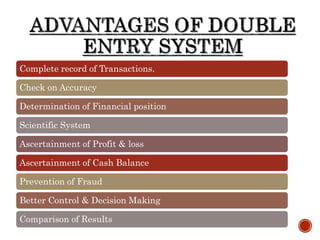
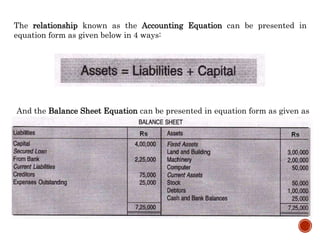
1) The accounting equation shows that a company's assets are always equal to its liabilities plus equity.
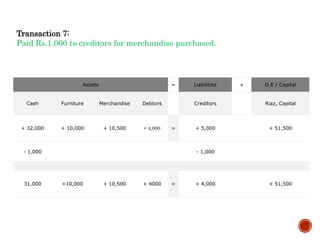
2) Double entry accounting requires every transaction to have equal debits and credits so the accounting equation remains balanced.
3) Examples of transactions that affect the accounting equation include purchasing inventory, receiving payment from customers, and paying expenses.