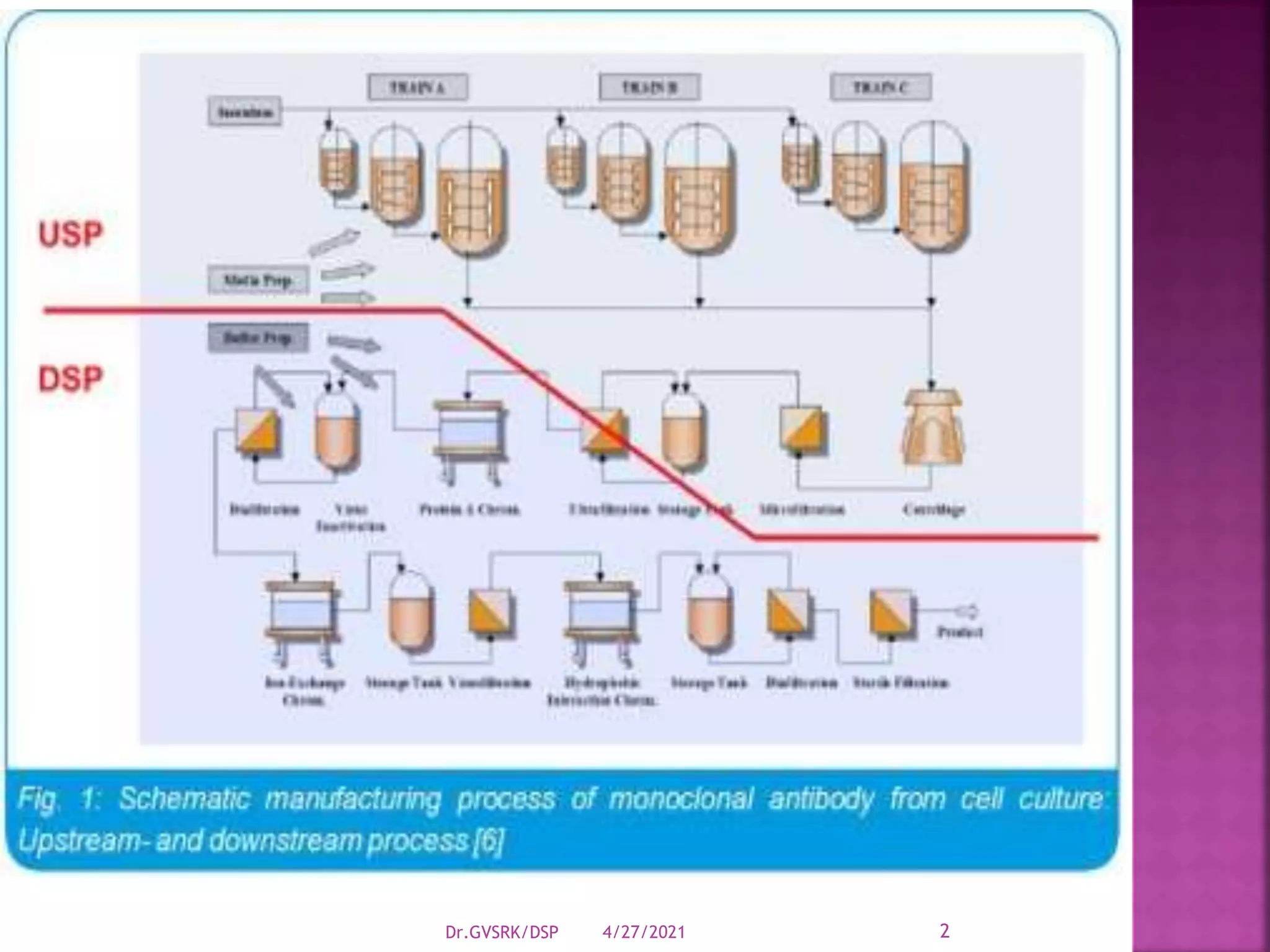
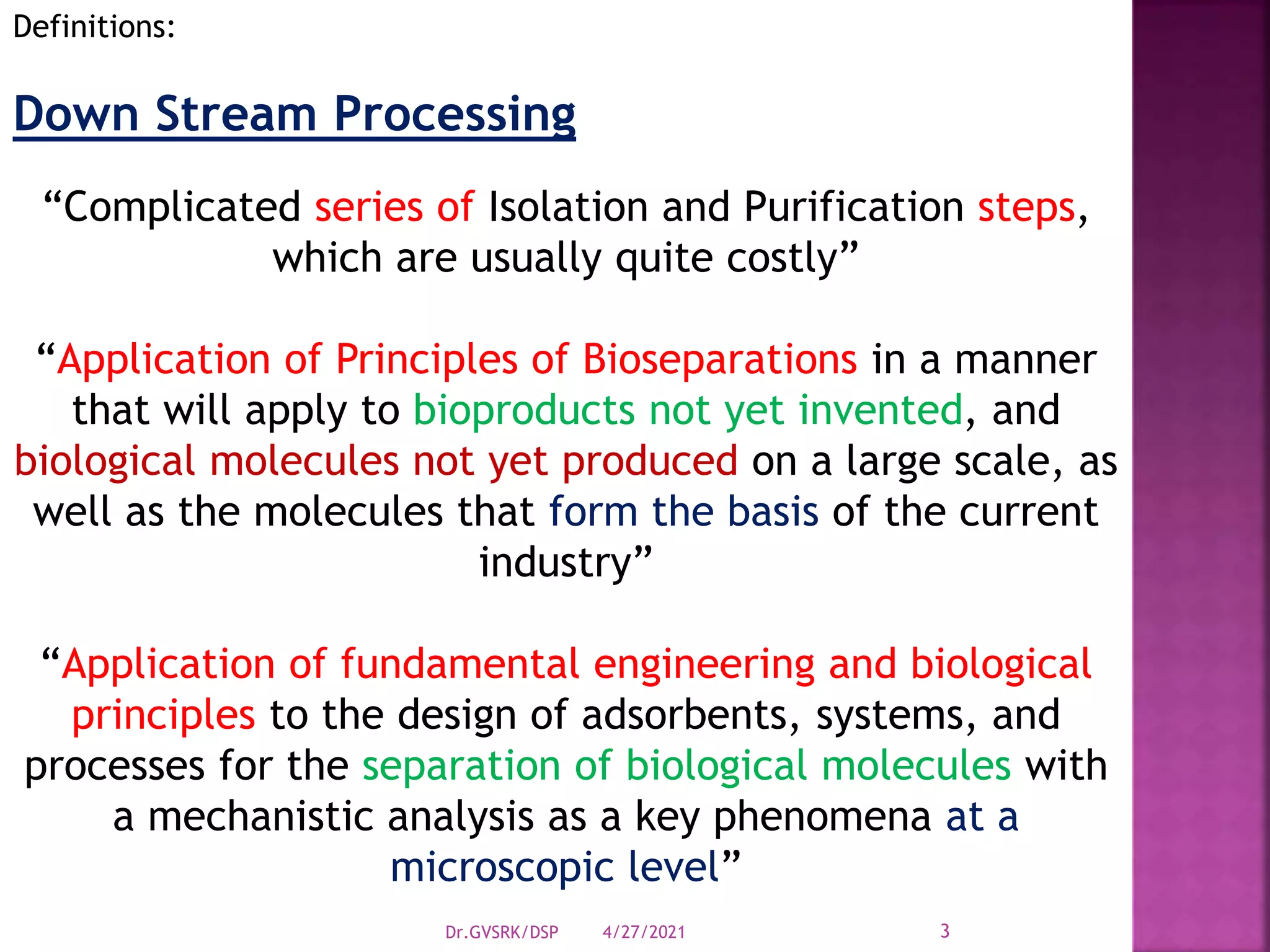
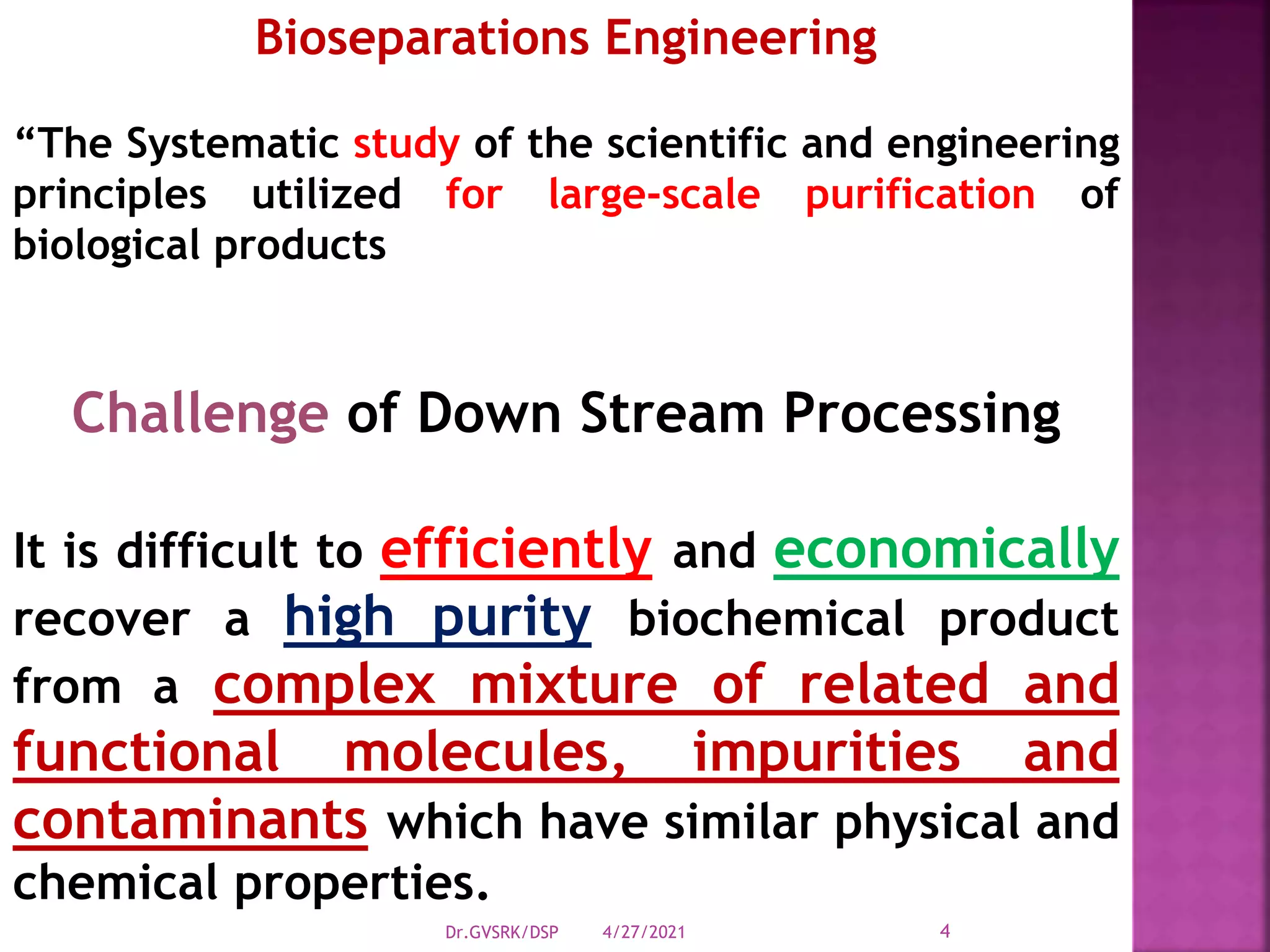
