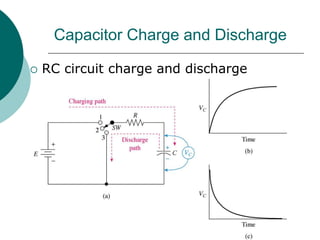
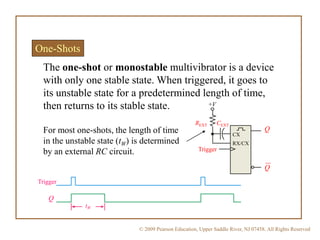
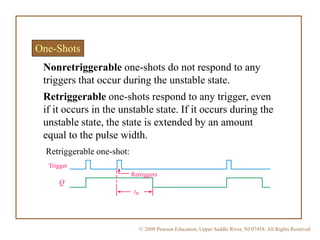
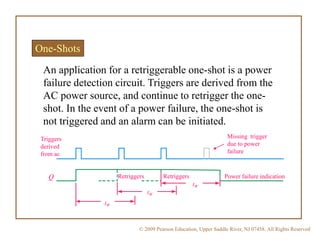
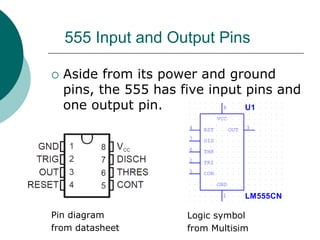
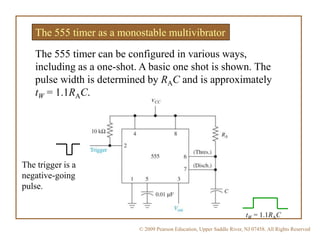
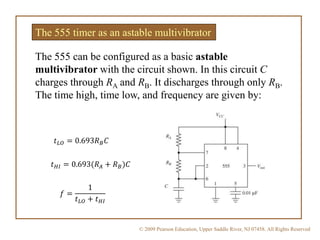
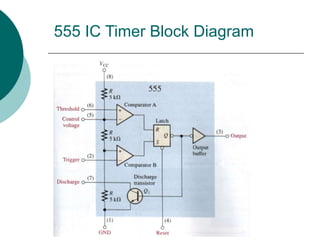
A multivibrator is a circuit that switches between two voltage levels. There are three types: bistable, which has two stable states; monostable (one-shot), which has one stable state and produces a single output pulse in response to a trigger; and astable (oscillator), which continuously switches between states with no trigger needed. Resistors and capacitors are often used to control the timing of monostable and astable multivibrators. The 555 timer IC can be configured as either a monostable or astable multivibrator.