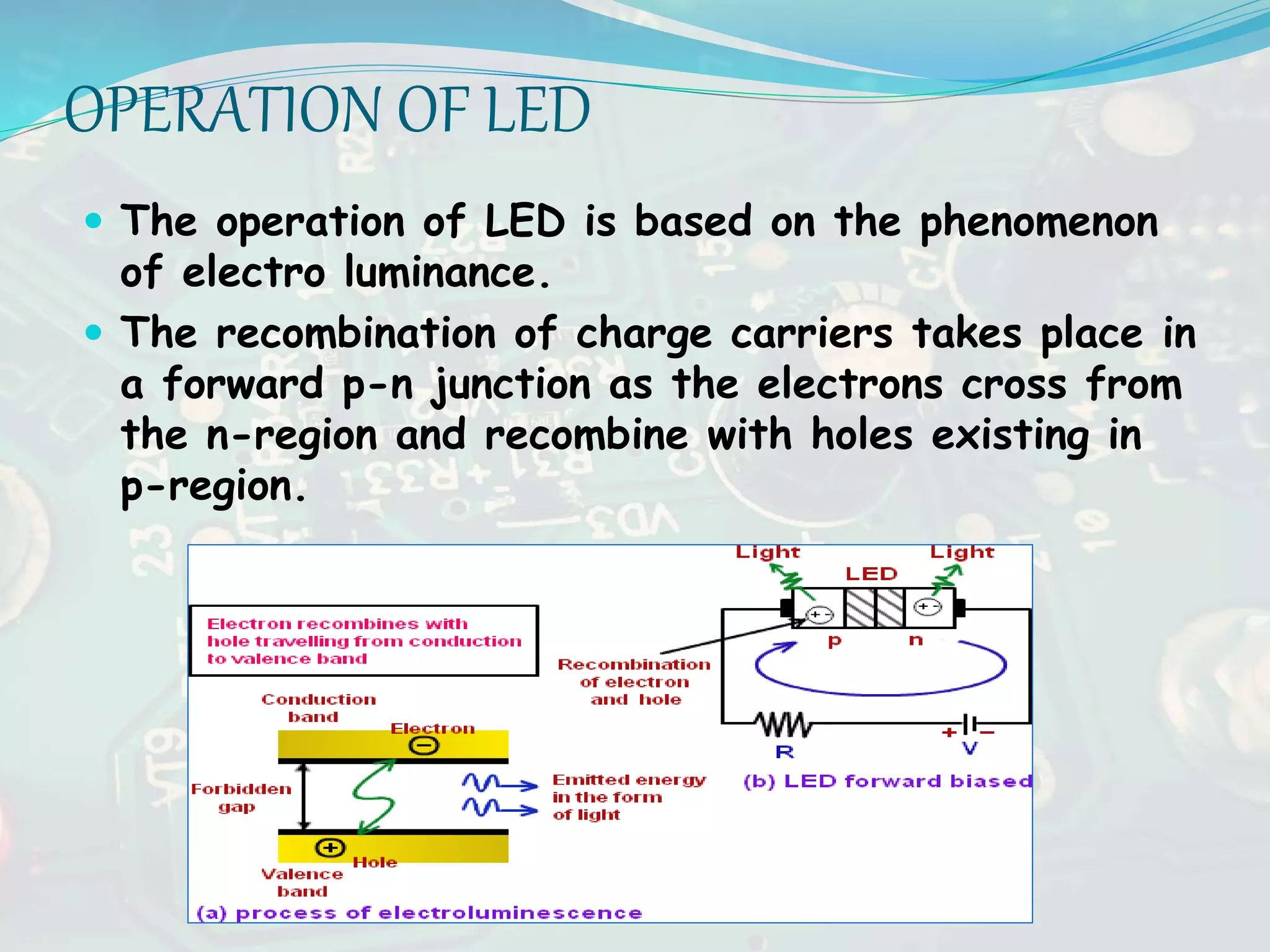
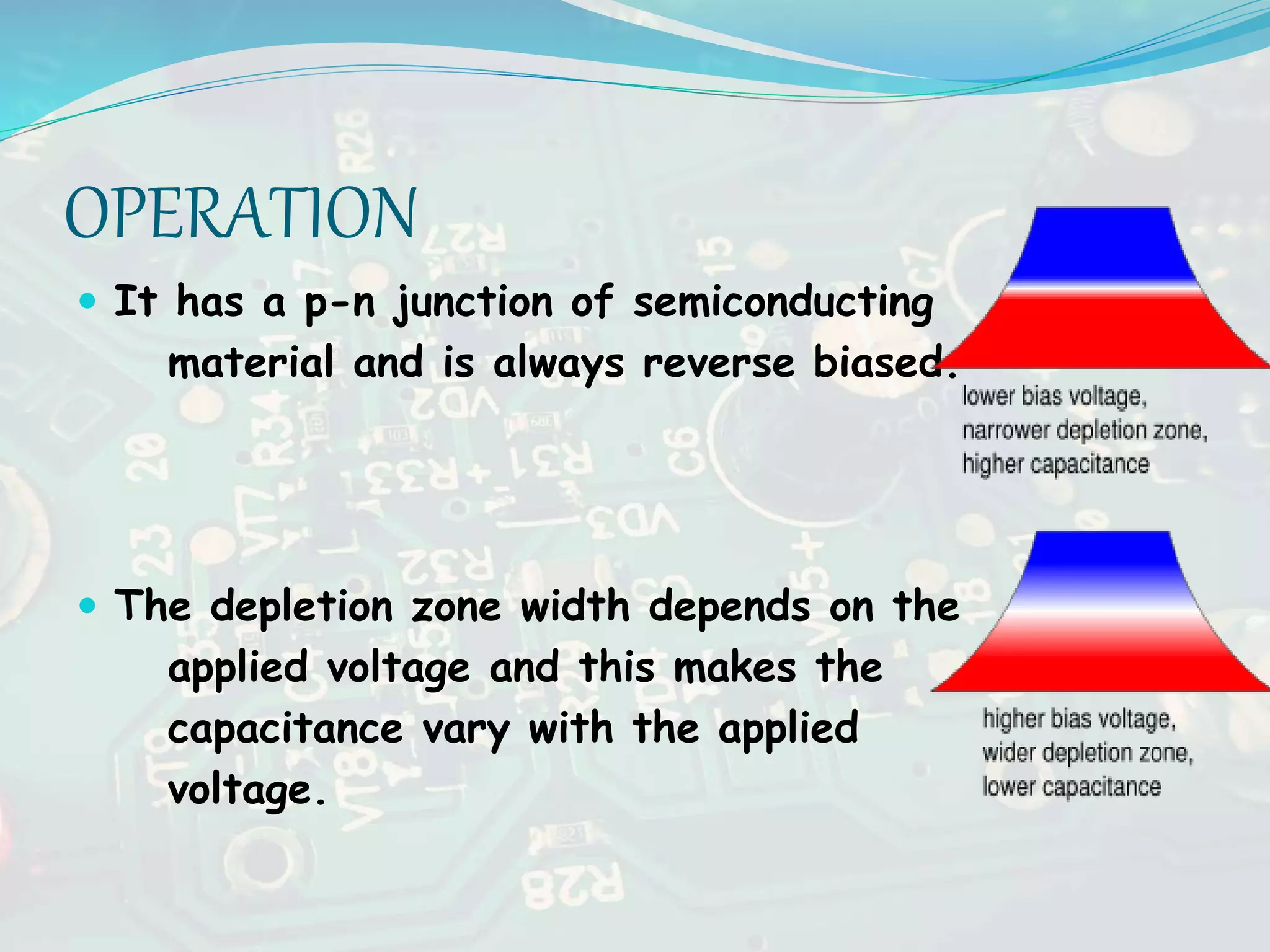
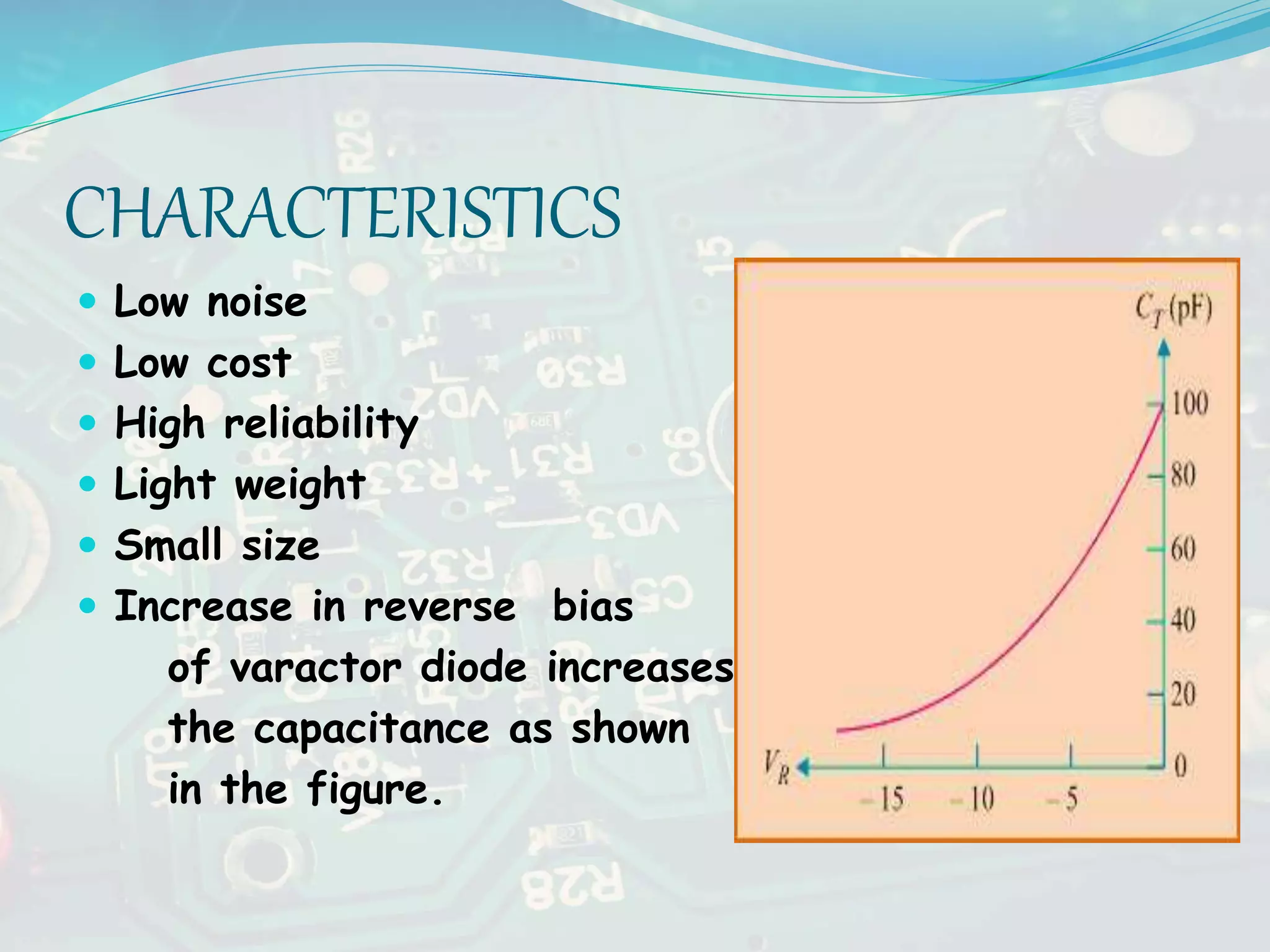
The document discusses basic electronics, focusing on LEDs and varactor diodes. LEDs are opto-electronic devices that convert electrical energy into light and offer advantages such as high efficiency and long life but are limited in color variety and more expensive than traditional lighting. Varactor diodes are nonlinear devices used for variable capacitance in microwave circuits, with applications in voltage tuning and FM wave generation.