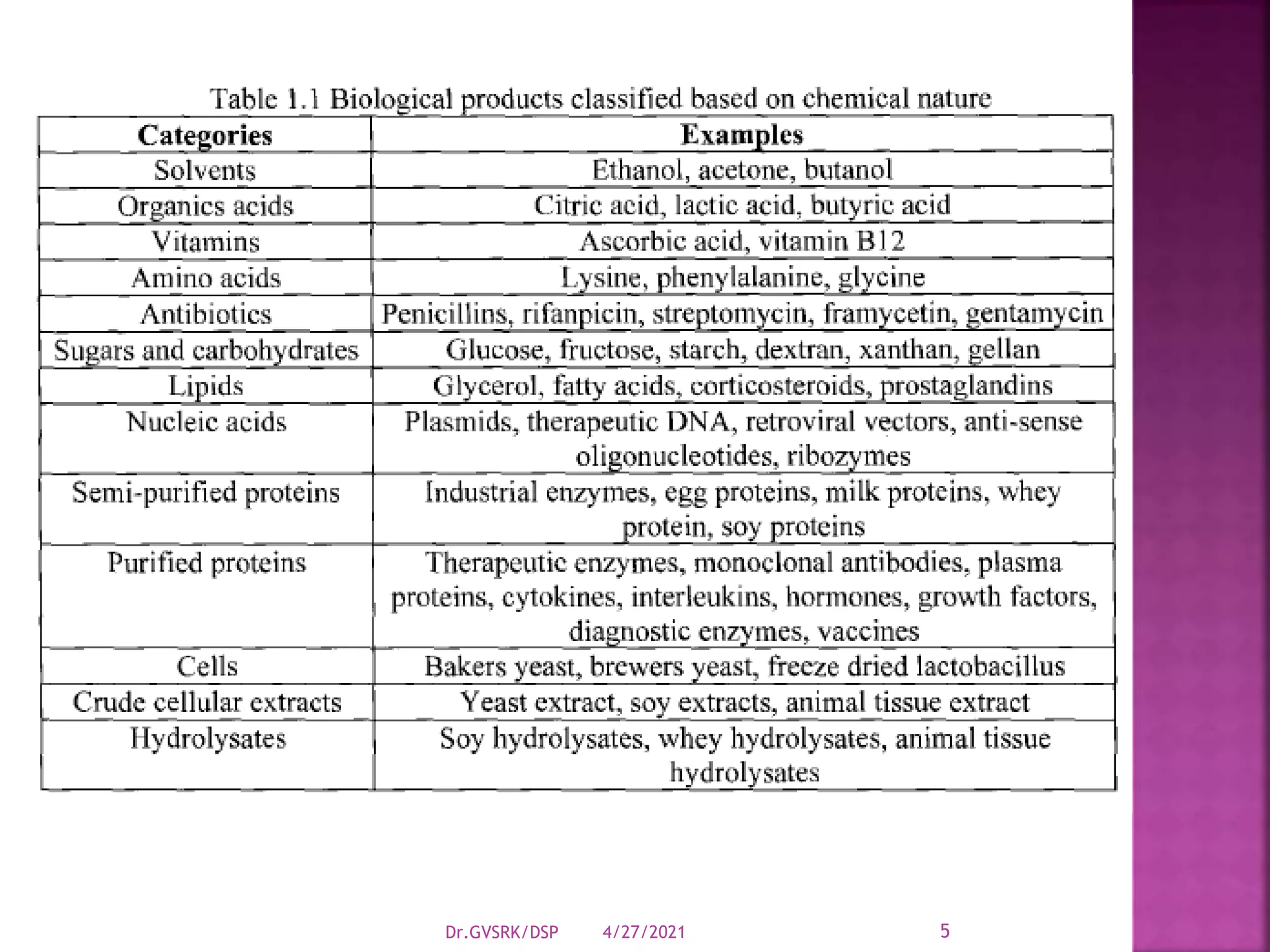
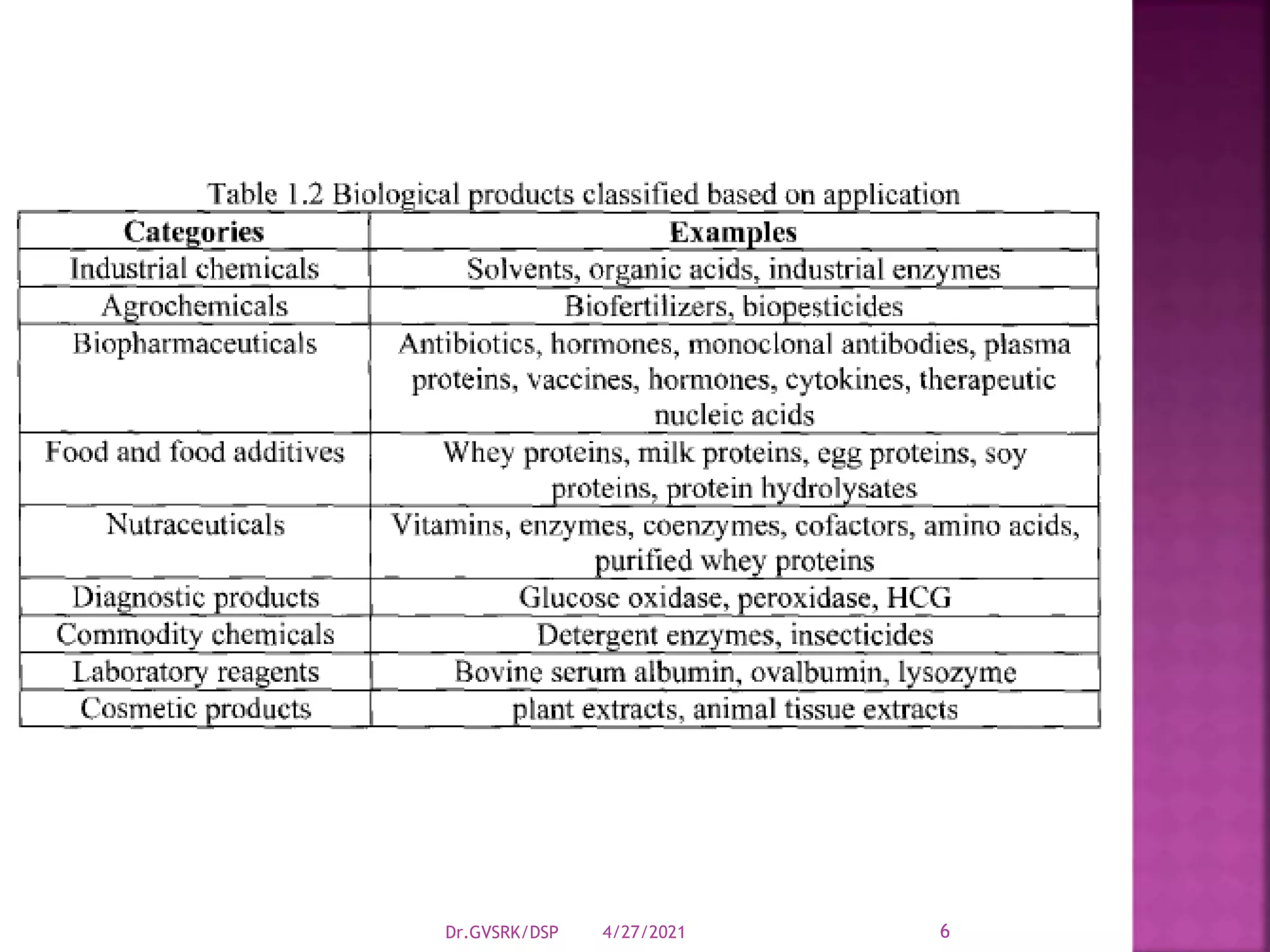
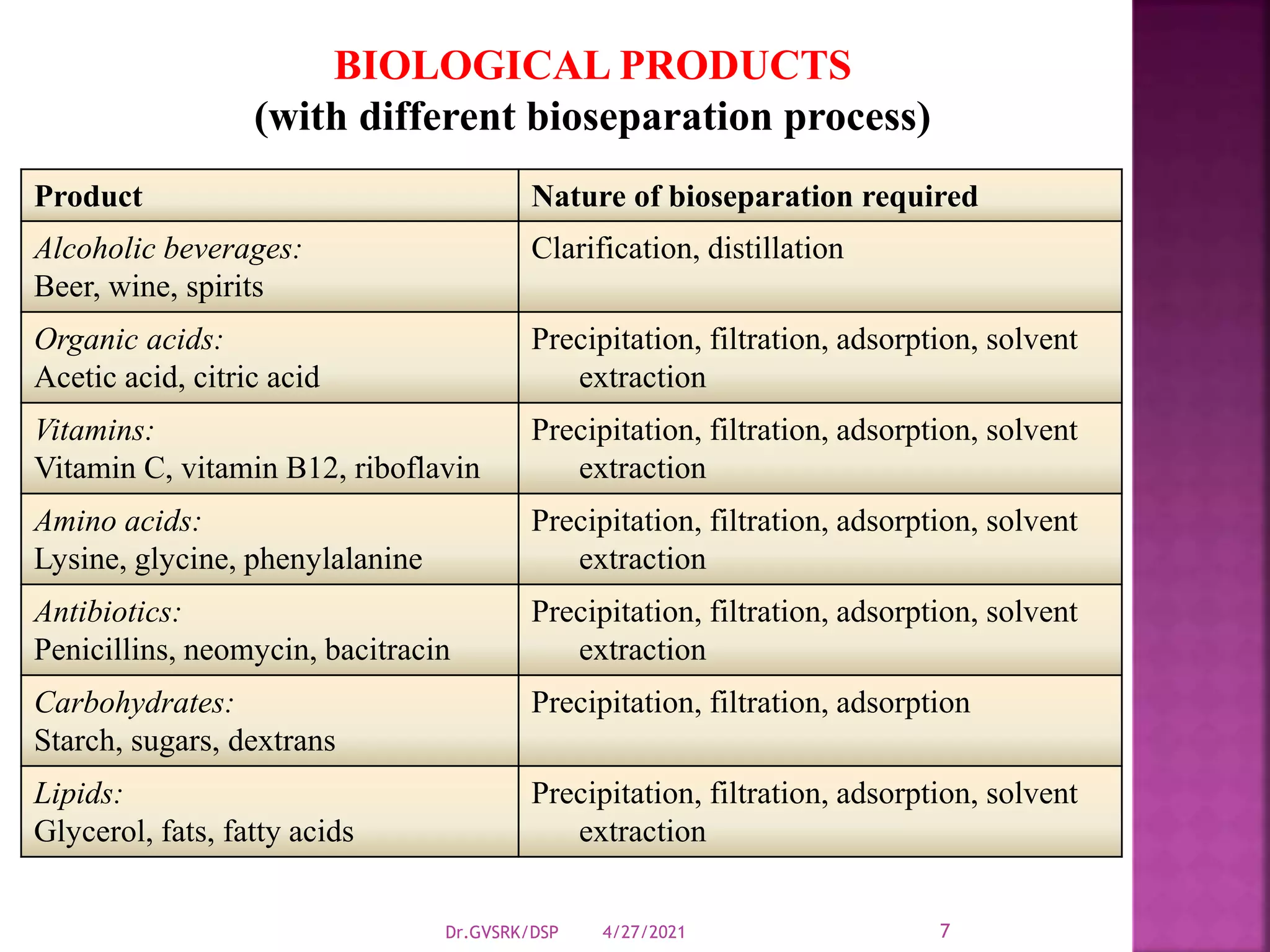
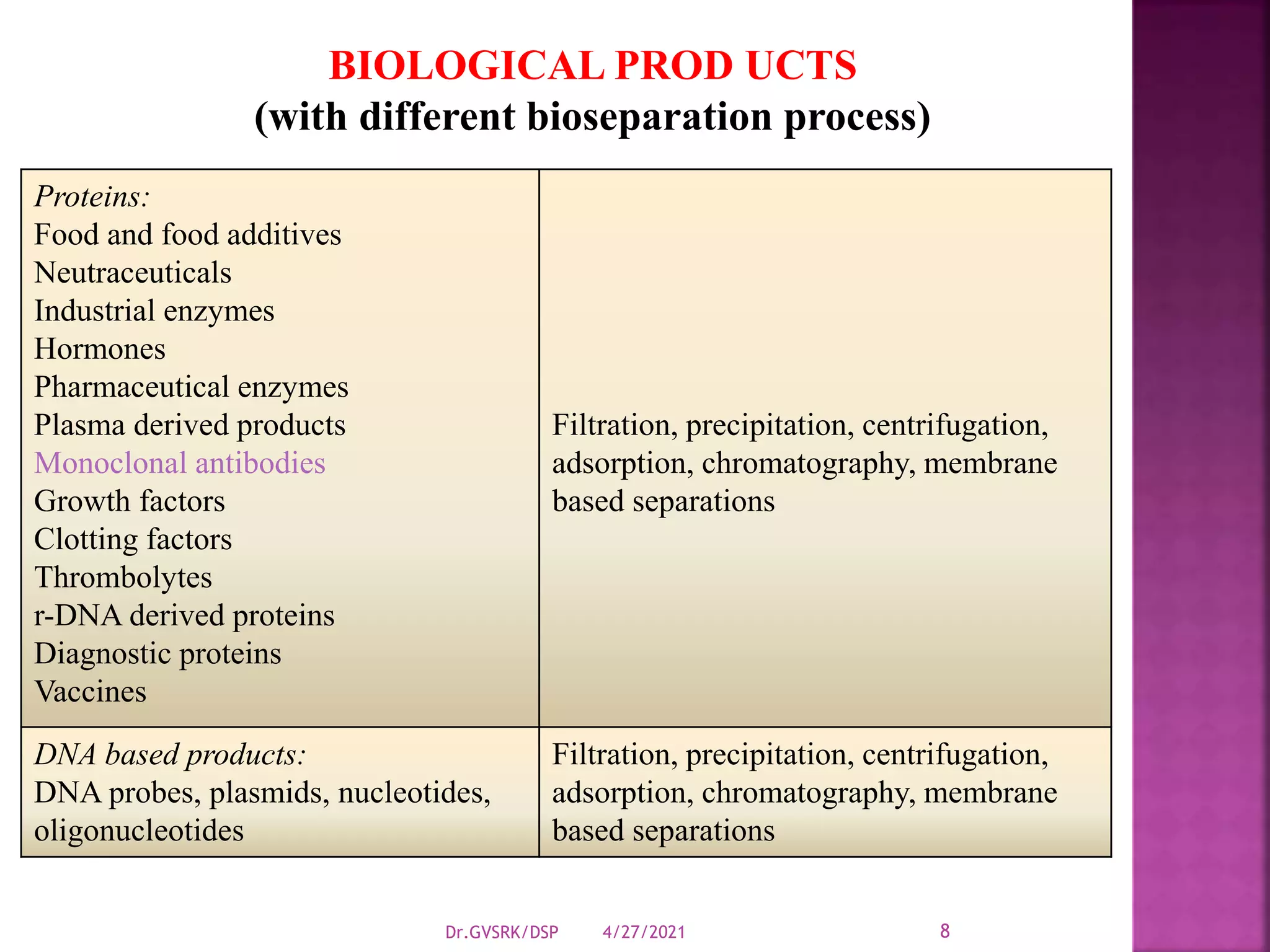
