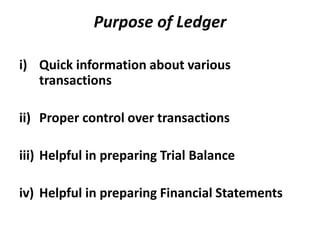
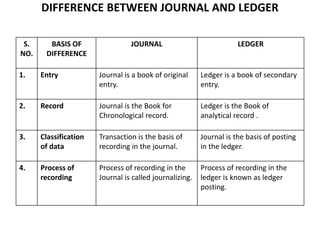
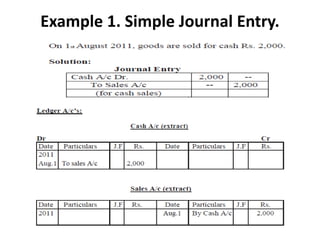
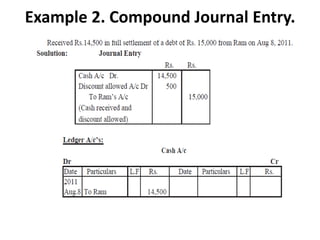
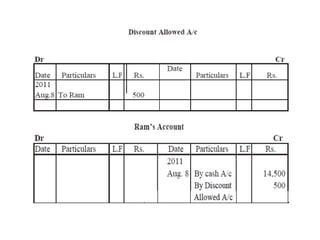
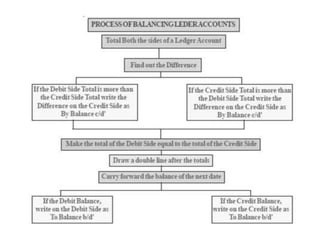
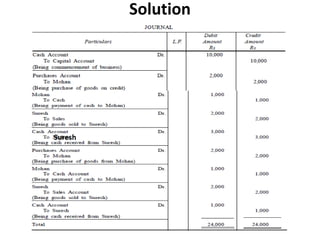
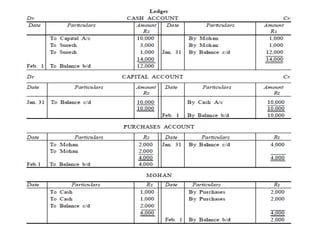
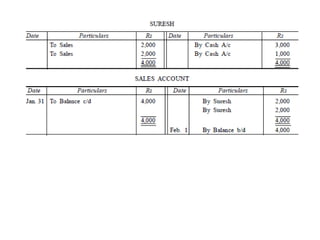
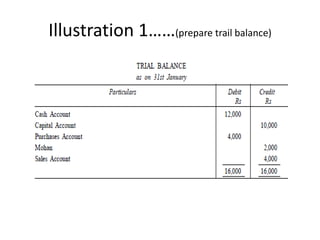
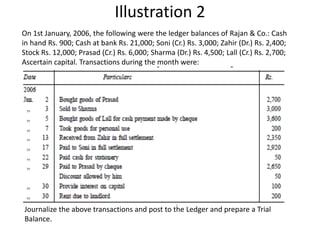
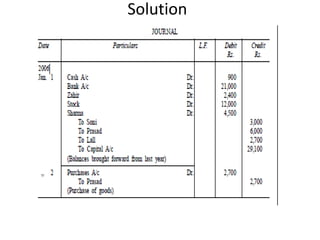
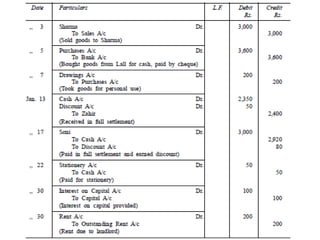
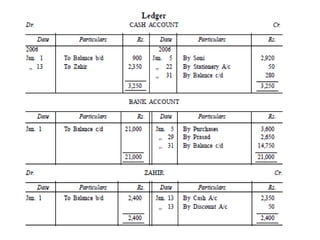
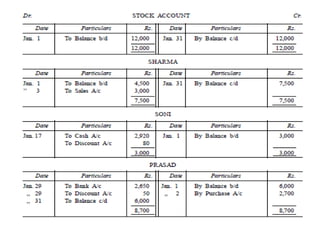
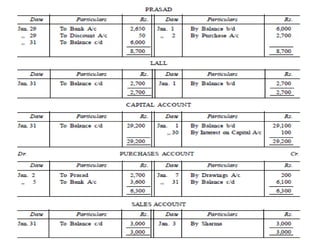
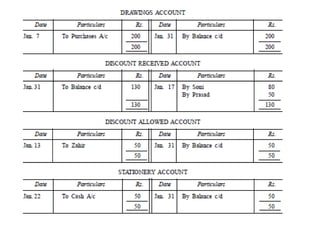
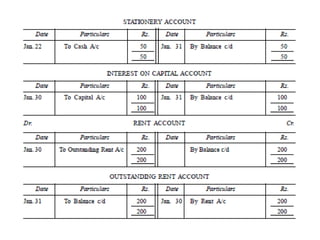
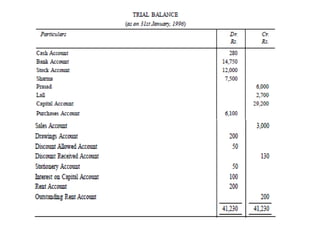
The document defines and explains key accounting concepts related to ledgers and trial balances. It begins by defining a ledger as the principal book of accounts where similar transactions are recorded under their appropriate accounts. It then discusses the features and purpose of ledgers, including that they contain various accounts, serve as the book of final entry, and help in preparing financial statements. The document also compares journals and ledgers, provides examples of ledger postings, and defines and explains the purpose and limitations of trial balances.