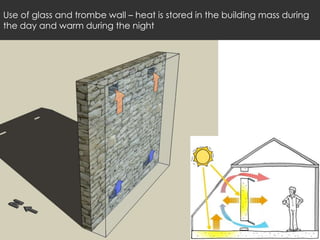
The document describes the climate and architecture of Leh, a mountainous region in India considered a cold desert. It has little vegetation and experiences cold, sunny weather with large daily and seasonal temperature variations and low humidity. Traditional architecture in Leh utilizes thick walls, insulation, and passive solar techniques like trombe walls to resist heat loss and promote heat gain within buildings to dampen indoor temperature variations.