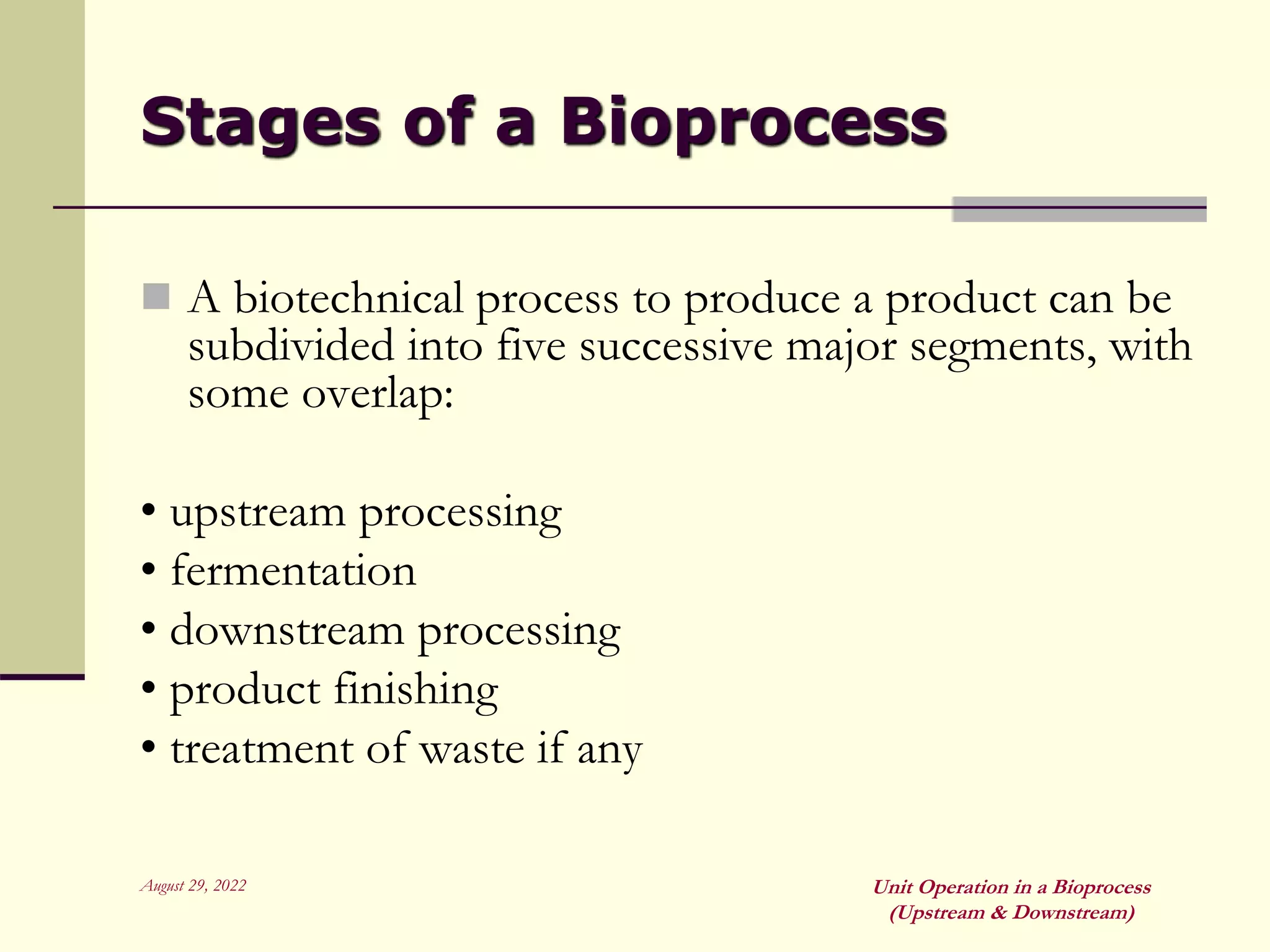
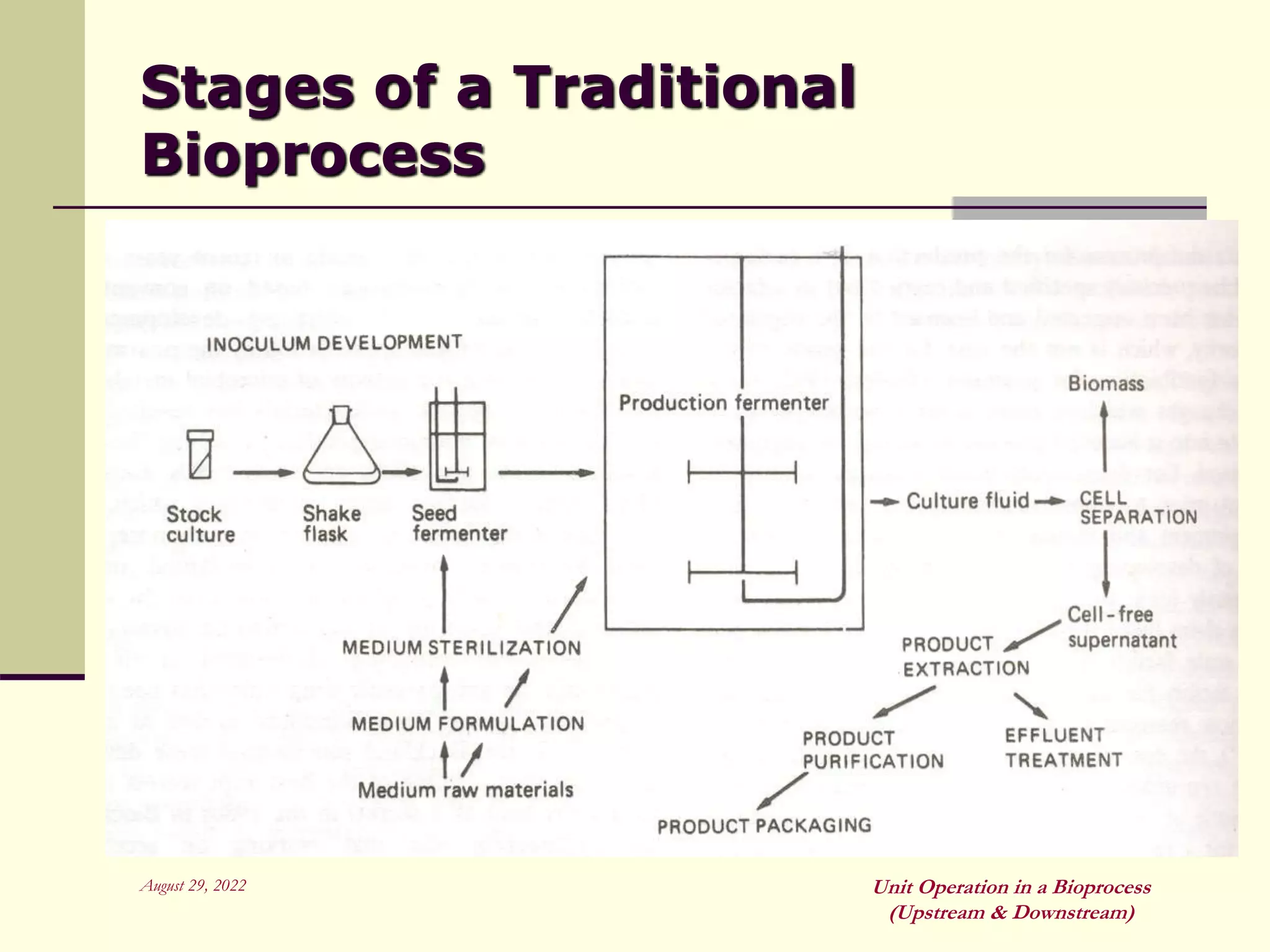
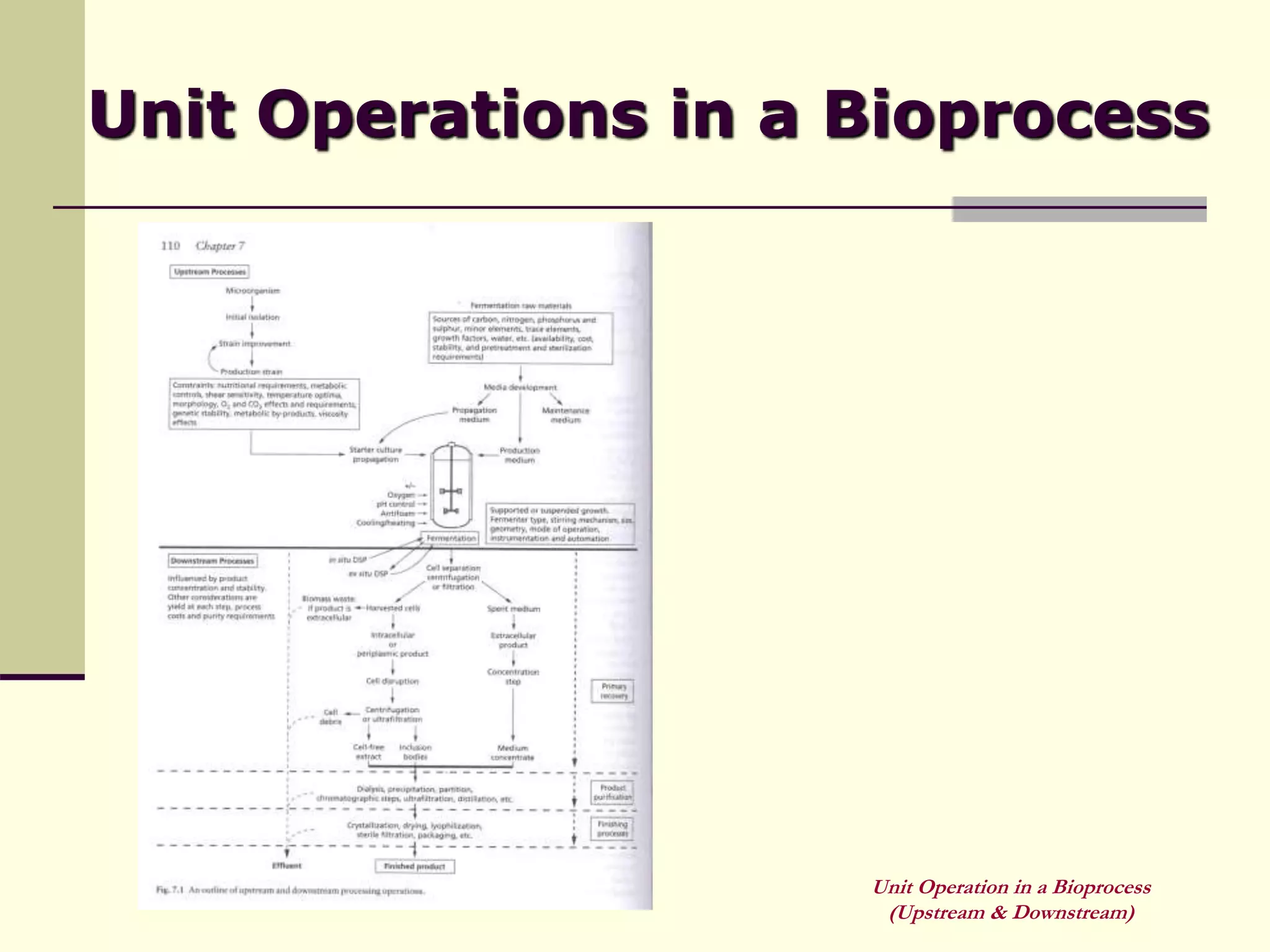