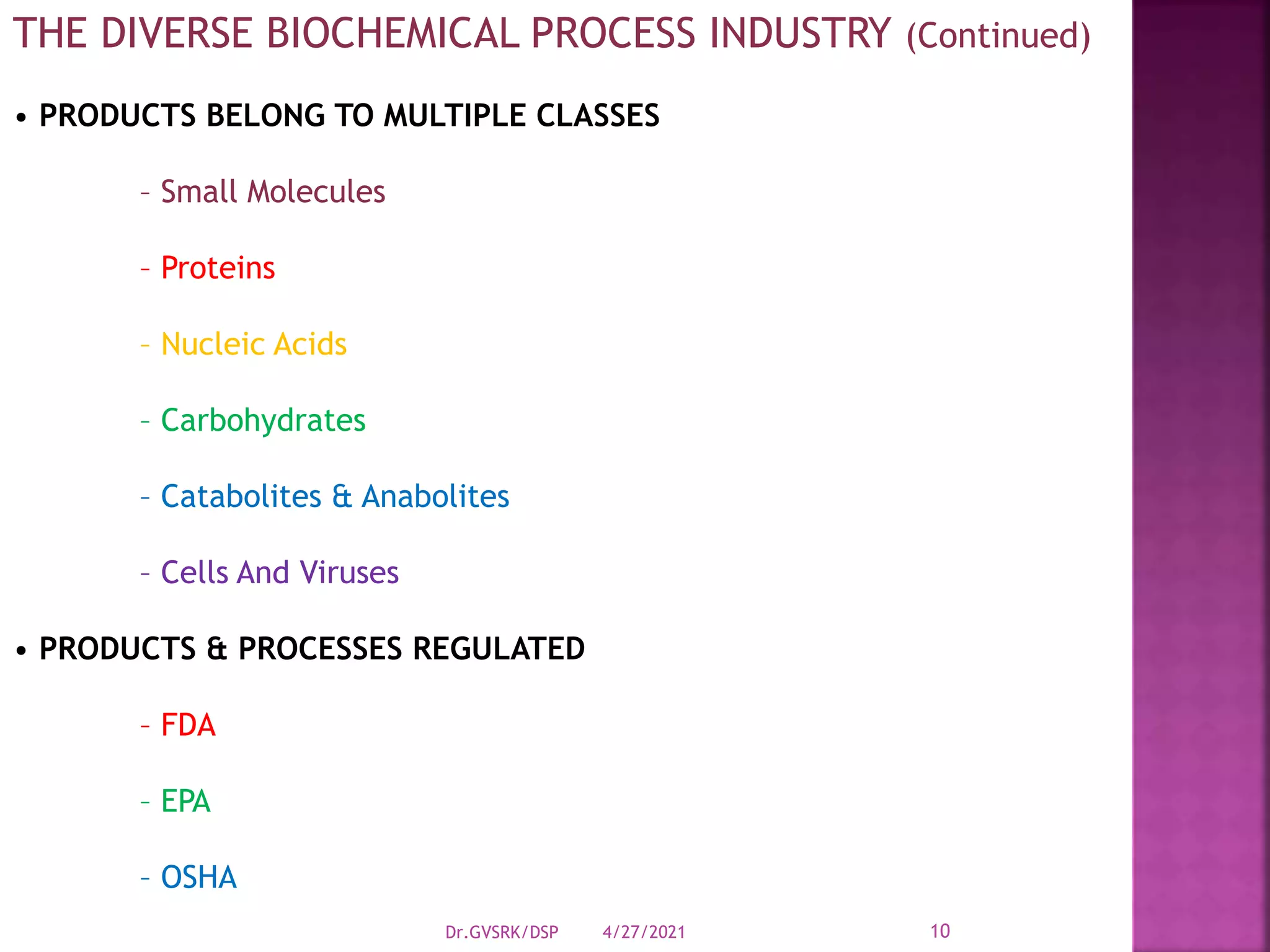
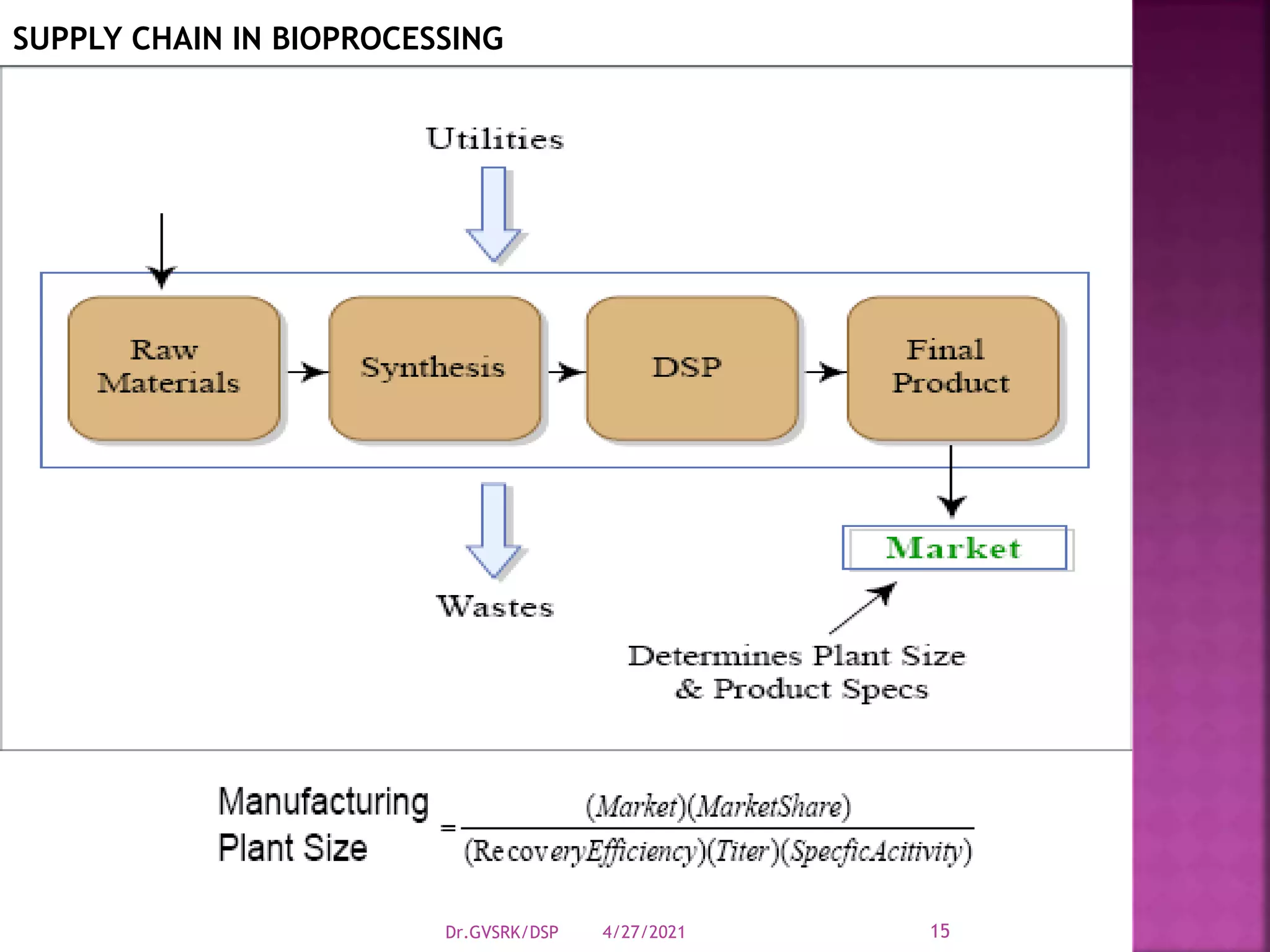
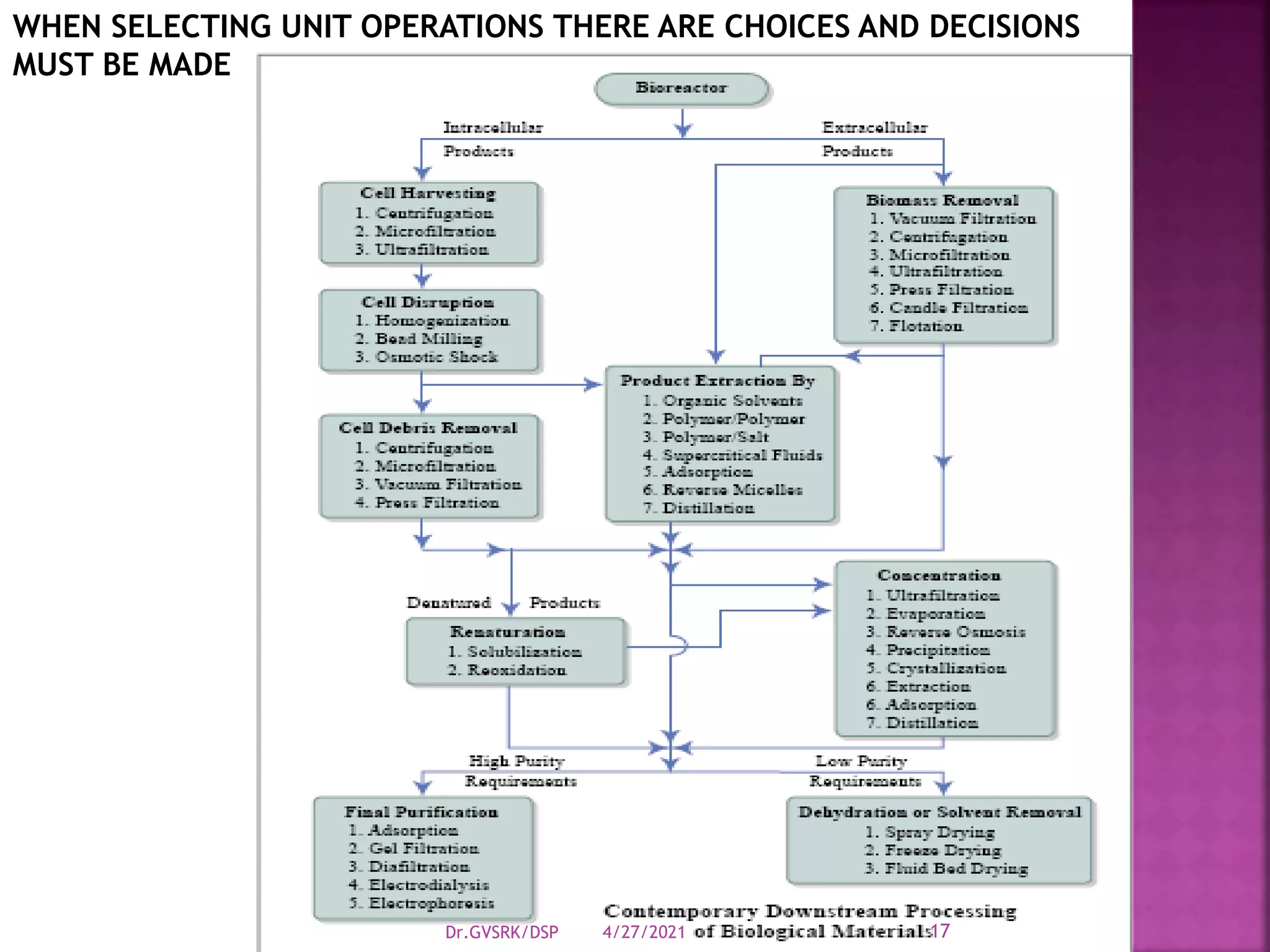
