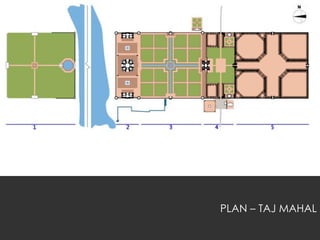
Mughal gardens were built in the Persian style of architecture and followed a char bagh layout of being divided into four quarters by pathways. Important Mughal rulers like Babur, Akbar, Jahangir, Shah Jahan and others built several gardens throughout India, incorporating elements like water pools, fountains, and canals. Shah Jahan's era marked the peak of Mughal garden design, exemplified by the Taj Mahal gardens. Mughal gardens featured symmetrical planning, architectural structures, and water elements designed with symbolic meanings.