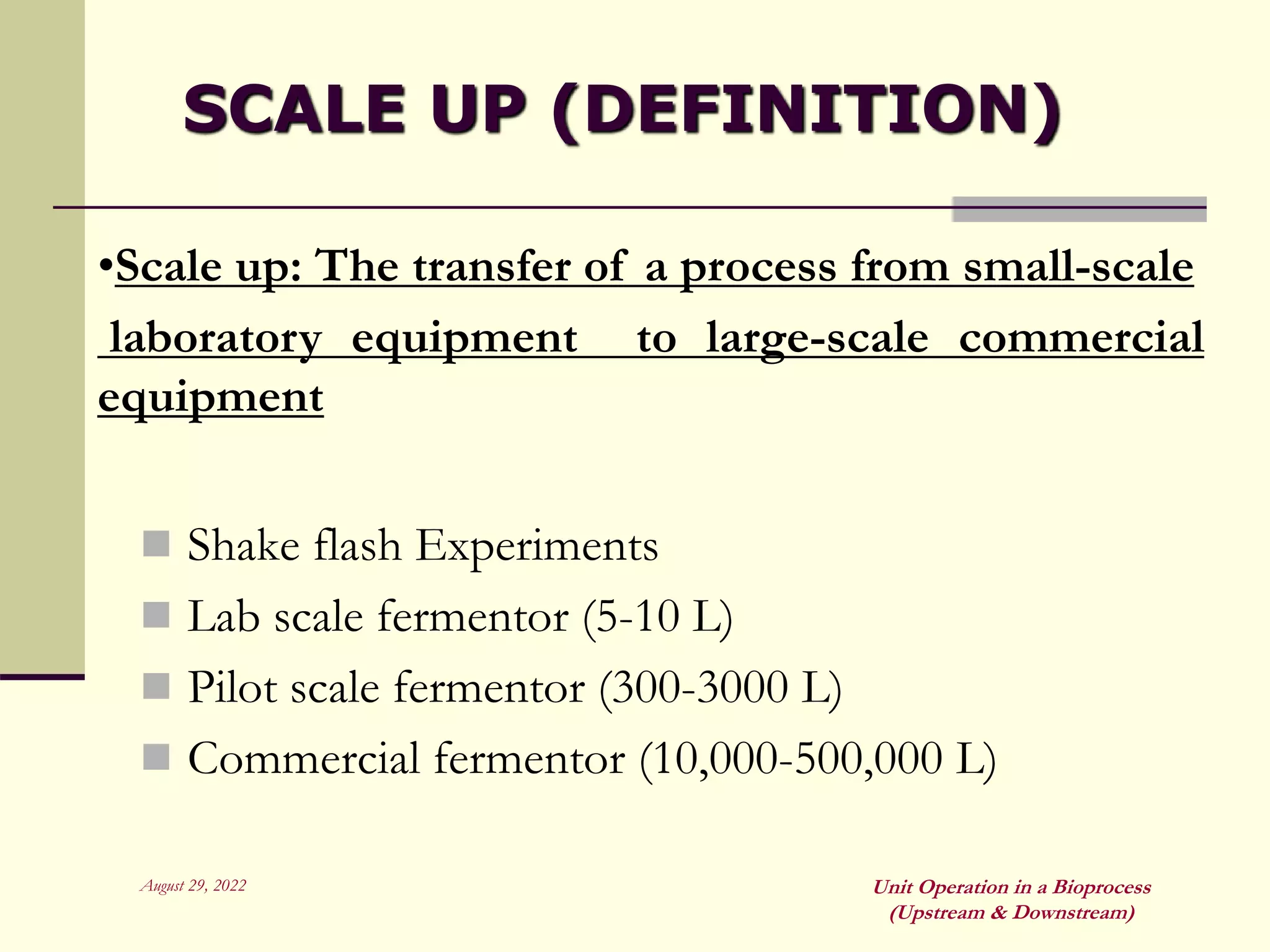
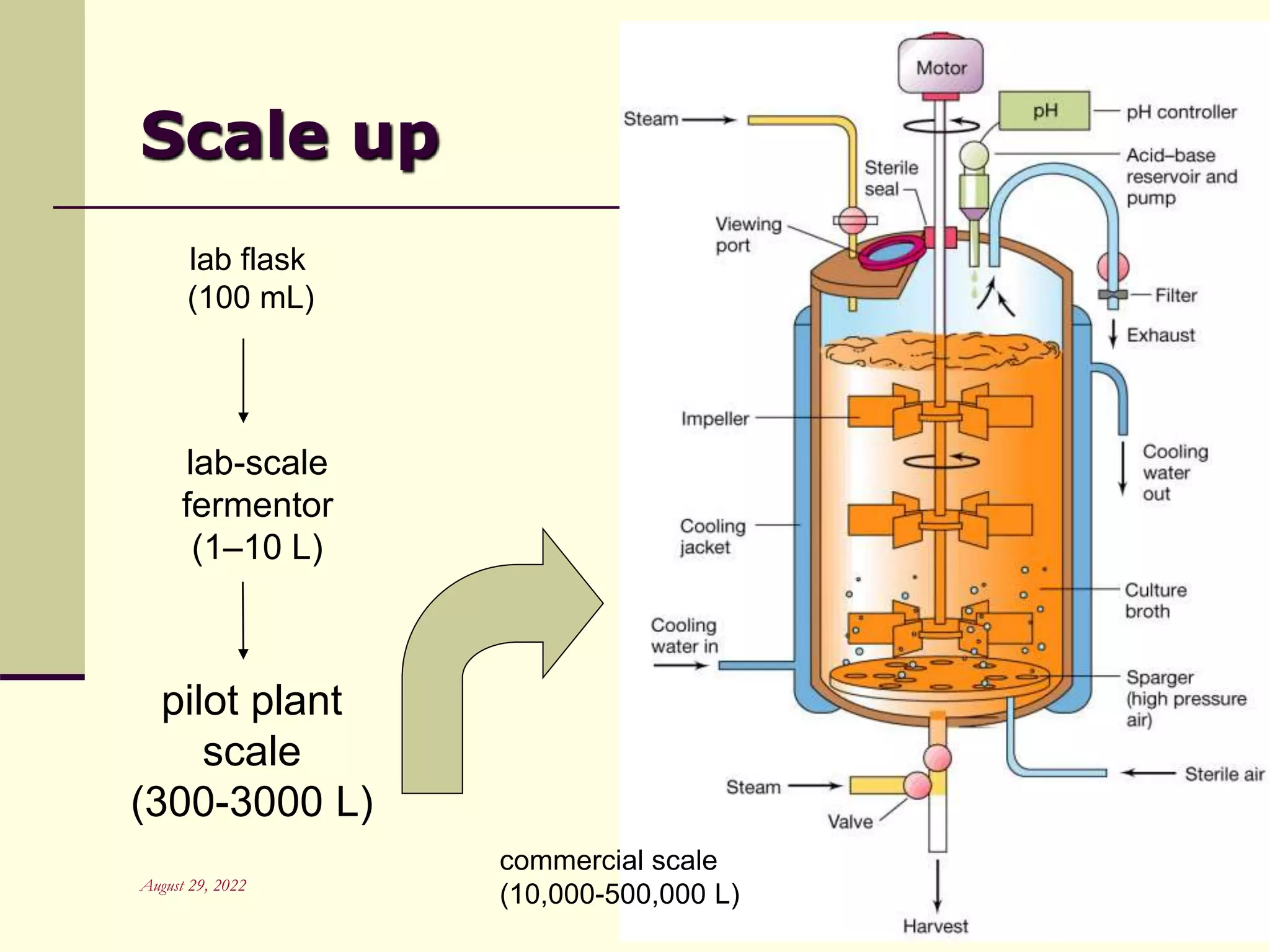
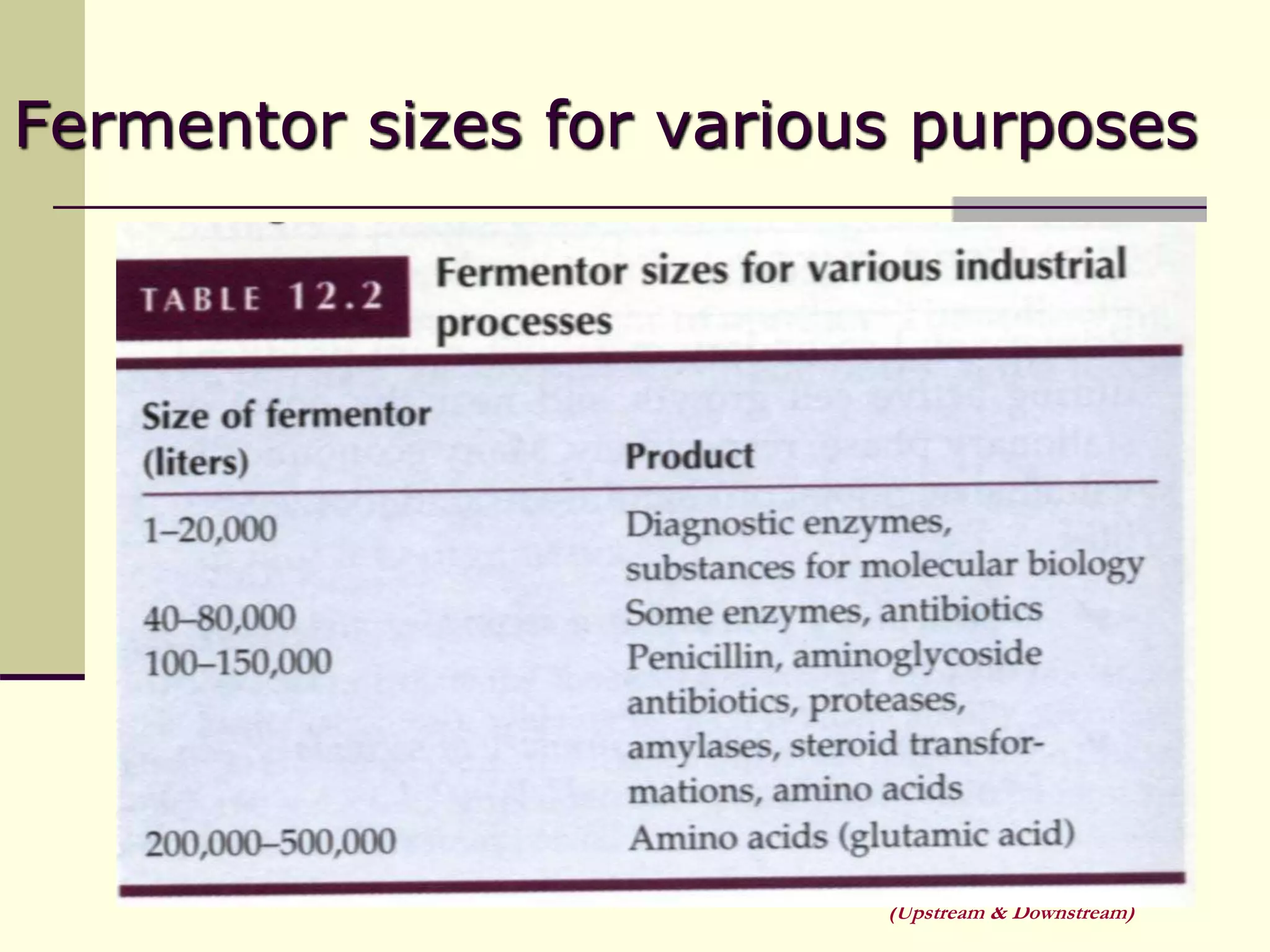
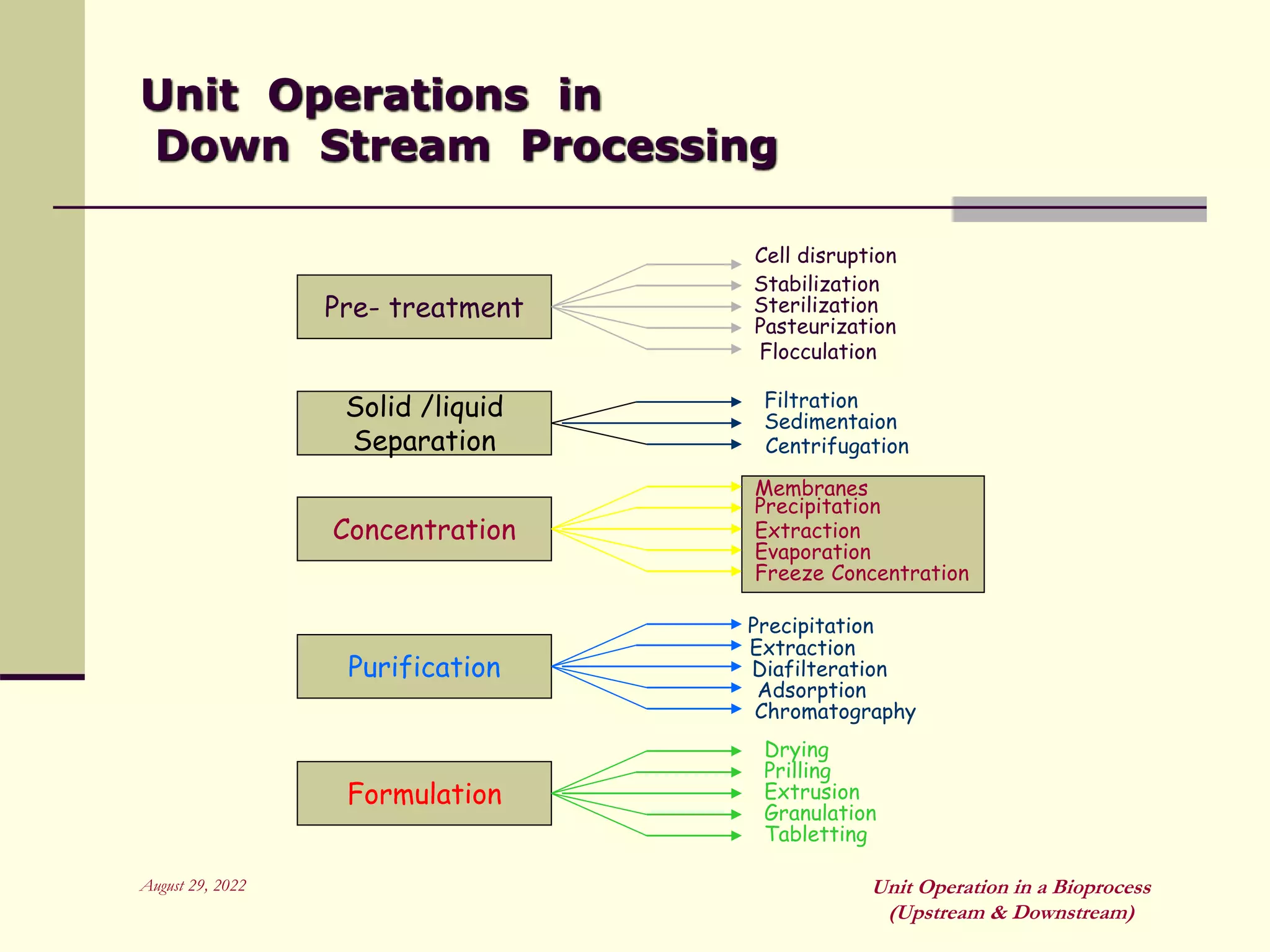