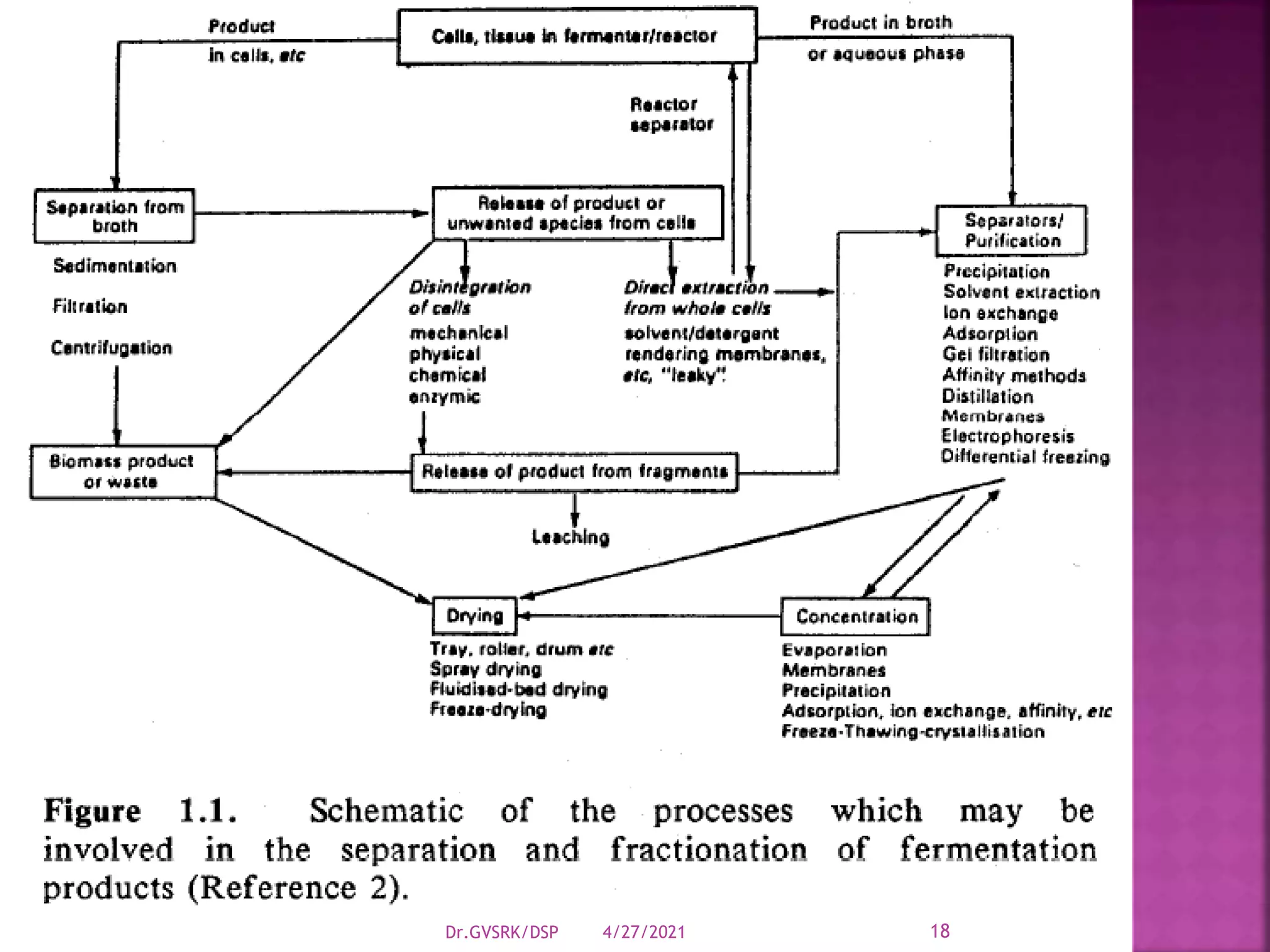
This document discusses downstream processing (DSP) in bioproduct manufacturing. It defines DSP as a series of isolation and purification steps to separate biological molecules from complex mixtures. DSP is challenging due to the similar properties of products, impurities, and contaminants. The document outlines various unit operations used in low, medium, and high resolution separation. It emphasizes that DSP is a major cost in bioproduct production and recovery method selection impacts overall economics. Proper method choice requires understanding the product properties, quality needs, and ability to scale the process.