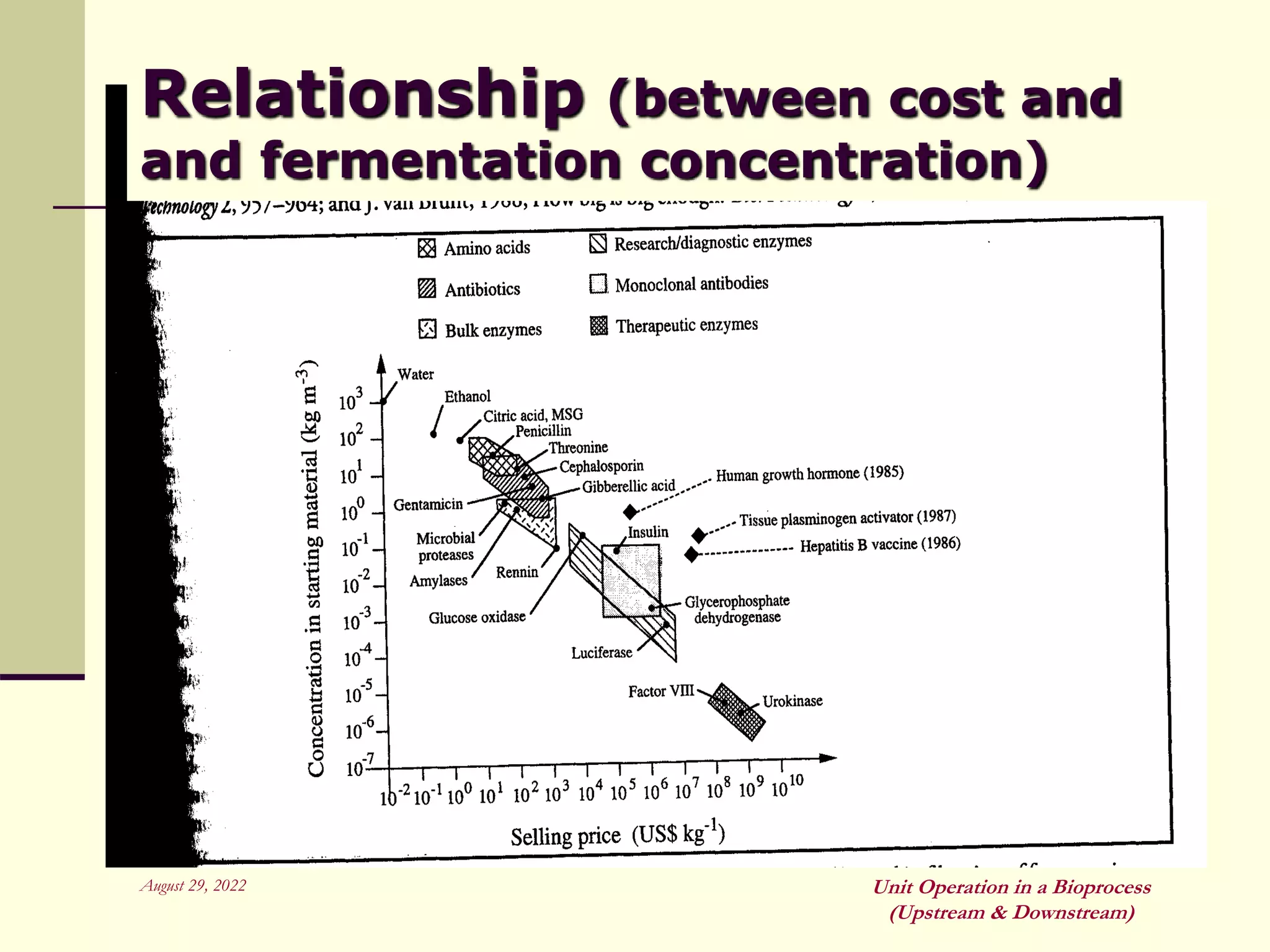
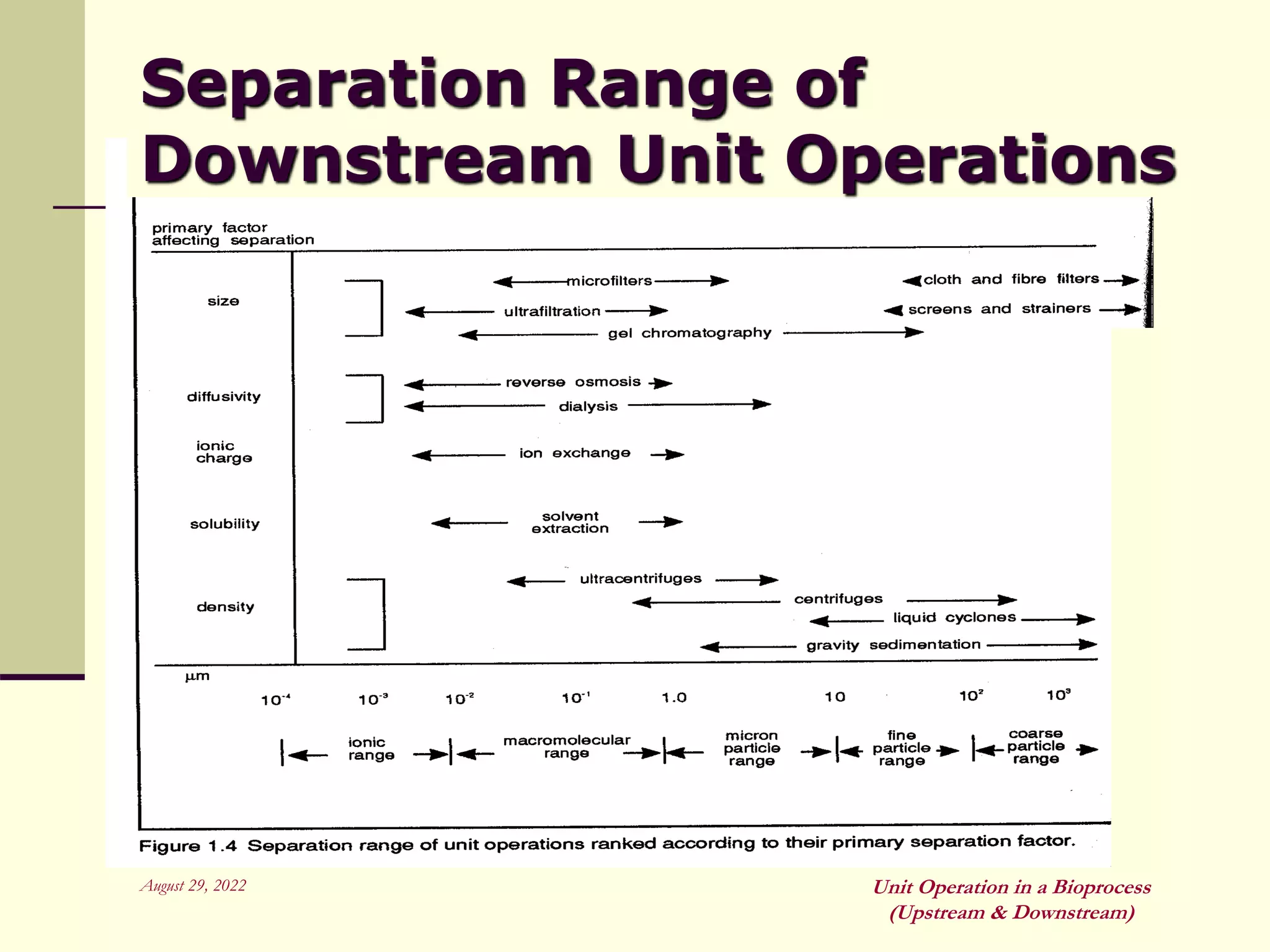
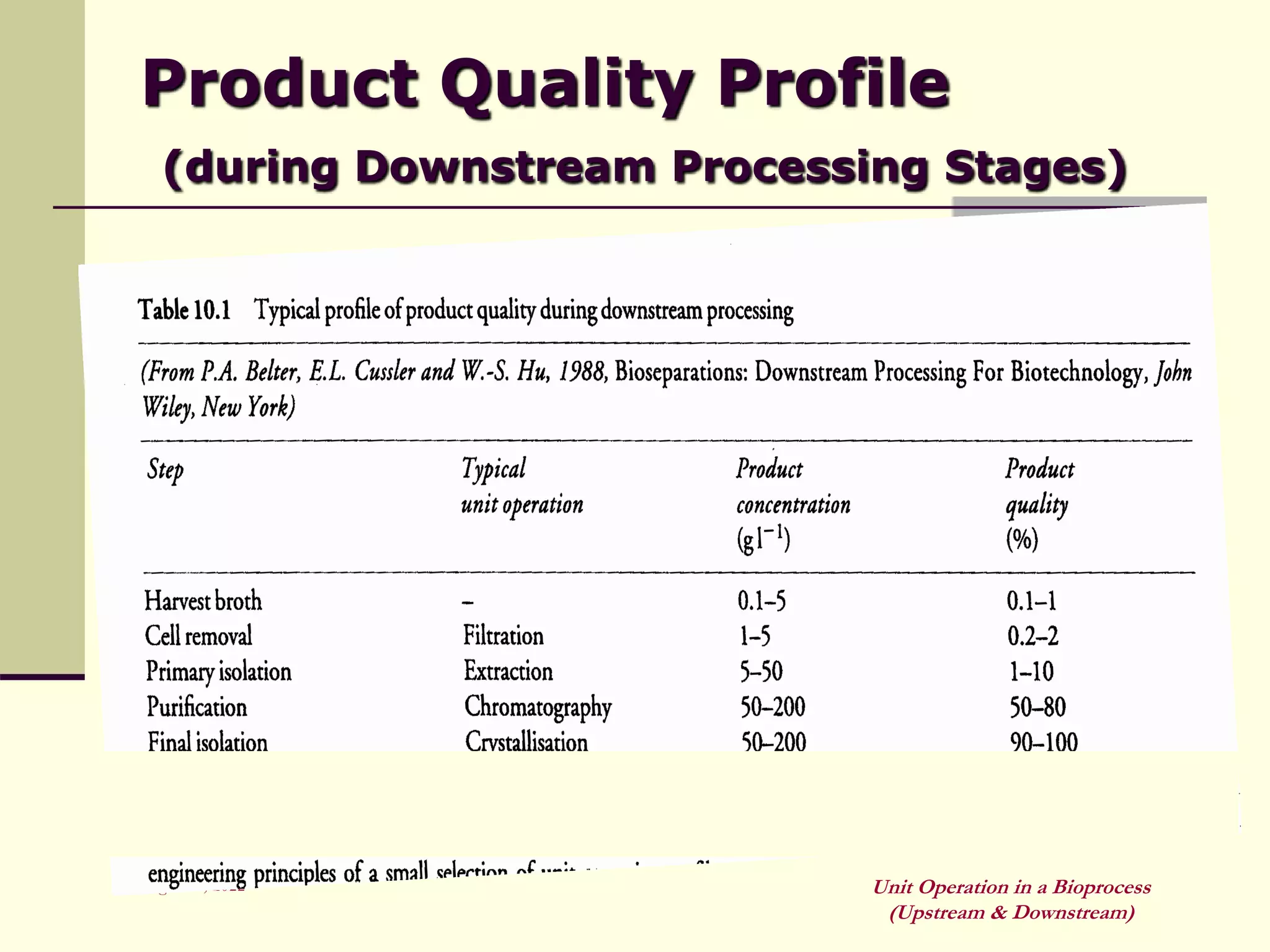
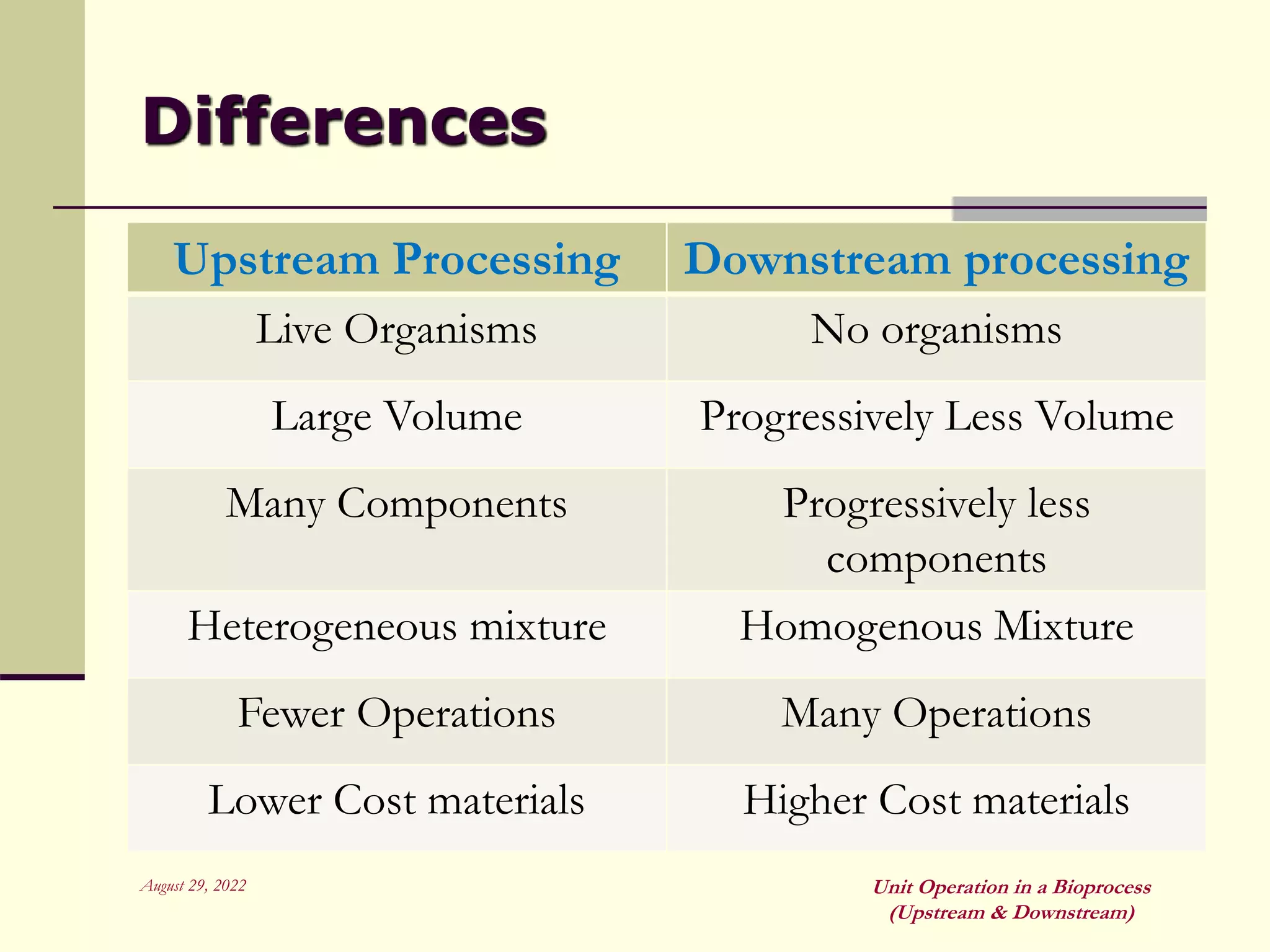
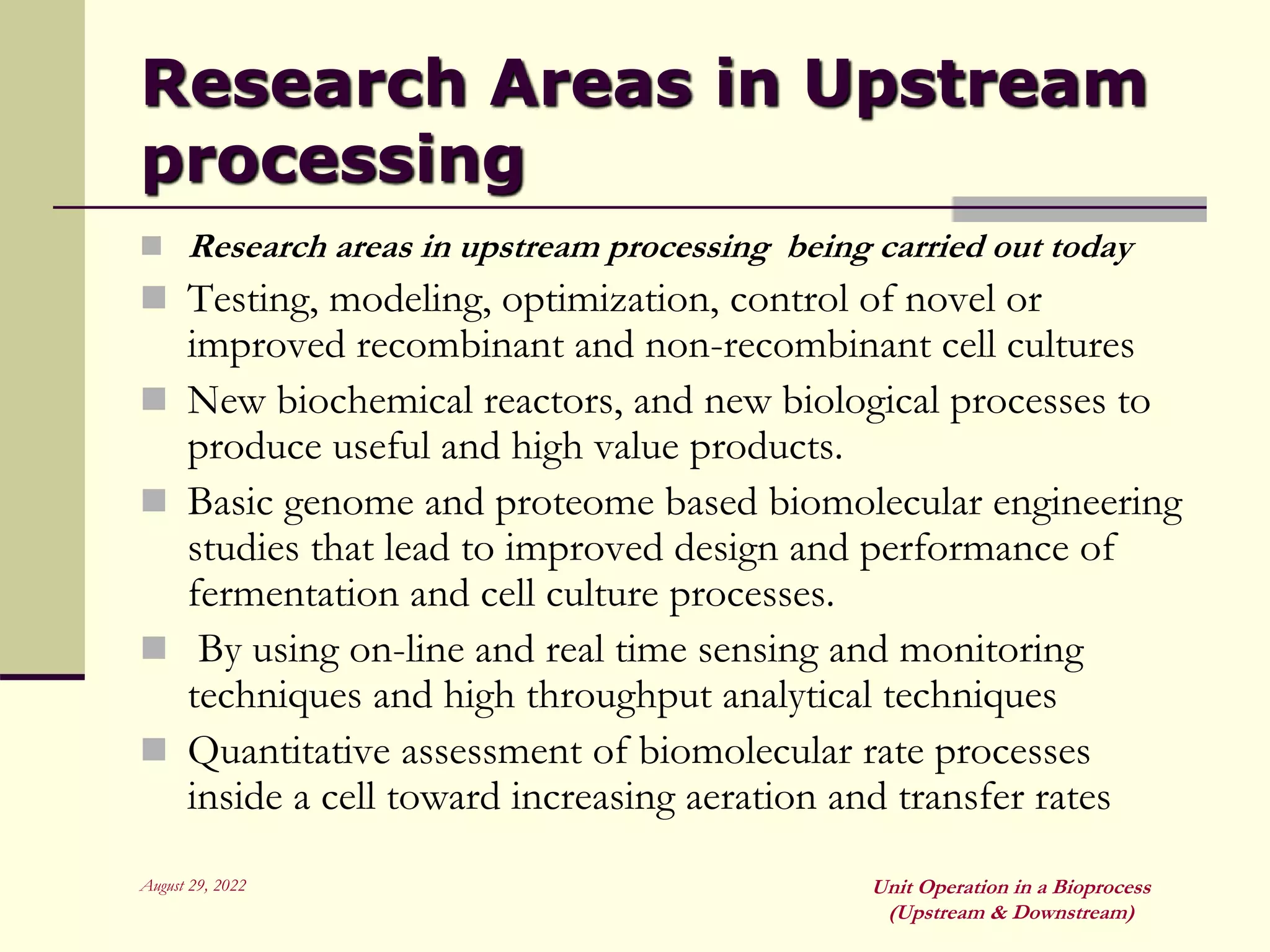
Unit operations are fundamental steps that make up chemical and bioprocess industries. They involve simple operations like mixing, separation, and heat and mass transfer that can be used across different manufacturing processes. In bioprocesses, upstream processing involves growing cells and preparing media, fermentation is the production stage, and downstream processing separates and purifies the desired product from the fermentation broth using multiple unit operations like filtration, centrifugation, and chromatography. Research aims to improve cell cultures, reactors, monitoring techniques, and downstream purification methods.